Comprehensive utilization method of ammonium chloride wastewater
An ammonium chloride and wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, metallurgical wastewater treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption and high treatment costs, and achieve the effect of reducing wastewater treatment costs and shortening wastewater treatment time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024]
[0025] The ammonium chloride wastewater produced in the rare earth smelting process is formed into a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and ammonium chloride. For example, ammonium chloride wastewater, hydrochloric acid solution and optionally water are mixed to obtain a hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride mixed solution. In the ammonium chloride wastewater generated during rare earth smelting, the concentration of ammonium chloride is generally 0.5-3.5mol / L. The concentration of the hydrochloric acid solution is not particularly limited, for example, the concentration of HCl may be 15-37wt%, including 37wt% concentrated hydrochloric acid. In some embodiments, the ammonium chloride wastewater, hydrochloric acid solution and water are uniformly mixed to obtain a hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride mixed solution. In other embodiments, the ammonium chloride wastewater and the hydrochloric acid solution are uniformly mixed to obtain a hydrochloric acid-ammonium chlor...
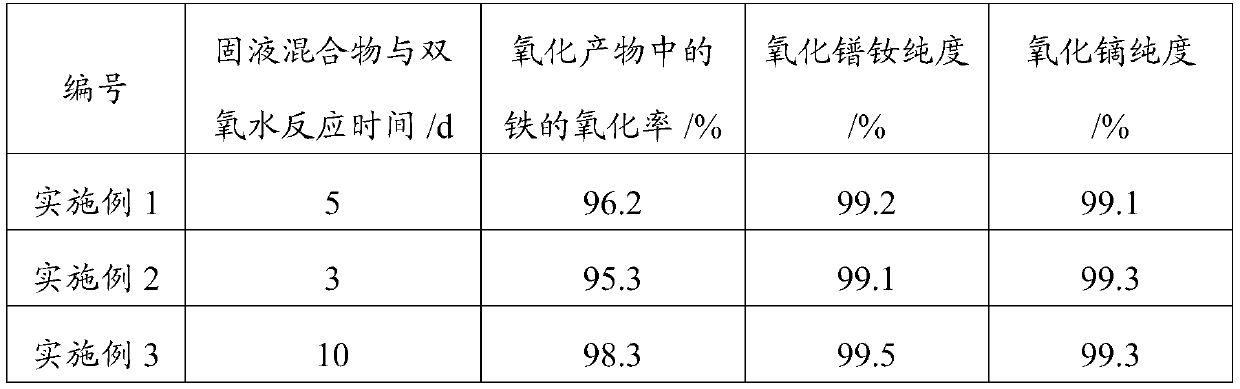
Embodiment 1
[0066] Mix the 3mol / L ammonium chloride waste water produced in the rare earth smelting process with concentrated hydrochloric acid and condensed water to obtain a mixed solution I of hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride (the concentration of HCl is 0.75mol / L, and the concentration of ammonium chloride is 1.7mol / L).
[0067] Mix 20 g of hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride mixed solution I with 100 g of NdFeB magnet waste (particle size less than 120 μm) to obtain a solid-liquid mixture. 2 g of hydrogen peroxide was added to the solid-liquid mixture, and the reaction was carried out in an air atmosphere at 25° C. to form the first reactant. When the water content of the first reactant was 2.7 wt%, 40 g of condensed water was added to the first reactant to continue the reaction to form the second reactant. When the water content in the second reaction material was 3.2 wt%, 40 g of condensed water was added to the second reaction material to continue the reaction. By analogy, c...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Mix the 3.5mol / L ammonium chloride waste water produced in the rare earth smelting process with concentrated hydrochloric acid and condensed water to obtain a mixed solution I of hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride (the concentration of HCl is 0.55mol / L, and the concentration of ammonium chloride is 0.5 mol / L).
[0072] 25g of hydrochloric acid-ammonium chloride mixed solution I and 100g of NdFeB magnet waste (particle size less than 120 μm) were uniformly mixed to obtain a solid-liquid mixture. 3 g of hydrogen peroxide was added to the solid-liquid mixture, and the oxidation reaction was carried out in an air atmosphere at 40° C. to form a first reactant. When the water content of the first reactant is 3.5 wt%, 50 g of condensed water is added to the first reactant material to continue the reaction to form the second reactant. When the water content in the second reactant was 2.8 wt%, 50 g of condensed water was added to the second reactant to continue the reaction. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com