Graphene supported palladium nanoparticle composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and graphene technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve problems such as lack of functional groups and hindrance of catalytic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
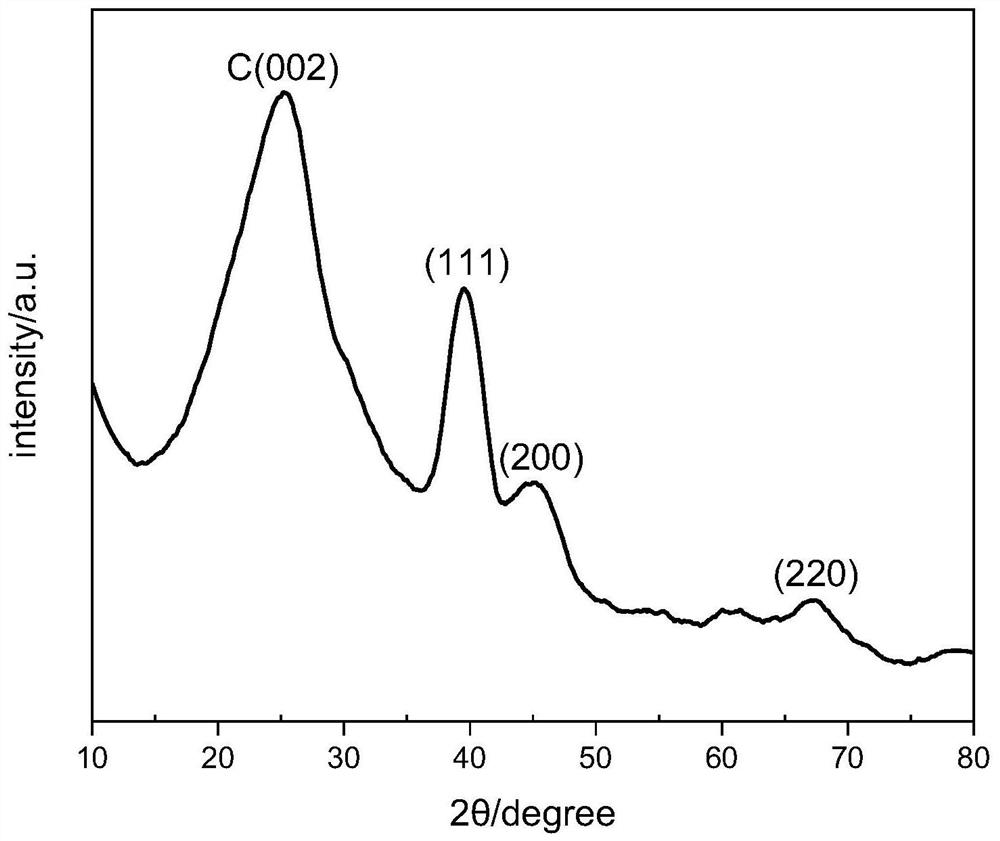
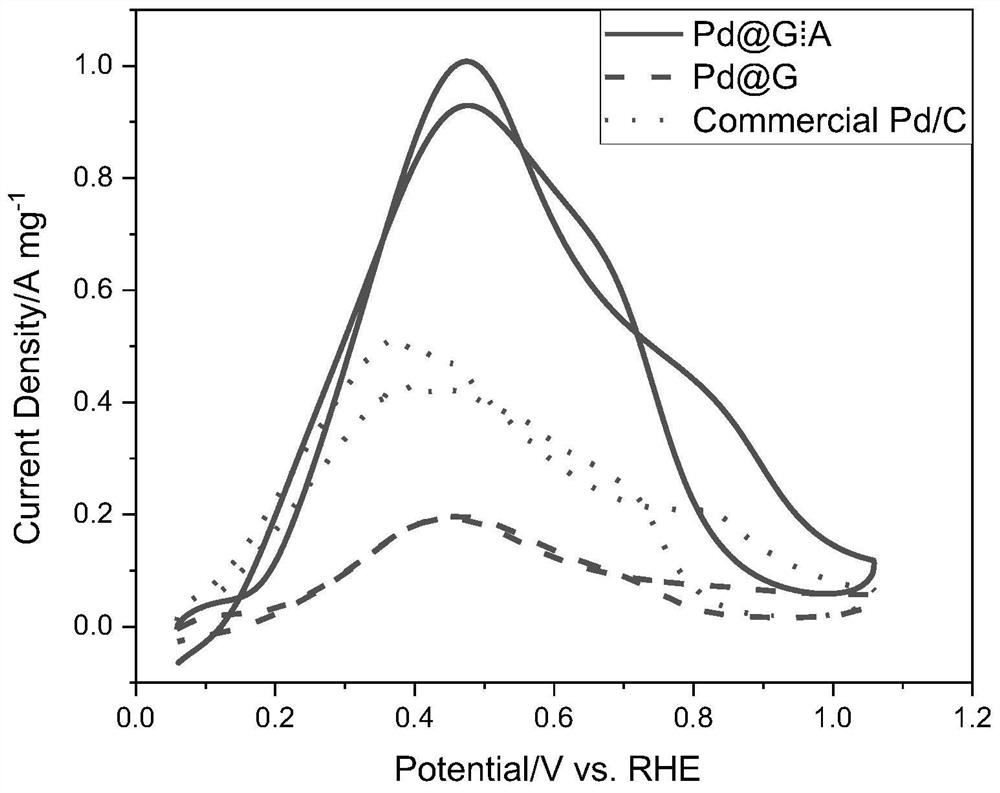
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Preparation of graphene-supported palladium nanoparticle composites
[0039]Add 2mg of adenine into 20mL of ethylene glycol, ultrasonicate until the adenine is evenly dispersed, then add 20mg of original graphene, ultrasonicate for 1h until the original graphene is evenly dispersed, then stir for 10h until part of the adenine is adsorbed on the surface of the original graphene. The binding sites were introduced on the graphene surface, and then 8.6mg Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 O, sonicate for 20min until the palladium source is evenly dispersed, then stir for 1h until Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 Palladium ions in O are effectively combined with the binding sites to obtain a reaction solution. After adding NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 12.5, reflux and stir at 150°C for 3 hours, then filter and wash, and dry the solid phase in a vacuum oven. 24 hours, that's all.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Preparation of graphene-supported palladium nanoparticle composites
[0048] Add 1mg of adenine to 20mL of ethylene glycol, ultrasonicate until the adenine is evenly dispersed, then add 4mg of original graphene, ultrasonicate for 1h until the original graphene is evenly dispersed, then stir for 10h until part of the adenine is adsorbed on the surface of the original graphene. The graphene surface introduces binding sites, and then adds 0.9mg Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 O, sonicate for 20min until the palladium source is evenly dispersed, then stir for 1h until Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 Palladium ions in O are effectively combined with the binding sites to obtain a reaction solution. After adding NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 11, reflux and stir the reaction at 150°C for 5 hours, then filter and wash the solid phase, and dry the solid phase in a vacuum oven. 12 hours, that's all.
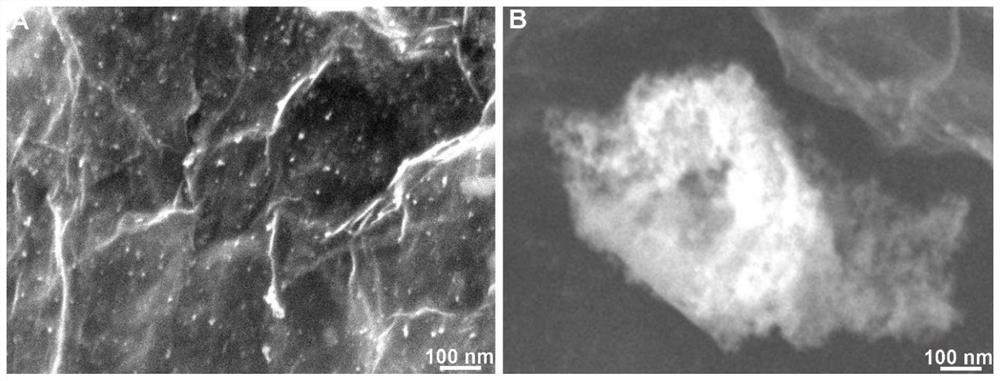
[0049] Figure 5 Be the FESEM figure of the composite material prepared in...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Preparation of graphene-supported palladium nanoparticle composites
[0053] Add 3mg of adenine into 30mL of ethylene glycol, ultrasonicate until the adenine is evenly dispersed, then add 24mg of original graphene, ultrasonicate for 2h until the original graphene is evenly dispersed, then stir for 12h until part of the adenine is adsorbed on the surface of the original graphene. The binding sites were introduced on the graphene surface, and then 10.3 mg Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 O, sonicate for 20min until the palladium source is evenly dispersed, then stir for 2h until Pd(NO 3 ) 2 2H 2 Palladium ions in O are effectively combined with the binding sites to obtain a reaction solution. After adding NaOH solution to adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 12.5, reflux and stir at 160°C for 4 hours, then filter and wash, and dry the solid phase in a vacuum oven. 24 hours, that's all.
[0054] Figure 7 Be the FESEM figure of the composite material prepared in embodiment 3, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com