Method for establishing an in vitro simulated liver disease model and its special three-dimensional medium
An in vitro simulation and culture medium technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of establishing a three-dimensional liver cell culture model for liver cells, and achieve the effects of easy acquisition, definite chemical composition, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
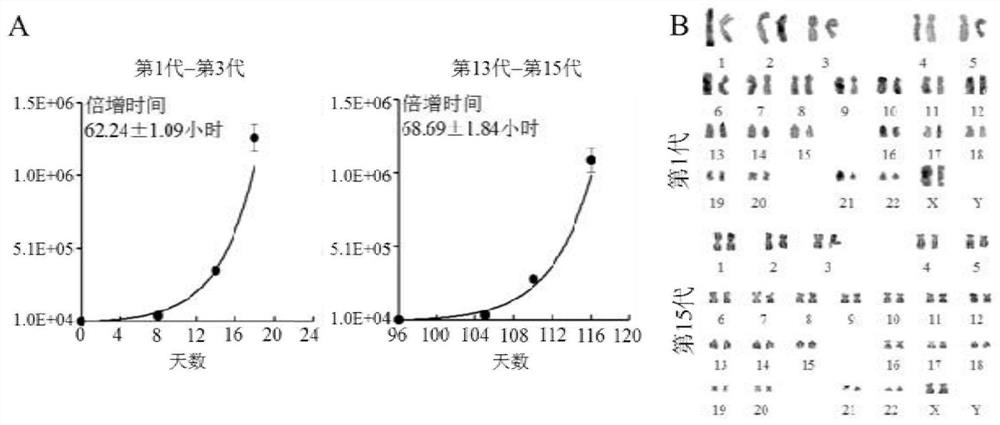
[0067] Example 1. Establishment of liver organoid culture system and phenotypic identification
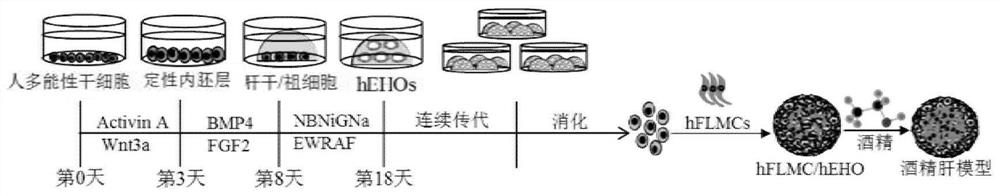
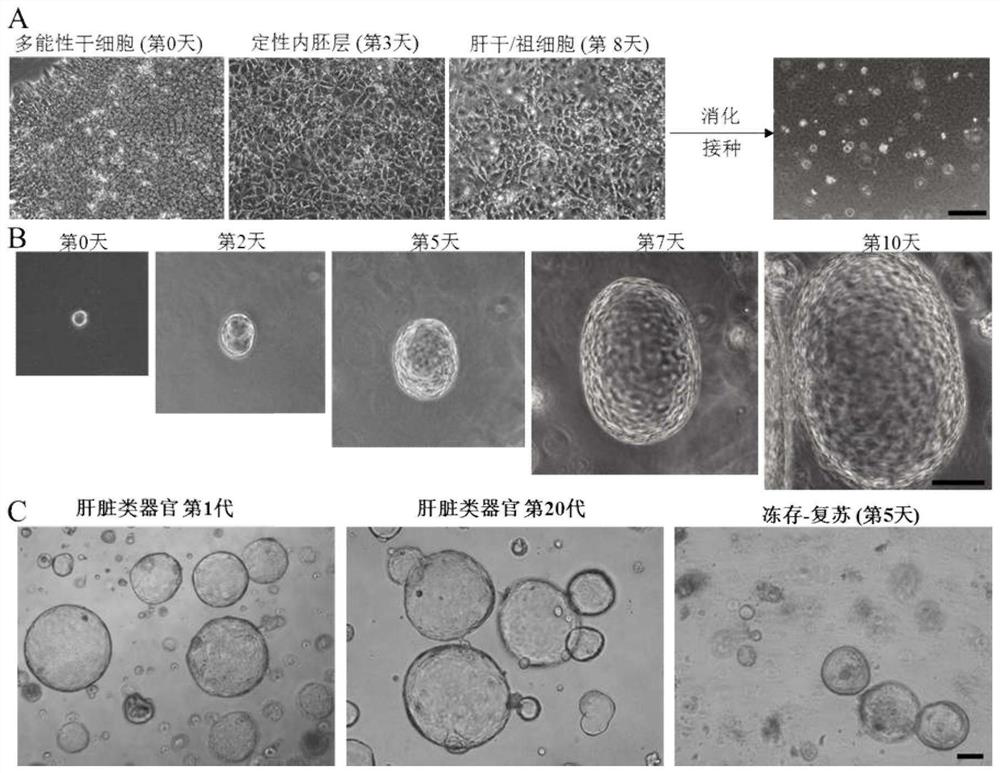
[0068] In this embodiment, pluripotent stem cells (cell line H9, human embryonic stem cells (human EmbryonicStem Cells), purchased from Wicell Research Center, USA) are used as starting cells, such as figure 1 As shown, hepatic organoids (hEHOs) were obtained sequentially through the qualitative endoderm stage and the liver stem / progenitor cell stage. Specifically include the following steps:
[0069] 1.1. Culture of cell line H9 cells
[0070] 1) Take Matrigel (Corning) out of the -80°C refrigerator one day in advance, and thaw it in a 4°C refrigerator. After it melts, dilute Matrigel at a ratio of 1:100 with pre-cooled DMEM / F12 medium (Gibco).
[0071] 2) Evenly spread the diluted Matrigel on a six-well plate, 1 mL per well, and incubate for 1 hour in a 37°C incubator for later use.
[0072] 3) Take out the H9 cells to be subcultured from the incubator at 37°C, suck off the wa...
Embodiment 2
[0182] Example 2: Establishment of an in vitro simulated liver disease model
[0183] like figure 1 As shown, this example establishes an in vitro model of alcoholic liver disease based on the co-culture of hEHOs and stromal cells obtained in Example 1. The stromal cells and the added medium components constitute the microenvironment for the differentiation of hEHOs and promote the induction of hEHOs to mature hepatocytes. Additional stromal cells were added as an indicator of whether alcohol-induced injury caused fibrosis. Usually, the fibrotic changes in the pathological injury of alcoholic liver are mainly the activation, proliferation and fibrosis of liver stromal cells. The purpose of adding stromal cells is to simulate the pathological phenomenon of alcoholic liver disease. The stromal cells used in this example can be a commercially available fetal liver stromal cell line (FL 62891 CRL-11005 TM ), commercially available mesenchymal stem cells, derived from isolated...
Embodiment 3
[0209] Example 3: Modeling Alcoholic Liver Disease in Vitro
[0210] like figure 1 As shown, this example uses the hFLMC / hEHO co-culture system established in Example 2 to simulate alcoholic liver disease in vitro by adding alcohol, specifically including the following methods:
[0211] 3.1. Alcohol treatment of hFLMC / hEHO co-culture system
[0212] 1) After hFLMC / hEHO co-cultivation for 14 days, the medium was replaced with HM medium supplemented with 100mM alcohol for 7 days as the alcohol treatment group, and the 96-well plate of the control group was replaced with alcohol-free HM medium for 7 days;
[0213] 2) Change the medium every day, and wrap the 96-well culture plate tightly with parafilm to prevent alcohol from volatilizing.
[0214] 3.2. Quantitative analysis of Dead / Live staining
[0215] 1) Collect the three-dimensional balls of the control group and alcohol-treated group in 3.1 above, discard the supernatant, and wash twice with PBS;
[0216] 2) Add 8 μM cal...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com