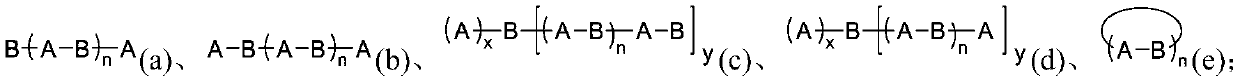Force-induced responsive supramolecular polymer
A supramolecular polymer and supramolecular technology, applied in the field of force-responsive supramolecular polymers, can solve limited, difficult to meet the needs of multifunctional and intelligent materials, and limited performance development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[1767] According to one embodiment of the present invention, at least one component of the mechanoresponsive supramolecular polymer contains at least one hard phase and at least one soft phase.
[1768] Wherein, the hard phase is a crystalline phase and / or a phase incompatible with the soft segment that are mixed and / or independently formed between the hard segments in the polymer, and form a phase-separation physical polymerization based on the hard segment and / or cross-linking; the soft phase is jointly formed by each soft segment in an amorphous state and other selectively existing supramolecular monomers that may or may not produce phase separation. The physical polymerization / crosslinking based on the hard segment enables the polymer to have similar physical properties after covalent polymerization / crosslinking, including but not limited to increased apparent molecular weight, elasticity, dimensional stability, and enhanced mechanical strength. Hard segment phase-separati...
Embodiment 1
[1924] In Example 1, compound a containing a mesensitizing group was used as an initiator to initiate ring-opening polymerization of 20 molar equivalents of ethylene oxide to obtain polyethylene glycol with a ligand group at one end and a hydroxyl group at the other end of the mesensizing group. The supramolecular monomer A is obtained by reacting polyethylene glycol with equimolar equivalents and 2,2':6',2"-terpyridine-4-formyl chloride under the catalysis of triethylamine.
[1925] Compound c was obtained by Sonogashira coupling reaction between equimolar equivalents of 9-acetylene anthracene and compound b. The equimolar equivalent of 2-methacryloyloxyethylphosphorylcholine and 3-mercapto-1,2-diol are subjected to a mercapto-ene click reaction to obtain a diol containing a phosphorylcholine ion group. Using potassium carbonate as a catalyst and tetrabutylammonium bromide as a phase transfer agent, react 20 molar equivalents of the obtained diol with 21 molar equivalents of ...
Embodiment 2
[1928] Example 2 The alcohol compound a containing a ligand group was reacted with excess succinoyl chloride under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain an acid chloride compound containing a ligand group. reacting the obtained acid chloride compound and excess diol compound b containing a lysensitizing group under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain an alcohol compound containing a sensitizing group of a ligand. The obtained alcohol compound and equimolar equivalent of 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide are reacted under the catalysis of triethylamine to obtain an initiator containing a mesensitizing group. With 1 molar equivalent of the obtained compound as an initiator, cuprous bromide and pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (PMDETA) are used as catalysts to initiate the polymerization of 30 molar equivalents of butyl acrylate and 20 molar equivalents of methyl methacrylate successively to obtain Polyacrylate-based supramolecular monomer A.
[1929] React equimolar equivalents of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com