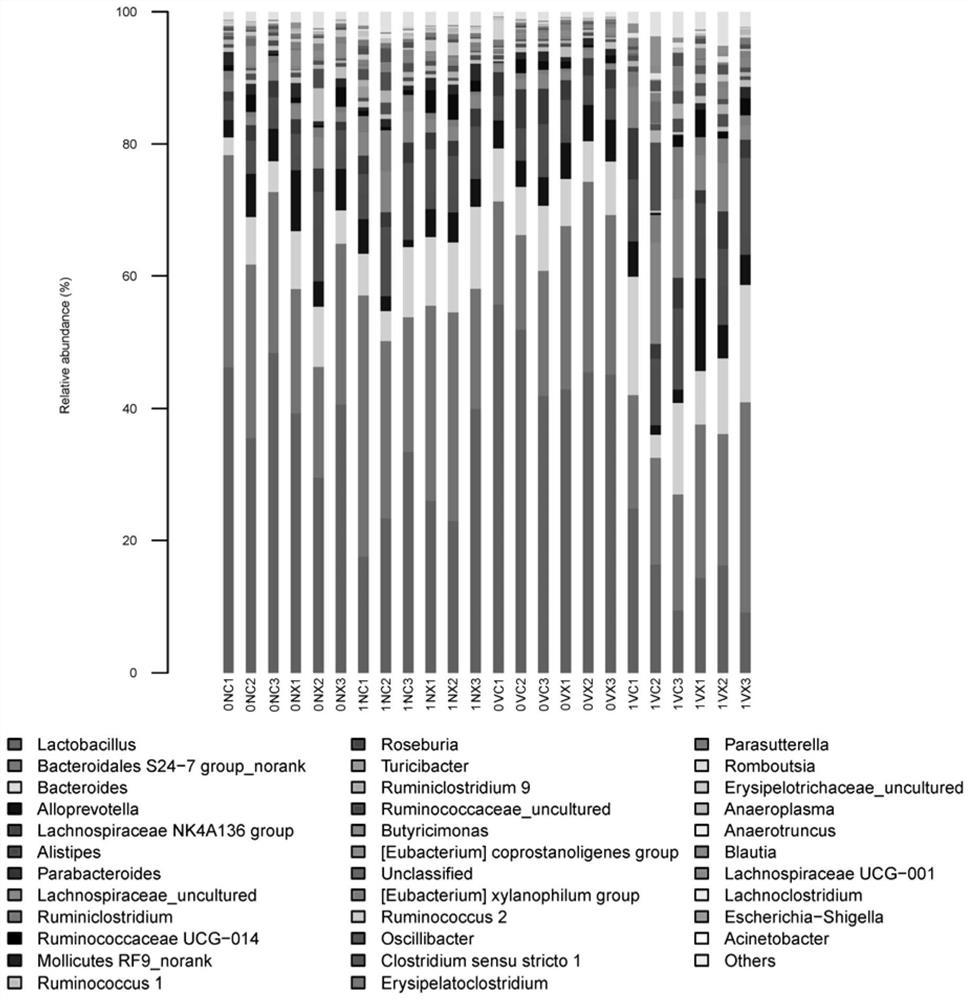
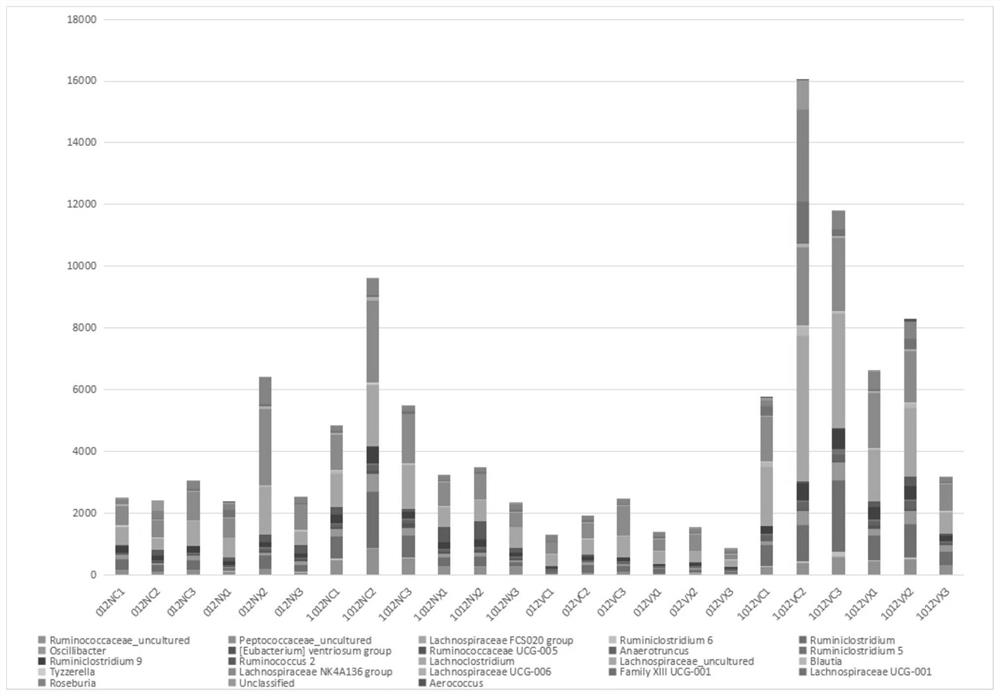
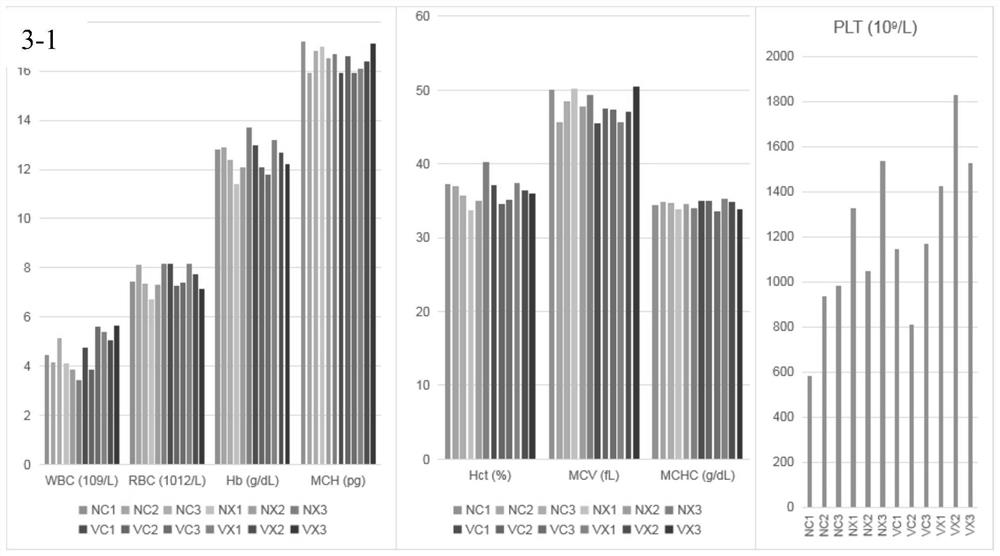
Method for evaluating biosafety by using mouse intestinal flora
A technology of biosafety and intestinal flora, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, biological testing, etc., can solve problems such as unclear impact on human health
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] (1) Isolation of bacteriophages from mid-Pacific ridge sediments:
[0046] 1. Weigh 10g of the mid-Pacific ridge sediment sample (see Table 1-1 for sample information) in a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 5mL of SM solution (25mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 20mM MgCl 2 ,pH=7.5), shake and resuspend for 20min;
[0047] 2. Centrifuge at 5000×g for 10 minutes at 4°C;
[0048] 3. Continue to add SM solution to the precipitate to resuspend, repeat 5 times;
[0049] 4. Combine the supernatants collected five times, first pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and then pass through a 0.22 μm filter membrane to filter and sterilize;
[0050] 5. Add PEG-6000 with a final concentration of 10% to the solution, and precipitate overnight;
[0051] 6. Centrifuge at 40000×g for 2 hours at 4°C;
[0052] 7. Resuspend the precipitate with an appropriate amount of sterile water;
[0053] 8. Take 10 μL of the virus solution, stain it with tungsten phosphate, and observe it with a transmission el...
Embodiment 2
[0107] (1) Isolation of phages from seamount sediments:
[0108] 1. Weigh 10g of seamount sediment samples in a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 5mL of SM solution (25mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 20mM MgCl 2 ,pH=7.5), shake and resuspend for 20min;
[0109] 2. Centrifuge at 5000×g for 10 minutes at 4°C;
[0110] 3. Continue to add SM solution to the precipitate to resuspend, repeat 5 times;
[0111] 4. Combine the supernatants collected five times, first pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and then pass through a 0.22 μm filter membrane to filter and sterilize;
[0112] 5. Add PEG-6000 with a final concentration of 10% to the solution, and precipitate overnight;
[0113] 6. Centrifuge at 40000×g for 2 hours at 4°C;
[0114] 7. Resuspend the precipitate with sterile water;
[0115] 8. Take 10 μL of the virus solution, stain it with tungsten phosphate, and observe it with a transmission electron microscope.
[0116] Table 2-1 Seamount sediment sample information
[0117] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com