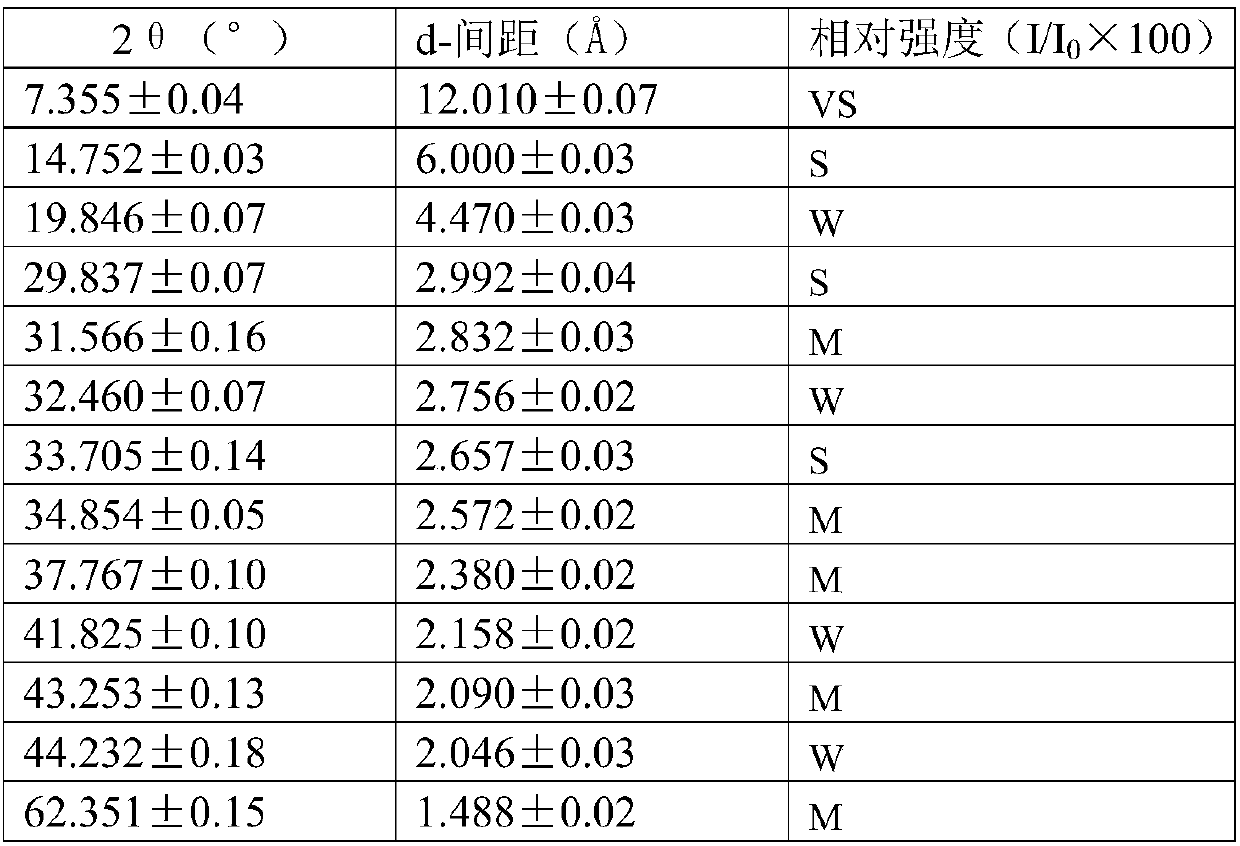
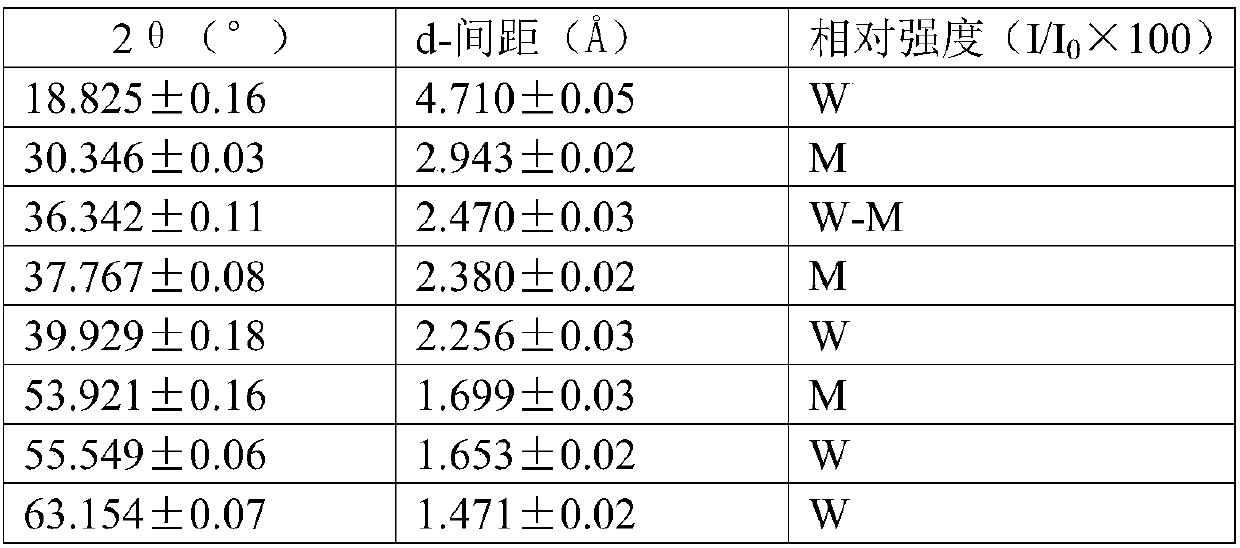
Method for producing divinyl benzene by dehydrogenating diethylbenzene
A technology of divinylbenzene and diethylbenzene, which is applied in the field of diethylbenzene dehydrogenation to produce divinylbenzene, can solve the problems of high monodiene ratio and insufficient conversion rate of diethylbenzene, and achieve high conversion rate and good The effect of technical effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Diethylbenzene and water are reacted with a dual-catalyst system in an isothermal bed reactor, wherein the upper layer is loaded with catalyst M for 65 milliliters, and the lower layer is filled with catalyst N for 35 milliliters. The reaction temperature is 600 ° C and the reaction pressure is normal pressure. Liquid space velocity is 0.5 hours -1 , The water vapor / diethylbenzene weight ratio was 3.0, and the catalyst system was purged with water vapor at 600° C. for 30 minutes before the reaction. The test results are listed in Table 1.
[0045] Wherein the preparation method of catalyst M is to be equivalent to 54.61 parts of Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide red, equivalent to 18.20 parts Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide yellow, equivalent to 9.80 parts K 2 Potassium carbonate of O, equivalent to 12.71 parts of CeO 2 of cerium oxalate, equivalent to 1.16 parts of MoO 3 ammonium molybdate, calcium carbonate equivalent to 1.35 parts of CaO, 0.02 parts of TiO 2 And 5.6 parts of sodium hyd...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Diethylbenzene and water are reacted with a dual-catalyst system in an isothermal bed reactor, wherein the upper layer is loaded with catalyst M for 65 milliliters, and the lower layer is filled with catalyst N for 35 milliliters. The reaction temperature is 600 ° C and the reaction pressure is normal pressure. Liquid space velocity is 0.5 hours -1 , The water vapor / diethylbenzene weight ratio was 3.0, and the catalyst system was purged with water vapor at 600° C. for 30 minutes before the reaction. The test results are listed in Table 1.
[0054] Wherein the preparation method of catalyst M is to be equivalent to 59.74 parts of Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide red, equivalent to 14.94 parts of Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide yellow, equivalent to 8.51 parts K 2 Potassium carbonate of O, equivalent to 10.62 parts of CeO 2 of cerium oxalate, equivalent to 1.25 parts MoO 3 Ammonium molybdate, calcium carbonate equivalent to 1.29 parts of CaO and 5.0 parts of sodium hydroxymethylcellulose we...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Diethylbenzene and water are reacted with a dual-catalyst system in an isothermal bed reactor, wherein the upper layer is loaded with catalyst M for 65 milliliters, and the lower layer is filled with catalyst N for 35 milliliters. The reaction temperature is 600 ° C and the reaction pressure is normal pressure. Liquid space velocity is 0.5 hours -1 , The water vapor / diethylbenzene weight ratio was 3.0, and the catalyst system was purged with water vapor at 600° C. for 30 minutes before the reaction. The test results are listed in Table 1.
[0059] Wherein the preparation method of catalyst M is to be equivalent to 57.61 parts of Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide red, equivalent to 14.40 parts Fe 2 o 3 Iron oxide yellow, equivalent to 7.67 parts K 2 Potassium carbonate of O, equivalent to 11.34 parts of CeO 2 of cerium oxalate, equivalent to 1.75 parts MoO 3 Ammonium molybdate, calcium hydroxide equivalent to 2.12 parts of CaO and 5.5 parts of sodium hydroxymethylcellulose were ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com