Reinforcing and lifting method for strip-shaped or box-shaped foundation building
A box-shaped foundation and strip-shaped foundation technology, which is used in construction, infrastructure engineering, soil protection and other directions to ensure stability, reduce damage, and ensure stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
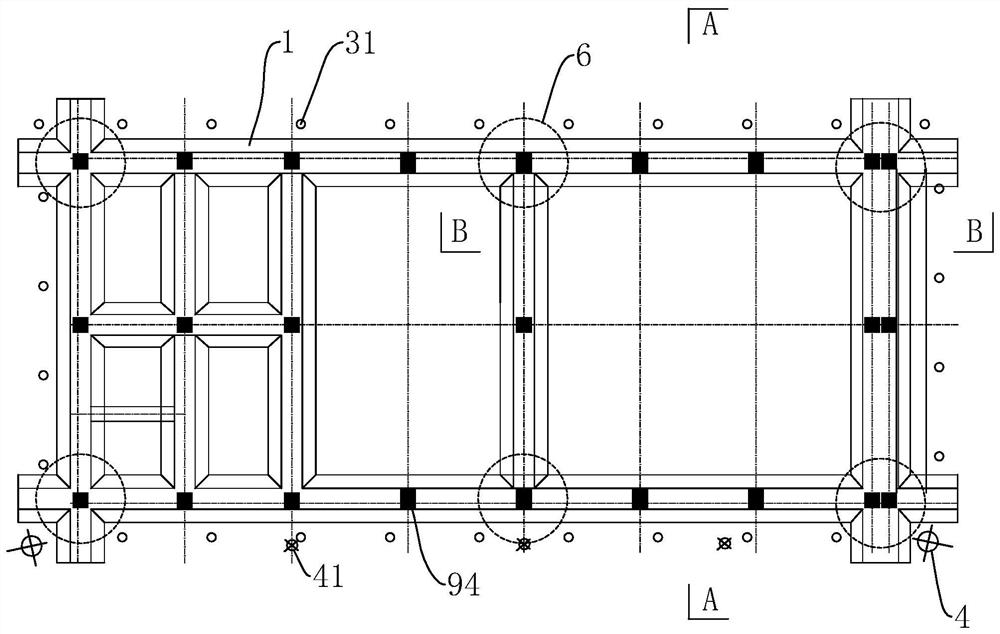
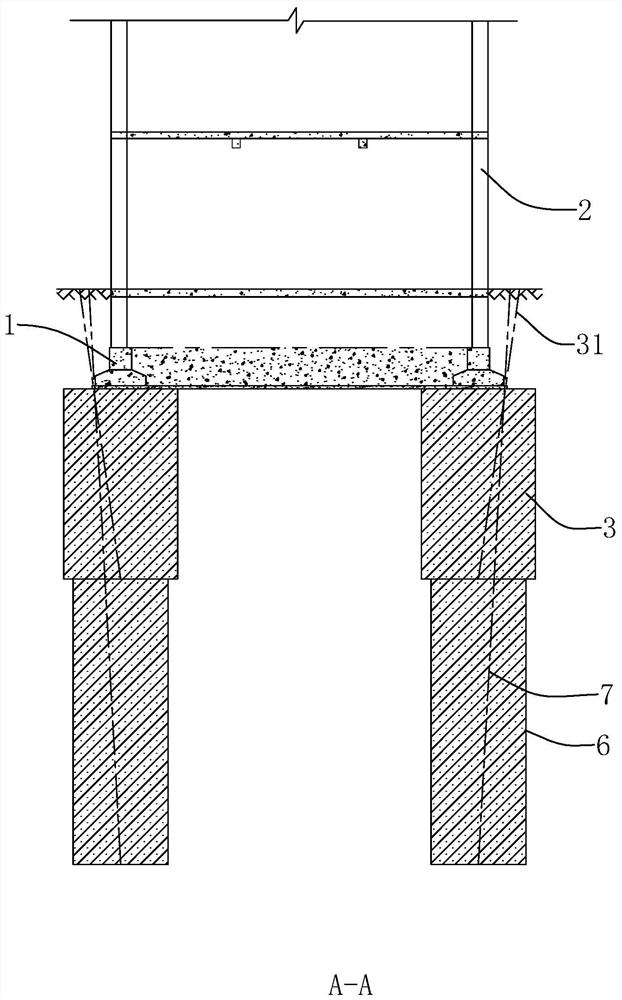
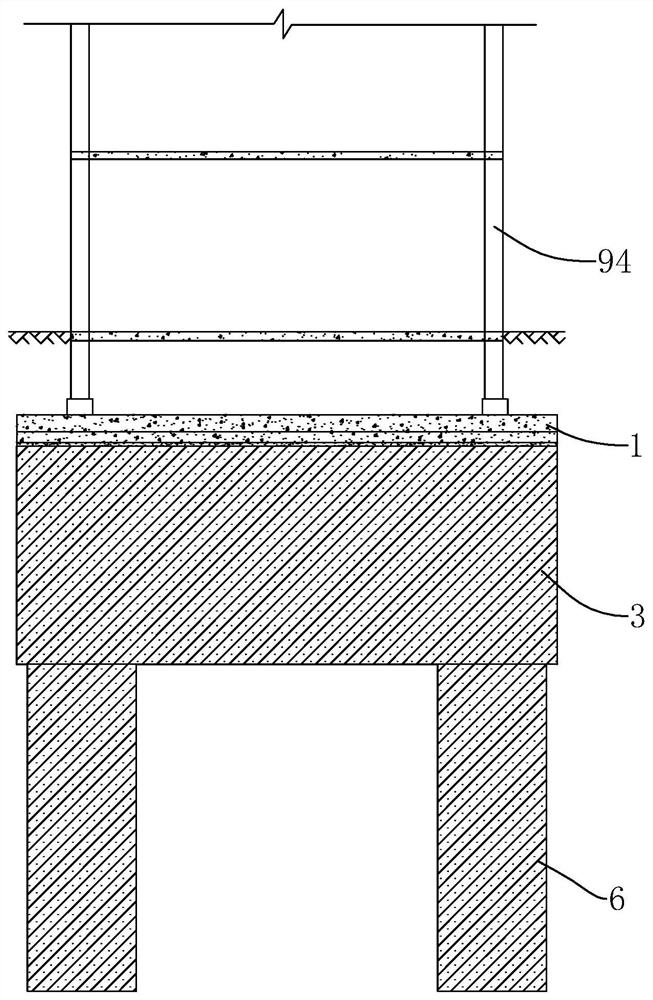
[0063] The invention discloses a method for strengthening and lifting a strip-shaped or box-shaped foundation building. This embodiment takes a strip-shaped foundation 1 building as an example for illustration. Such as figure 1 As shown, a building with a strip foundation 1 includes intersecting strip foundations 1 , and structural columns 94 are arranged at intervals on the strip foundation 1 , and walls are arranged between the structural columns 94 . The reinforcement lifting method includes the following steps:
[0064] S1. Layout of measuring points: a plurality of measuring points are evenly arranged around the outer contour of the building, which can be arranged on the strip foundation 1, preferably at the position of the structural column 94; use a level to measure the elevation of each measuring point, according to the measured The elevation of the points determines that the side of the four corners of the building where the two points with the largest settlement are...
Embodiment 2
[0088] When the foundation of the building is a special stratum such as collapsible loess and miscellaneous fill, the drilling and grouting operations shall adopt the integral forward grouting process instead of the integral backward grouting. Because the overall retreat grouting construction needs to drill the drill pipe to the design depth at one time, during the process of drilling to the design depth, the water sprayed from the drill bit will soften the surrounding soil, resulting in secondary settlement of the building. When drilling in collapsible loess, although the drilling speed is fast and there is not much water out of the drill bit, the plan of drilling to the design depth at one time cannot be adopted because the collapsible loess will subside when it meets water. When drilling in miscellaneous fill soil layers, backfilled flakes are often encountered. When drilling into flakes, the drilling speed slows down and more water is released from the drill bit, which will...
Embodiment 3
[0102] This embodiment mainly introduces the reinforcement and lifting of the box-shaped foundation building. The difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 is that all the above strip foundations 1 are equivalent to the partition wall 10 in the box foundation, and the above-mentioned outer wall is equivalent to the partition wall 10 located on the outermost periphery in the box foundation, and the reinforcement injection The grout hole 31, the lifting hole 4 and the pile foundation hole 7 all need to penetrate the bottom plate 101 of the box foundation.
[0103] When raising buildings with box foundations, it is preferred, as in Figure 17 As shown in , each corner of the building on the lifting side is correspondingly arranged with two lifting holes 4, and the two lifting holes 4 are respectively located on the outside of the two mutually perpendicular outer contour lines of the strip foundation 1; Directly below exterior wall 2.
[0104] After the lifting step of S4, and between...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com