Fermentation process of Clostridium thermocellum with high cellulase production
A cellulase and fermentation process technology, applied in the directions of enzymes, bacteria, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low fermentation enzyme activity, and limited wide application, achieve optimization of fermentation culture conditions, improve cellulase activity, fermentation The effect of process optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1. Seed medium: cellobiose 10g / L, corn steep liquor 12g / L, tripotassium citrate 2g / L, citric acid monohydrate 1.25g / L, sodium sulfate 1g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L , sodium bicarbonate 2.5g / L, ammonium chloride 1.5g / L, urea 5g / L, yeast extract 1g / L, magnesium chloride hexahydrate 50g / L, ferrous chloride tetrahydrate 0.1g / L, dihydrate Calcium chloride 0.2g / L, cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate lg / L, pyridoxamine dihydrochloride 0.02g / L, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.004g / L, D-biotin 0.002g / L, vitamin B 12 0.02g / L, vitamin B l 0.002g / L, the pH value is natural.
[0020] 2. Strain activation: Inoculate the laboratory-preserved strains into the seed medium at an inoculation amount of 1%, activate and cultivate at 60°C, activate 2-3 generations in the same way, and continue to cultivate in the seed medium to obtain thalassemia bacillus bacteria.
[0021] 3. Fermentation medium: under the basic conditions of the seed medium, add 10g / L microcrystalline cellulose.
...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: optimization of fermentation culture conditions
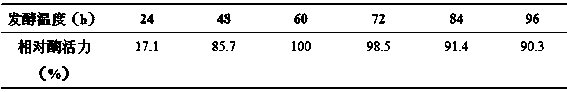
[0025] Keeping other conditions unchanged, different fermentation temperatures were set, respectively 30, 40, 50, 55, and 60°C, and the cellulase activity was measured after the fermentation was completed. The results are shown in Table 1. It was found that the enzyme activity of the bacteria was the highest at 55°C, so 55°C was selected as its fermentation temperature. Control other conditions unchanged, set different culture time, respectively 24h, 48h, 60h, 72h, 84h, 96h, measure the cellulase activity after the end of fermentation. The results are shown in Table 2. With the increase of fermentation time, the enzyme activity showed an upward trend, reached the peak at 60 hours of fermentation, and began to decline at 96 hours. Therefore, the fermentation is stopped after 60 hours, which can greatly save the fermentation cost.
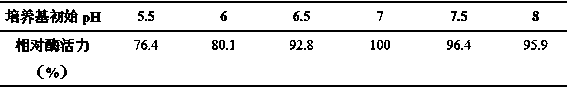
[0026] Control other conditions unchanged, set different initial pH of medi...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: process enlargement
[0035] Pick up 200 μL of the glycerol tube to store the strain, transfer it to 25 mL of seed medium, culture it at a constant temperature of 55°C, and activate the strain, transfer the activated strain to a 50mL fermentation medium according to the inoculation amount of 2%, and cultivate it at a constant temperature of 55°C for 24 hours to obtain First-class seed liquid.
[0036] Seed medium: cellobiose 10g / L, corn steep liquor 12g / L, tripotassium citrate 2g / L, citric acid monohydrate 1.25g / L, sodium sulfate 1g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L, carbonic acid Sodium Hydrogen 2.5g / L, Ammonium Chloride 1.5g / L, Urea 5g / L, Yeast Extract 1g / L, Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate 50g / L, Ferrous Chloride Tetrahydrate 0.1g / L, Chloride Dihydrate Calcium 0.2g / L, cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate lg / L, pyridoxamine dihydrochloride 0.02g / L, p-aminobenzoic acid 0.004g / L, D-biotin 0.002g / L, vitamin B 12 0.02g / L, vitamin B l 0.002g / L, the pH ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com