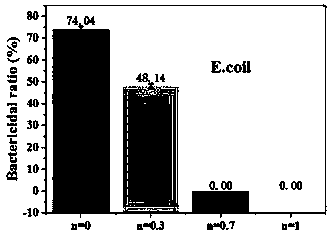
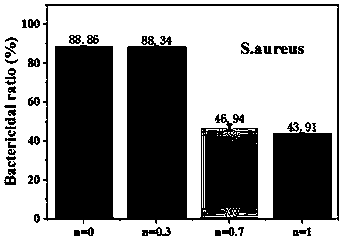
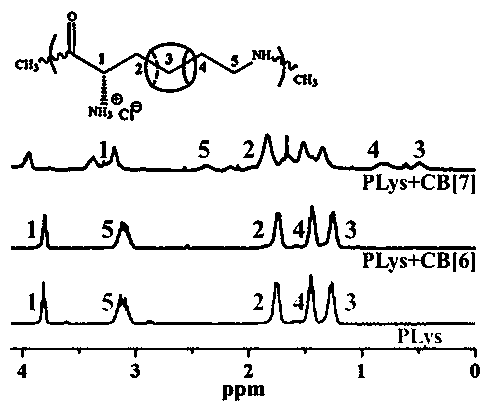
Enzymatic gelatin-based hydrogel with controllable blood-coagulation and antibacterial properties and preparation method of hydrogel
A hydrogel and gelatin-based technology, applied in the field of biomaterial preparation, can solve problems such as thrombosis and wound healing, and achieve the effects of prolonging the service life, avoiding the risk of drug resistance, and having good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1) Weigh 5 g of gelatin into a centrifuge tube, add 1.5 ml of phosphate buffer solution, place in a constant temperature water bath, adjust the temperature to 50°C, and stir until completely dissolved to obtain a gelatin solution;
[0033] 2) Weigh 0.04 g of cucurbituril [7] and 0.02 g of polylysine into a centrifuge tube, add 2 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and place the mixed solution in ultrasonic for 10 min to make it evenly dispersed;
[0034] 3) Weigh 0.04 g of transglutaminase into a centrifuge tube, add 1 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and obtain a transglutaminase solution;
[0035] 4) Mix the gelatin solution obtained in step 1) with the mixed solution obtained in step 2), and stir to make them evenly mixed;
[0036] 5) Add the enzyme solution obtained in step 3) to the solution in step 4) that was mixed uniformly above, and stir to make it evenly mixed, and transfer the above solution to a hydrogel mold, place it in a constant temperature oscillato...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1) Weigh 5 g of gelatin into a centrifuge tube, add 1.5 ml of phosphate buffer solution, place in a constant temperature water bath, adjust the temperature to 50°C, and stir until completely dissolved to obtain a gelatin solution;
[0039] 2) Weigh 0.02 g of polylysine into a centrifuge tube, add 2 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and obtain a polylysine solution;
[0040] 3) Weigh 0.04 g of transglutaminase into a centrifuge tube, add 1 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and obtain a transglutaminase solution;
[0041] 4) Mix the gelatin solution obtained in step 1) with the polylysine solution obtained in step 2), and stir to make them evenly mixed;
[0042] 5) Add the enzyme solution obtained in step 3) to the solution in step 4) that was mixed uniformly above, and stir to make it evenly mixed, and transfer the above solution to a hydrogel mold, place it in a constant temperature oscillator, and adjust the temperature to At 45°C, react for 8 h to obtain the hydr...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 1) Weigh 5 g of gelatin into a centrifuge tube, add 1.5 ml of phosphate buffer solution, place in a constant temperature water bath, adjust the temperature to 50°C, and stir until completely dissolved to obtain a gelatin solution;
[0045] 2) Weigh 0.06 g of cucurbituril [7] and 0.02 g of polylysine into a centrifuge tube, add 2 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and place the mixed solution in ultrasonic for 10 min to make it evenly dispersed;
[0046] 3) Weigh 0.04 g of transglutaminase into a centrifuge tube, add 1 ml of phosphate buffer to dissolve, and obtain a transglutaminase solution;
[0047] 4) Mix the gelatin solution obtained in step 1) with the mixed solution obtained in step 2), and stir to make them evenly mixed;
[0048] 5) Add the enzyme solution obtained in step 3) to the solution in step 4) that was mixed uniformly above, and stir to make it evenly mixed, and transfer the above solution to a hydrogel mold, place it in a constant temperature oscillato...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com