Method for detecting cutting efficiency of gene editing target
A technology of gene editing and cutting efficiency, applied in the fields of animal genetic engineering and gene editing, can solve the problems of increasing the cost and time of gene editing, and achieve the effect of sensitive detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
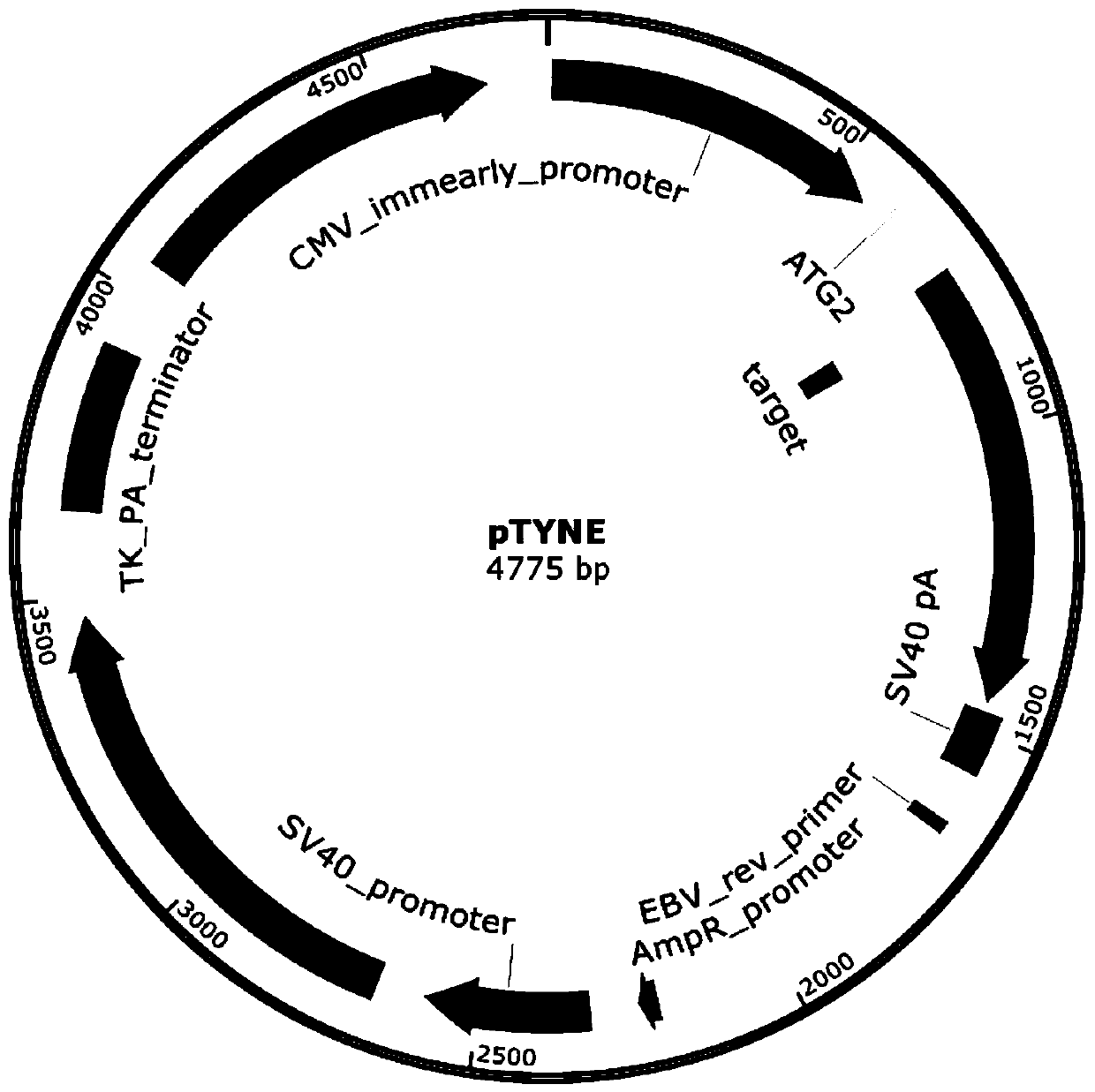
[0043] A method for constructing a frameshift mutant EGFP reporter gene carrier according to the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the implementation steps are as follows:
[0044] (1) Construct the carrier of frameshift mutation EGFP reporter gene, take green fluorescent protein as the frameshift mutation reporter gene carrier pTYNE of reporter gene, utilize restriction endonuclease XbaI, NotI in the frameshift mutation reporter gene carrier pTYNE of reporter gene Insert the frameshift mutant EGFP reporter gene downstream of the start codon ATG, cut the synthetic product, and obtain the carrier of the frameshift mutant EGFP reporter gene;
[0045] (2) The carrier of the frameshift mutant EGFP reporter gene constructed in step (1) is transferred into eukaryotic cells; the frameshift mutant EGFP reporter gene is cloned into the eukaryotic expression vector between the CMV promoter and the SV40 terminator.
Embodiment 2
[0047] A method for detecting gene editing target site cutting efficiency described in the present invention, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, the implementation steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) Construct two spCas9 and sgRNA co-expression vectors, the frameshift mutation reporter gene vector pTYNE with green fluorescent protein as the reporter gene, and the initiation code of the frameshift mutation reporter gene vector pTYNE using restriction endonucleases Insert spCas9 and sgRNA reporter gene downstream of the sub-ATG, one of which expresses a positive sgRNA that can cut the reporter gene carrier pTYNE; the other expresses a negative sgRNA that cannot cut the reporter gene carrier pTYNE; the steps are as follows:
[0049] 1) Negative and positive sgRNA expression cassettes were synthesized in vitro;
[0050] 2) EcoRV linearized spCas9 and sgRNA co-expression vector spCas9gRNA1;
[0051] 3) Recombine the positive sgRNA expression cassette to the downstream of the U6 promo...
Embodiment 3
[0065] A method for detecting gene editing target site cutting efficiency described in the present invention, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, the pTYNE reporter gene vector was used to verify the knockout target of the human TP53 gene, and the implementation steps were as follows:
[0066] (1) Design two targets according to the sequence of exon 4 of human TP53;
[0067] Target 1: acctgccctgtgcagctgtggg; Target 2: ttgattccacaccccccgcccgg;
[0068] (2) Construct the pTYNE-TP53 verification vector; connect the partial sequence of the fourth exon of TP53 to the pTYNE vector through the XhoI and HindIII restriction sites, and verify the cutting efficiency of the target through the pTYNE vector. The constructed vector is named pTYNE- TP53; Schematic diagram of the pTYNE-TP53 vector insert sequence after the construction is completed (such as Figure 4 );
[0069] 3. Construct target 1 and target 2 into spCas9 / gRNA1 vector to obtain Cas9 and gRNA co-expression vectors spCas9 / gRNA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com