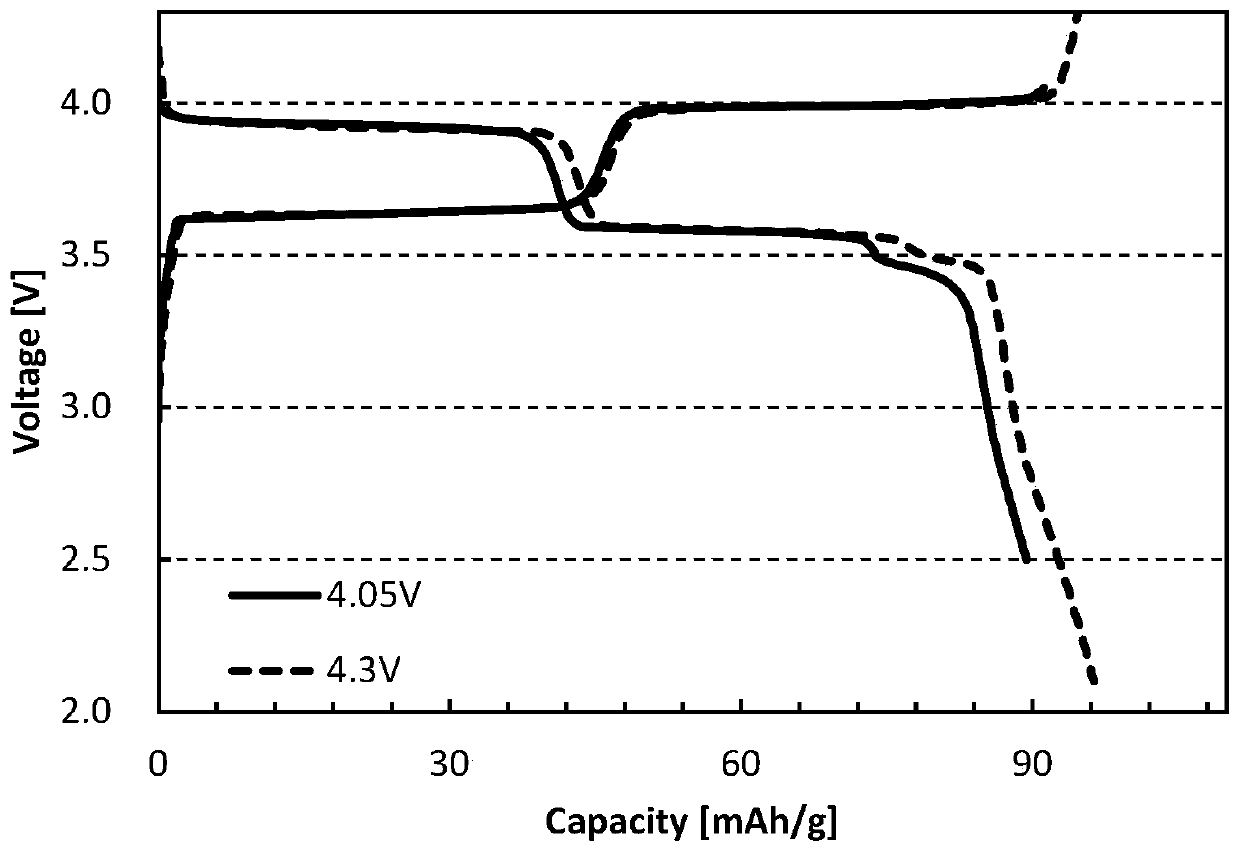
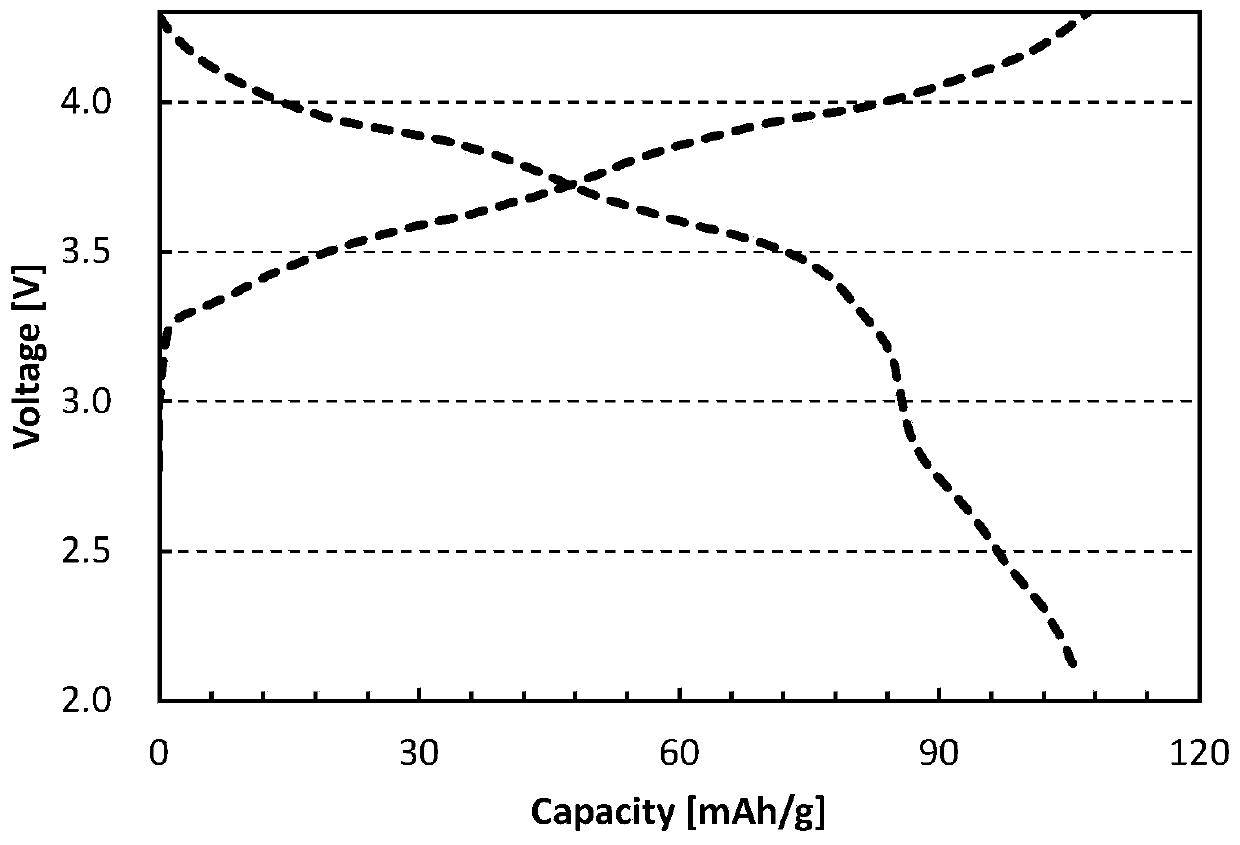
Positive electrode active material, positive electrode plate and sodium ion battery
A technology of positive active materials and positive pole pieces, applied in active material electrodes, positive electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of poor rate performance and cycle performance, obstacles to the commercialization of sodium-ion batteries, and low capacity, and achieve Effects of high rate performance and cycle performance, high ion conductivity and electronic conductivity, and high structural stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] Next, a method for preparing the positive electrode active material in this application will be explained. According to this preparation method, the above-mentioned positive electrode active material can be prepared. The preparation method includes the following steps:
[0052] S10. Add copper salt, manganese salt and optionally salt containing M element to the solvent according to the stoichiometric ratio to prepare a mixed solution.
[0053] S20, adding the precipitating agent and the complexing agent to the mixed solution to prepare a reaction solution, and adjusting the pH value of the reaction solution within a predetermined range.
[0054] S30. Allow the reaction solution to undergo a co-precipitation reaction at a predetermined temperature and stirring rate, separate and collect the resulting co-precipitation product, wash the precipitated product several times with an appropriate amount of solvent, and dry it at a predetermined temperature to obtain a transition metal...
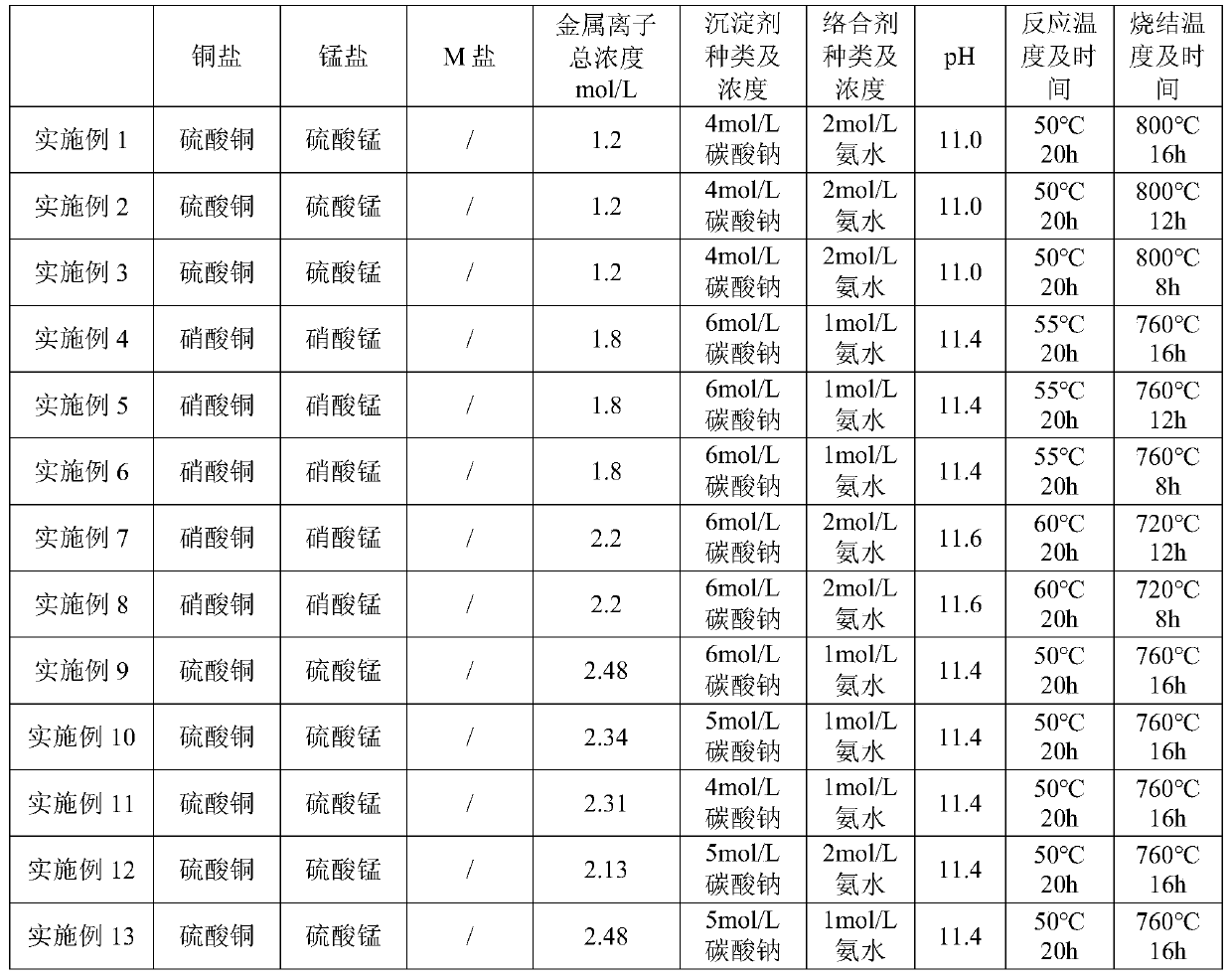
Embodiment 1
[0104] Preparation of positive electrode active material
[0105] S10. Dissolve copper sulfate pentahydrate and manganese sulfate monohydrate in deionized water under the protection of an inert atmosphere according to the stoichiometric ratio to prepare a mixed solution, wherein the total concentration of metal ions is 1.2 mol / L.
[0106] S21: Disperse the precipitant sodium carbonate in deionized water to prepare a precipitant solution, wherein the concentration of sodium carbonate is 4 mol / L. Ammonia water with a concentration of 2mol / L was used as the complexing agent solution.
[0107] S22: Add the precipitant solution and the complexing agent solution to the mixed solution to obtain a reaction solution, and control the pH of the reaction solution to 11.0.
[0108] S30. Let the reaction solution react for 20 hours at 50°C and 800 rpm stirring speed, separate and collect the obtained co-precipitation product, wash the precipitated product several times with an appropriate amount o...
Embodiment 2~19 and comparative example 1~3
[0120] Similar to Example 1, the difference is that the reaction parameters in the preparation step of the positive electrode active material are adjusted. The specific parameters are shown in Table 1 below.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com