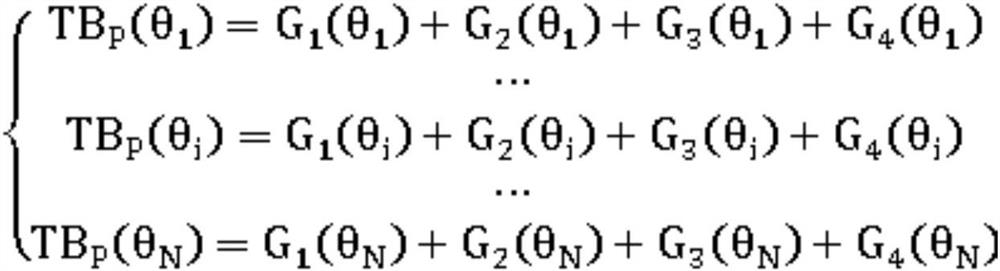Method for separating passive microwave remote sensing mixed pixel component soil radiation signals
A passive microwave remote sensing and mixed pixel technology, which is applied in the field of microwave remote sensing, can solve the problems of spatial heterogeneity, mixed pixel surface parameter inversion, low spatial resolution, and large difference in microwave radiation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
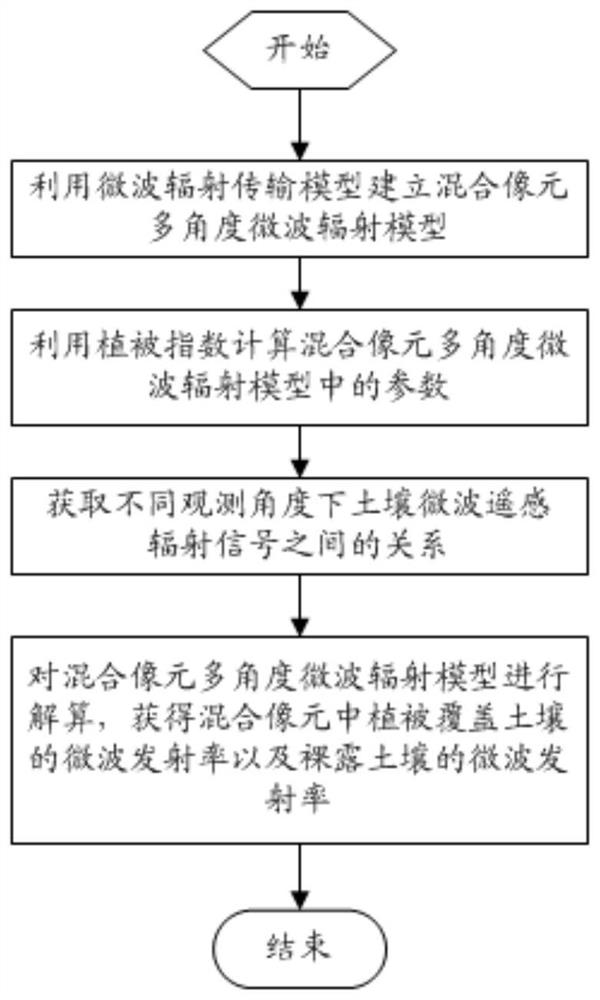
[0039] Embodiment 1, a method for separating soil radiation signals of passive microwave remote sensing mixed pixel components, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0040] S1) establish a microwave radiation transfer model, and use the microwave radiation transfer model to establish a mixed pixel multi-angle microwave radiation model;
[0041] S2) Using the vegetation index to calculate the parameters in the mixed pixel multi-angle microwave radiation model;
[0042] S3) Establish a soil radiation simulation database and a bare soil surface emission theoretical model, and obtain the relationship between soil microwave remote sensing radiation signals under different observation angles according to the soil radiation simulation database and the bare soil surface emission theoretical model;
[0043] S4) Using the parameters in the mixed pixel multi-angle microwave radiation model in step S2) and the relationship between the soil microwave remote sensing radi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com