Nano zero-valent iron composite material with superstrong reducibility and photocatalytic performance
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and composite materials, which is applied in special compound water treatment, reduced water/sewage treatment, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. It can solve problems such as difficult preparation of composite materials, environmental pollution, and operator hazards. Achieve the effect of simple preparation method, simple method and simplified preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Summary of the invention: the preparation method of the nano zero-valent iron composite material with super-reducibility and photocatalytic performance of the present invention.
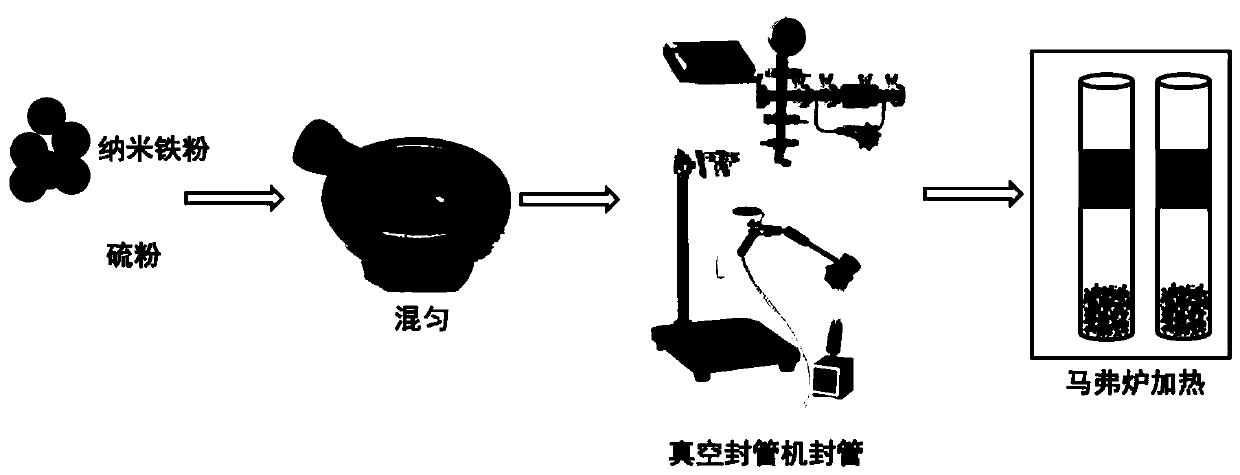
[0050] The synthesizing schematic diagram of the nano zero-valent iron composite material with super-reducibility and photocatalytic properties provided by the present invention is as follows figure 1 Shown, its specific preparation method is:
[0051] First, weigh a certain proportion of iron powder and sulfur powder, and mix them evenly; then, the obtained mixed solid is added into a quartz tube according to a certain mass / volume ratio, and the quartz tube is placed on a tube sealing machine, and after vacuuming, use hydrogen oxygen The gas generated by the machine is burned to seal the tube and heated in a muffle furnace for a period of time; the obtained product is washed with an organic solvent to remove excess S powder, and a nano-zero-valent iron composite material with supe...
Embodiment 2
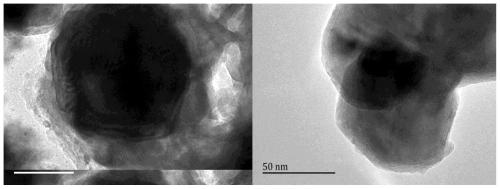
[0052] Example 2: Structural characterization of nano-zero-valent iron composites with super-reducibility and photocatalytic properties of the present invention
[0053] This example is a structural characterization of nano-zero-valent iron composite materials with super reducing and photocatalytic properties, as follows:
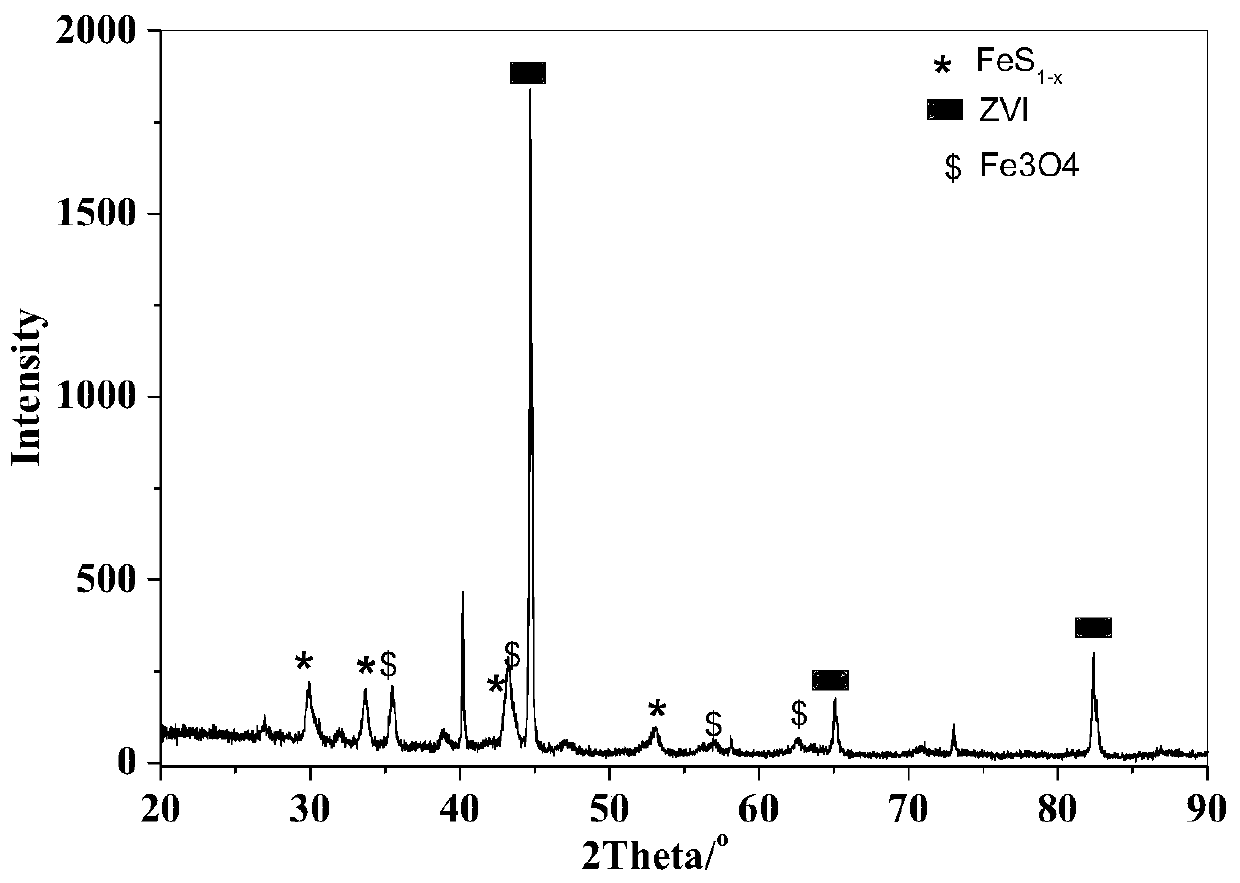
[0054] 1. XRD spectrum
[0055] The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the nano-zero-valent iron composite with super reducing and photocatalytic properties was obtained on a b / max-RB Diffractometer (Rigaku, Japan), using nickel to filter Cu Kα rays, and the scanning range was from 10 ° to 80°, the scanning speed is 4° / min.
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, the FeS 1-x / Fe 3 o 4 On the XRD spectrum of the @Fe composite material, the diffraction peaks at 29.6°, 33.4°, 43.1° and 51.6° represent the monoclinic Fe in the shell 7 S 8 (JCPDS No.29-0723); the diffraction peaks with diffraction angles of 35.4°, 43.5°, 56.8° and 62.4° represent Fe with i...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 : The present invention has the reduction / photocatalytic performance test of nanometer zero-valent iron composite material with super-reducibility and photocatalytic performance
[0076] In this embodiment, Cr(VI) and Pb(II) are selected as representatives of highly toxic inorganic pollutants, and nitrophenol, methyl orange and methylene blue are representatives of refractory organic pollutants. The reduction / photocatalytic energy of the Fe composites was tested.
[0077] The operation steps of the test are as follows: prepare 50 mL of each pollutant standard solution, wherein the concentrations of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) are respectively 1 mM, the concentration of methyl orange is 50 mg / L, and the concentration of each nitrobenzene and methylene blue is 20 mg / L , placed in a 100mL polyethylene plastic vial, add 25mg FeS 1-x / Fe 3 o 4 @Fe composite material, so that the reducing agent / catalyst concentration is 0.5g / L. Shake the reaction solution in a shaker; i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com