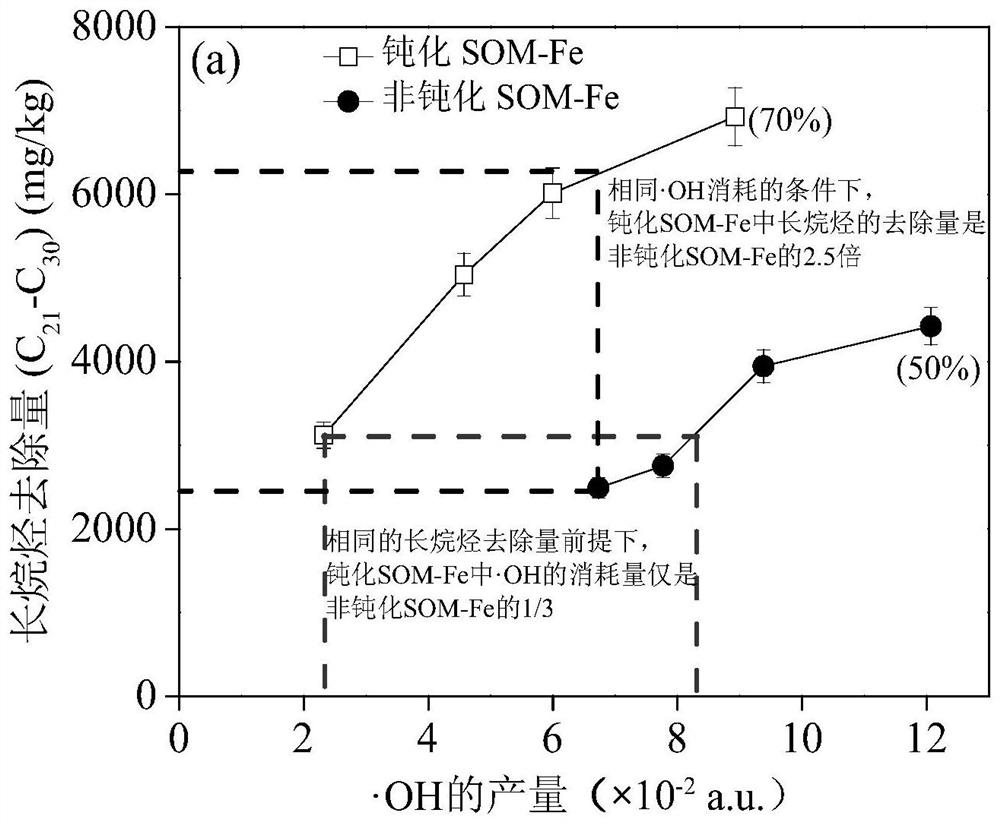
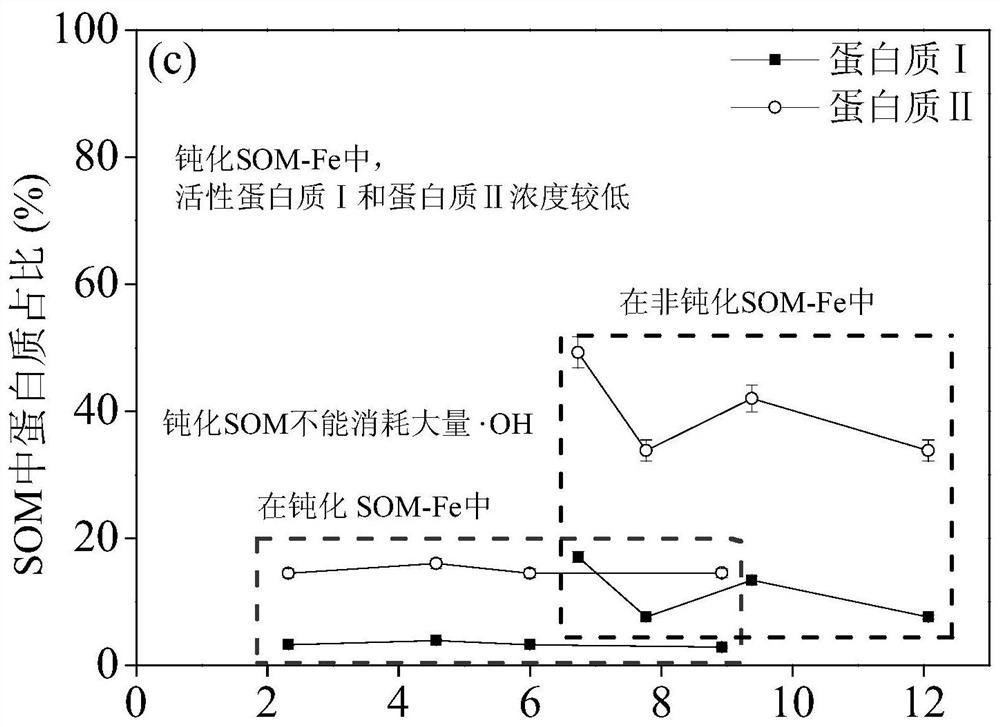
Method for directionally oxidizing crude oil in soil by passivating SOM through iron regulation and control and passivated soil
A technology for iron regulation and soil application in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, restoration of polluted soil, soil conditioning materials, etc., can solve the problems of increasing costs, consuming free radicals, and SOM consumes a large amount of hydroxyl radicals, etc., to achieve directional oxidation Improvement, effect of good application potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] 1) Passivation of organic matter in oily soil
[0052] According to the mass ratio, mix the oily soil, the concentration of 2.9mmol / L ferric sulfate, the concentration of 50mmol / L hydrogen peroxide passivator and water 60:0.2:1.0:50 uniformly, control the pH to 7, and rotate at 130r / min at room temperature The reaction was shaken for 24 hours, filtered, centrifuged, and the filtrate was freeze-dried at -50°C to obtain passivated oily soil.
[0053] 2) The passivated oily soil obtained in step 1) is mixed with oxidant and water in a mass ratio of 50:0.4:60, and placed on an oscillator to continuously oscillate for directional oxidation reaction. Under normal temperature conditions, the reaction is 36h to complete the iron-regulated passivation. The process of directional oxidation of crude oil in soil by SOM.
[0054] After the reaction, the directional oxidation amount of petroleum hydrocarbon is as high as 650mg / kg, the functional group carbonyl in SOM is passivated, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The divalent iron salt used is 5.8mmol / L ferrous chloride, and the passivating agent is 5mmol / L sodium hydroxide.
[0057] 1) Passivation of organic matter in oily soil
[0058] According to the mass ratio, mix oily soil, ferrous chloride with a concentration of 5.8mmol / L, sodium hydroxide passivator with a concentration of 25mmol / L and water 70:0.1:0.6:55, and control the pH to 7 at room temperature. The reaction was shaken at 135r / min for 36h, filtered, centrifuged, and the filtrate was freeze-dried at -50°C to obtain passivated SOM oily soil.
[0059] 2) Mix the oily soil with the passivated SOM obtained in step 1) with the oxidant and water in a mass ratio of 60:0.5:80, and place it on an oscillator to continuously oscillate the oxidation reaction, and react for 24 hours under normal temperature conditions to complete the iron-regulated passivation SOM The process of directional oxidation of crude oil in the soil.
[0060] After the reaction, the directional oxidation amou...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The divalent iron salt used is 8.7mmol / L ferric sulfate, and the passivating agent is 100mmol / L sodium hydroxide.
[0063] 1) Passivation of organic matter in oily soil
[0064] According to the mass ratio, mix oily soil, molar concentration of 8.7mmol / L ferric sulfate, molar concentration of 100mmol / L sodium hydroxide passivator and water 50:0.3:0.5:70 uniformly, control pH to 7, and rotate speed at room temperature The reaction was shaken at 140r / min for 48h, filtered, centrifuged, and the filtrate was freeze-dried at -50°C to obtain passivated SOM oily soil.
[0065] 2) The passivated SOM oily soil obtained in step 1) is mixed with oxidant and water in a mass ratio of 40:0.4:100, and placed on a shaker to continuously oscillate the directional oxidation reaction, and react for 48 hours at room temperature to complete the iron-regulated passivation The process of directional oxidation of crude oil in soil by SOM.
[0066] After the reaction, the directional oxidation amount ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com