Human dental pulp cell separation culture method
A technique for separating and culturing dental pulp cells is applied in the field of human cell culture, which can solve the problems that dental pulp stem cells are not easy to adhere to, affect the effect of cultivation, and consume a lot of time, so as to improve the effect of adherence and reduce time and economic costs. , the effect of improving the adherence rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0041] A method for isolating and culturing human dental pulp cells, comprising the steps of:
[0042] S1: Collect completely extracted orthodontic teeth of healthy people (12-25 years old), clean the surface with 75% ethanol, drill grooves about 1 mm deep on both symmetrical sides along the long axis of the teeth with a split drill, and seal the teeth with a large steel wire. Cut it in half, take out the pulp tissue with dental tweezers; wash it with PBS buffer solution with 1% double antibody and cut it into pieces smaller than 1mm3, add 0.3% type Ⅰ collagenase and 0.4% neutral protease, mixed evenly, digested at 37°C for 1 hour, gently pipetting the discrete single-cell clumps to obtain dental pulp cells, and kept them for later use;
[0043] S2: Wash the dental pulp cells with PBS buffer, centrifuge at 1000r / min for 5min to collect the cells, and repeat the washing and centrifugation operations; resuspend the pellet with the primary medium added with glucomannan and sodium...
experiment example 1
[0046] identification test
[0047] (1) Immunofluorescence detection experiment (this experiment is carried out after more than 12 passages)
[0048] Dental pulp cells were cultured by the above method, and the passaged cells obtained were detected by immunofluorescence, the results showed vimentin, type I collagenase, type III collagenase, alkaline phosphatase, BMP and dentin-specific non-collagen Phosphoproteins were all positive, indicating that the cultured cells were indeed dental pulp cells.
[0049] (2) Cell morphology observation experiment
[0050] During the culture process, the above-mentioned cells were placed under an inverted phase-contrast microscope for continuous observation every day. The growth status and basic shape of the cells can be seen: the cells can grow on the iron wall on the second day of culture, and some colonies grow, and the colony growth cells are round. Shaped or oval, the cells are small and closely arranged, the cells at the edge of the c...
experiment example 2
[0054] Comparison experiment of wall attachment
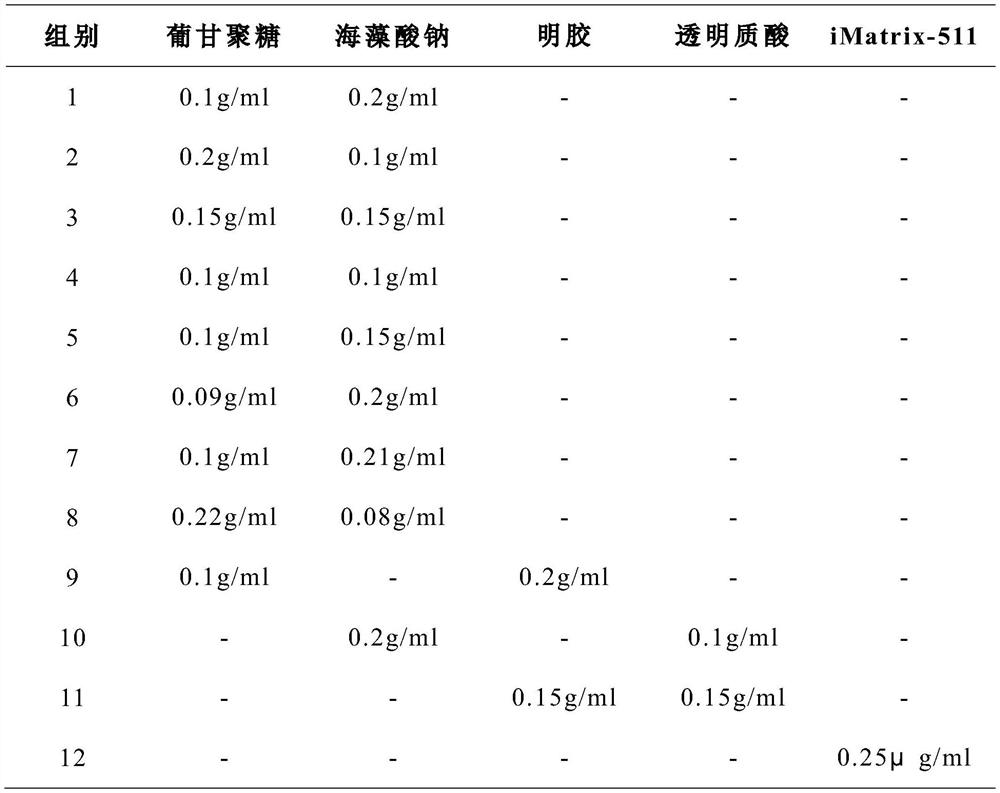
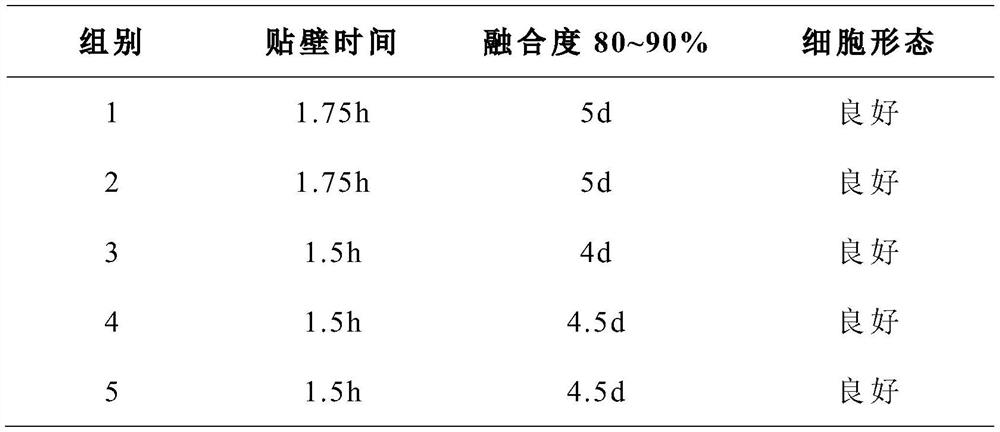
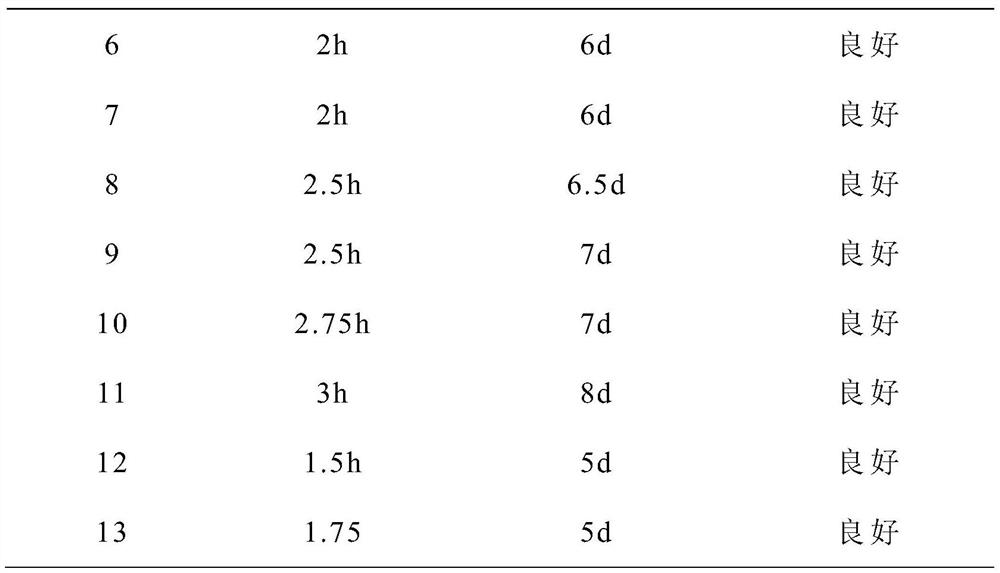
[0055] The formulations shown in Table 1 were used to configure primary culture media with different proportions, and the same source of dental pulp tissue was cultured in the method provided in the examples, and the growth of cells in each group was compared; in addition, gelatin and transparent The Petri dish was coated with uric acid, and the control experiment was carried out in the same way. The growth of cells in each group is shown in Table 2 (where the adherence status was observed every 15 minutes, and the fusion status was observed every 12 hours).
[0056] Table 1 primary culture medium formula (unlisted ingredients in the table are all the same as the examples)
[0057]
[0058] Table 2 Cell growth
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] As can be seen from Table 2, the time for the adherence time and fusion degree of 1-5 groups to reach 80-90% are significantly lower than those of 6-11 groups, and are equivalent to 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com