High-salt-tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain as well as construction method and application thereof
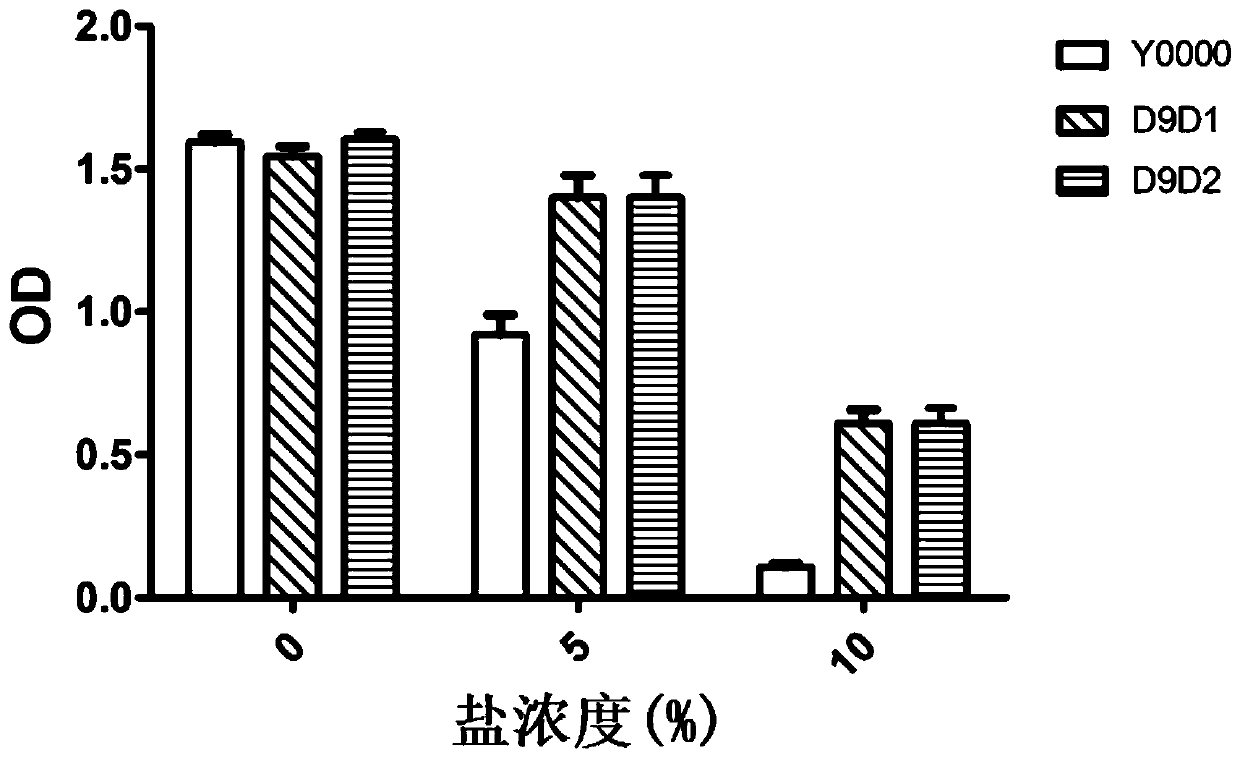
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and construction method, applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, can solve problems such as the need to improve salt tolerance, and achieve the effects of shortening fermentation period, high salt tolerance, and increasing unsaturated fatty acid content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment one (construction and identification of recombinant plasmid)
[0034] 1. Amplification of the target gene
[0035] Aspergillus oryzae 3042 was cultured at 30°C for 3 days, then sampled, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored in a -70°C refrigerator; total RNA was extracted using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA), and the operation method was according to the kit provided by the company Instructions are carried out. After extraction, DNase I (RNase-free) from Fermentas Company was used to remove the remaining genomic DNA in the total RNA. The total RNA was then reverse-transcribed to synthesize the first strand of cDNA. The specific method was operated according to the instructions of the TIANScript cDNA First Strand Synthesis Kit (Beijing Tiangen Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). Primer amplification is designed according to the target gene sequence, and specific fragments are recovered.
[0036] The primers are as follows (the underlined part is the res...
Embodiment example 2
[0043] Implementation Case 2 (Acquisition of Recombinant Bacteria)
[0044] 1. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0045] Take yeast competent cells stored at -80°C and thaw on ice. Prepare the premix: PEG240μL, 1M LiAc36μL, Carrier DNA 10μL, target plasmid 5μL, add sterile deionized water to make up to 360μL. Add the premix solution containing the target plasmid into the competent cells, and repeatedly blow and aspirate the sediment to completely suspend the yeast cells in the premix solution. Incubate in a water bath at 30°C for 30 minutes, mix well every 10 minutes; heat shock in a water bath at 42°C for 30 minutes, mix well every 10 minutes. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, remove the supernatant, add 100μL of sterile deionized water to suspend the precipitate, spread the bacterial solution on the SD-Ura medium plate, and incubate at 30°C for 2 days.
[0046] 2. Identification and storage of positive clones
[0047] Positive clones were identified by bacterial...
Embodiment example 3
[0048] Implementation case three (26S rRNA identification experiment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain of the present invention)
[0049] Yeast genomic DNA was extracted and purified using the method of Sambrook et al. (1989). Using the extracted and detected qualified genomic DNA as a template, the primer pair NL1 (5'-GCATATCAATAAGCGGAGGAAAAG-3') and NL4 (5'-GGTCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG-3') were selected for PCR amplification of the 26S rRNA gene sequence according to Solieri et al. ( 2007), the gene sequence sequencing was completed by Shanghai Sangon Sequencing Company.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com