A method for surface layering and path planning for in-situ 3D printing
A 3D printing and path planning technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, manufacturing auxiliary devices, etc., can solve problems such as poor molding accuracy, incomplete bonding of rat tissue defect edges, and complex algorithms, and achieve the goal of reducing computing time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
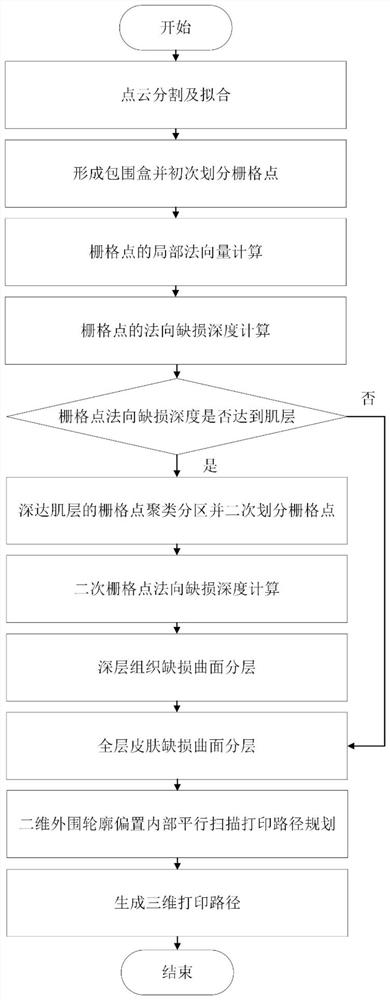
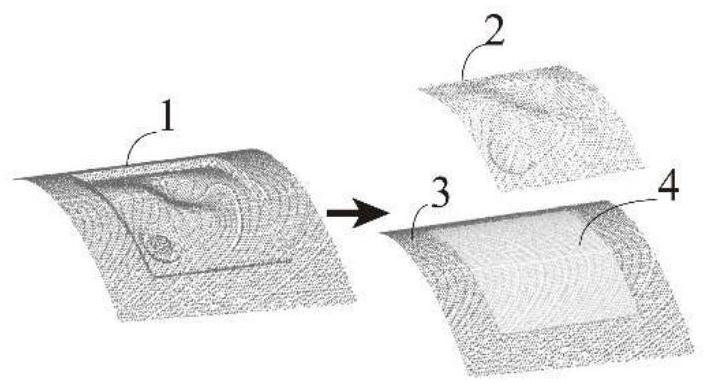
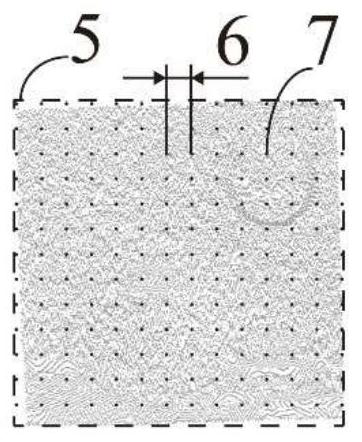
[0081] The complex skin tissue defect model is a 30mm×30mm curved three-dimensional structure with a depth range of 2mm-5mm. The in-situ 3D printing process used is extrusion gelatin and sodium alginate composite hydrogel, and the line width of the extruded material is 0.6mm. Use the scanning device in the in situ printing system to obtain the wound point cloud of the skin defect model and the point cloud of the surrounding intact skin. According to the method in the patent, the grid size of the first grid division is 3mm, the grid size of the second grid division is 0.2mm, and the maximum calculated tissue defect depth is 4.95mm. The area with tissue defect depth more than 2 mm is divided into deep tissue defect area, the surface layer height of deep tissue defect area is 0.5 mm, and the number of surface layers is 7 layers. The layered height of the curved surface of the full-thickness skin defect is 0.5 mm, and the number of layered surfaces is 4 layers. The in-situ 3D pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com