Preparation method of self-supporting ferronickel phosphide composite nanosheet
A self-supporting, nano-sheet technology, applied in the direction of phosphide, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the development of lithium-ion batteries, low abundance, uneven distribution of lithium resources, etc., to achieve rich iron sources, not easy to fall off, The effect of the electrochemical performance advantage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Add 1 mmol Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 2 mmol Fe(NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O, 6 mmol NH 4 F and 15 mmol CO(NH 2 ) 2 Place it in a beaker and add 70 mL of deionized water. Use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution evenly. Transfer the solution to a 100 mL reactor, add foamed nickel (3cm 2 ), the nickel-iron composite precursor was prepared after hydrothermal reaction at 120 ℃ for 4 h. The nickel-iron composite precursor is dried at a constant temperature and placed in the sintering equipment, under a nitrogen atmosphere, 0.2g NaPO 2 H 2 ·H 2 O was placed in the air inlet of the sintering equipment with a distance of 10 cm from the nickel-iron composite precursor. The temperature was increased from room temperature at a rate of 2 ℃ / min to 350 ℃ for phosphating reaction for 2 h to obtain self-supporting nickel-iron-phosphorus composite nanosheets.
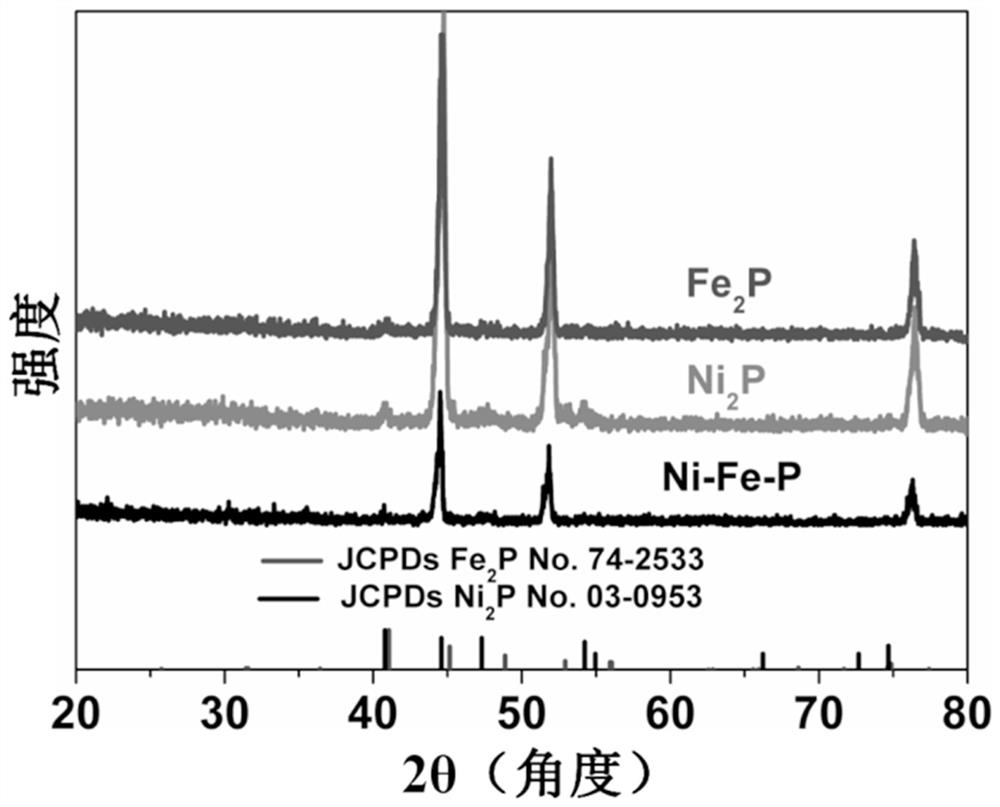
[0032] figure 1 It is the comparison between the XRD and the standard card of the composite material and the single material of nickel phosphide ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Add 1 mmol Ni(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 6 mmol NH 4 F and 15 mmol CO(NH 2 ) 2 Place it in a beaker and add 70 mL of deionized water. Use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution evenly. Transfer the solution to a 100 mL reactor, add foam nickel (3cm 2 ), the precursor was prepared after hydrothermal reaction at 120 ℃ for 4 h. The prepared precursor is dried at a constant temperature and placed in a sintering equipment. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 0.2g NaPO 2 H 2 ·H 2 O is placed in the air inlet of the sintering equipment and is separated from the precursor by 10 cm. The temperature is increased from room temperature at a rate of 2 ℃ / min to 350 ℃ for phosphating reaction for 2 h to obtain nickel phosphide nanosheets.
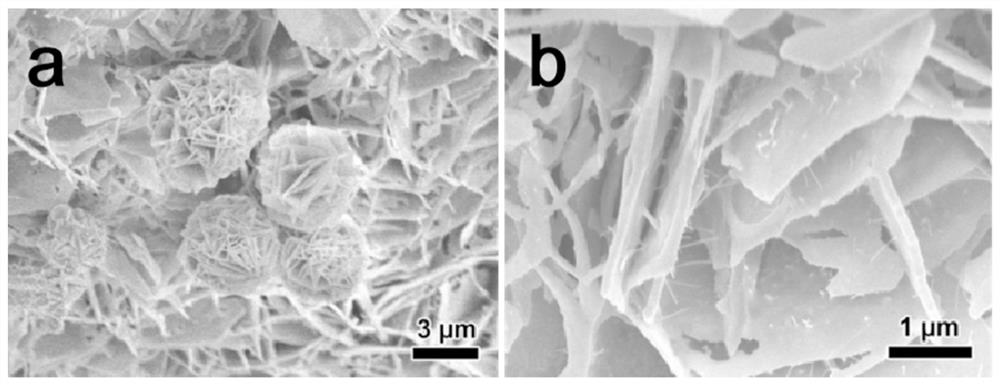
[0035] Nickel phosphide (Ni 2 P) See XRD of nanosheets figure 1 Shown. Picture 8 This is the SEM image of a single nickel phosphide material before recycling, showing that the sample has a nanoplate structure and the nanoplatelets are composed of small particles. P...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Add 2 mmol Fe(NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O, 6 mmol NH 4 F and 15 mmol CO(NH 2 ) 2 Place it in a beaker and add 70 mL of deionized water. Use a magnetic stirrer to stir the solution evenly. Transfer the solution to a 100 mL reactor, add foam nickel (3cm 2 ), the precursor was prepared after hydrothermal reaction at 120 ℃ for 4 h. The prepared precursor is dried at a constant temperature and placed in a sintering equipment. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 0.2g NaPO 2 H 2 ·H 2 O is placed in the air inlet of the sintering equipment with a distance of 10 cm from the precursor, and the temperature is increased from room temperature at a rate of 2 ℃ / min to 350 ℃ for phosphating reaction for 2 h to obtain iron phosphide nanosheets.
[0038] Iron phosphide nanosheets (Fe 2 P) XRD diagram see figure 1 Shown. Picture 11 This is the SEM image of a single iron phosphide material before cycling, showing that the sample has a nanosheet structure and the nanosheets self-assemble into balls. Picture 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com