Targeted disruption of t cell and/or HLA receptors
A cell and zinc finger nuclease technology, applied in the field of targeted destruction of T cells and/or HLA receptors, can solve the problem of cells that cannot cause graft-versus-host disease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
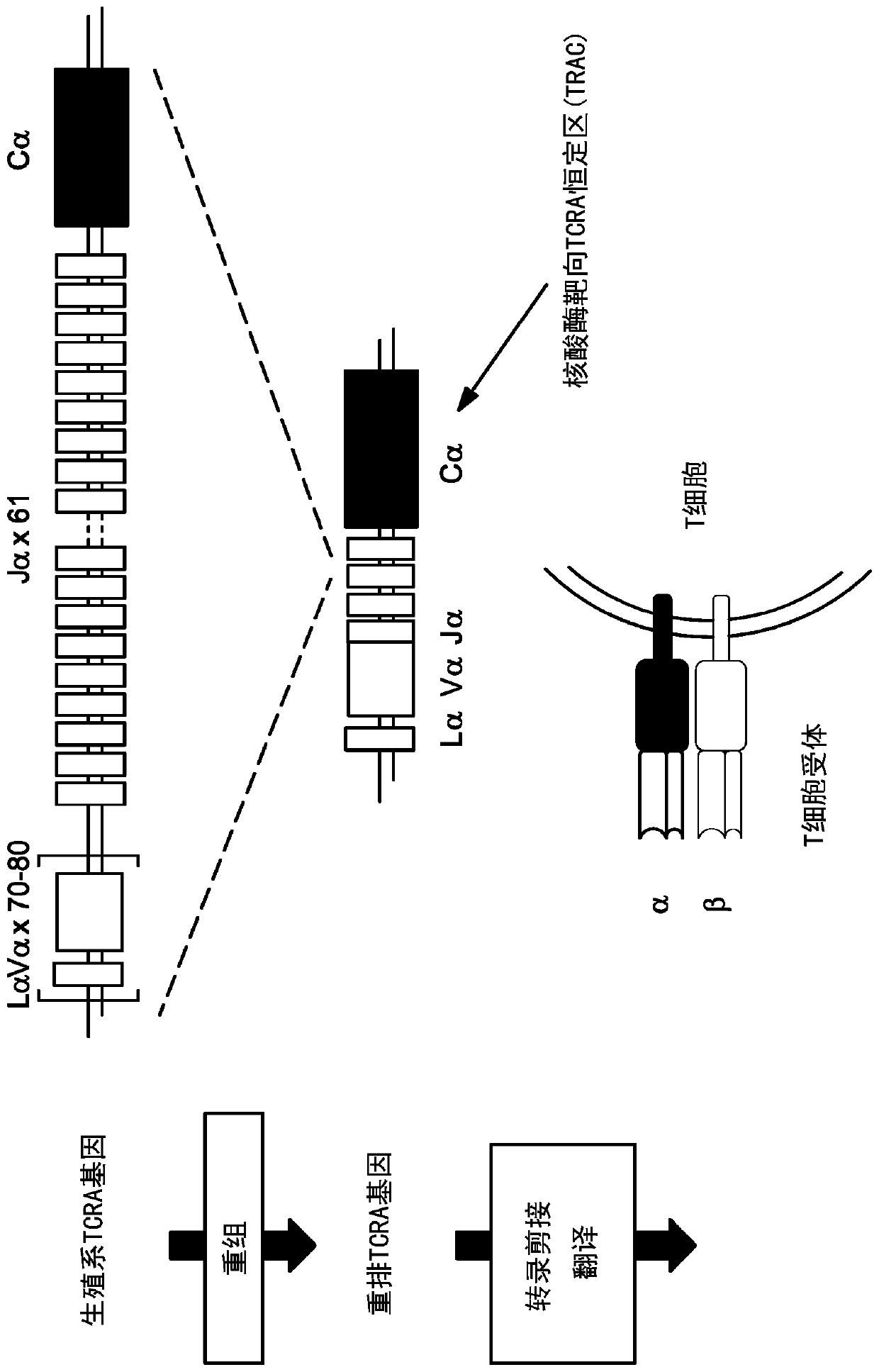
[0214] Example 1: Design of TCR-specific nucleases
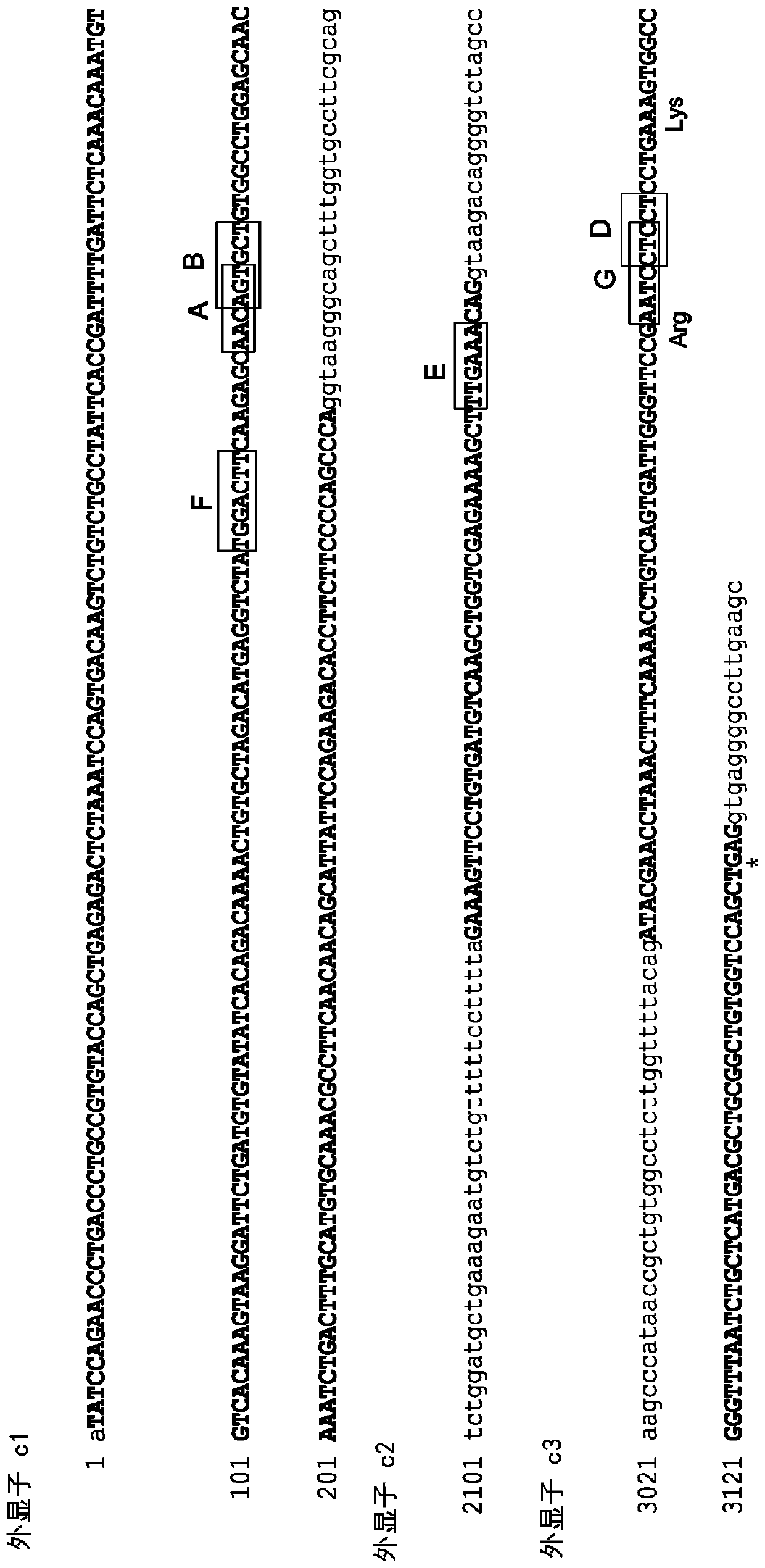
[0215] TCR-specific ZFNs were constructed to site-specifically introduce double-strand breaks at the TCRα (TCRA) gene. The design of ZFNs is generally described in, Urnov et al. (2005) Nature 435(7042): 646-651, Lombardo et al. (2007) Nat Biotechhol. 25(11): 1298-306, and US Patent Publication No. 2008 / 0131962; 2015 / 016495; 2014 / 0120622; and 2014 / 0301990 and US Patent No. 8,956,828. ZFN pairs target different sites in the constant region of the TCRA gene (see Figure 1). The recognition helices and target sequences of exemplary ZFN pairs are shown in Table 1 below. The target sites of the TCRA zinc finger designers are shown in the first column. Nucleotides in the target site targeted by the ZFP recognition helix are indicated in upper case; nucleotides not targeted are indicated in lower case. The linker used to connect the Fokl nuclease domain and the ZFP DNA binding domain is also shown (see, US Patent Publication No....
Embodiment 2
[0227] Example 2: In vitro nuclease activity
[0228] ZFNs described in Table 1 were used to test nuclease activity in K562 cells. To test for cleavage activity, plasmids encoding the paired human TCRA-specific ZFN pairs described above were transfected into K562 cells with either plasmid or mRNA. K562 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and grown as recommended in RPMI medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% qualified fetal bovine serum (FBS, Cyclone). For transfection, the ORFs of the active nucleases listed in Table 1 were cloned into expression vectors optimized for mRNA production containing 5' and 3' UTRs and a synthetic poly-A signal. mRNA was generated using the mMessage mMachine T7 Ultra kit (Ambion) following the manufacturer's instructions. In vitro synthesis of nuclease mRNA using a pVAX-based vector containing a T7 promoter, an appropriate nuclease, and a poly-A motif, or a pGEM-based vector, or a PCR amplicon for in vitro The poly-A...
Embodiment 3
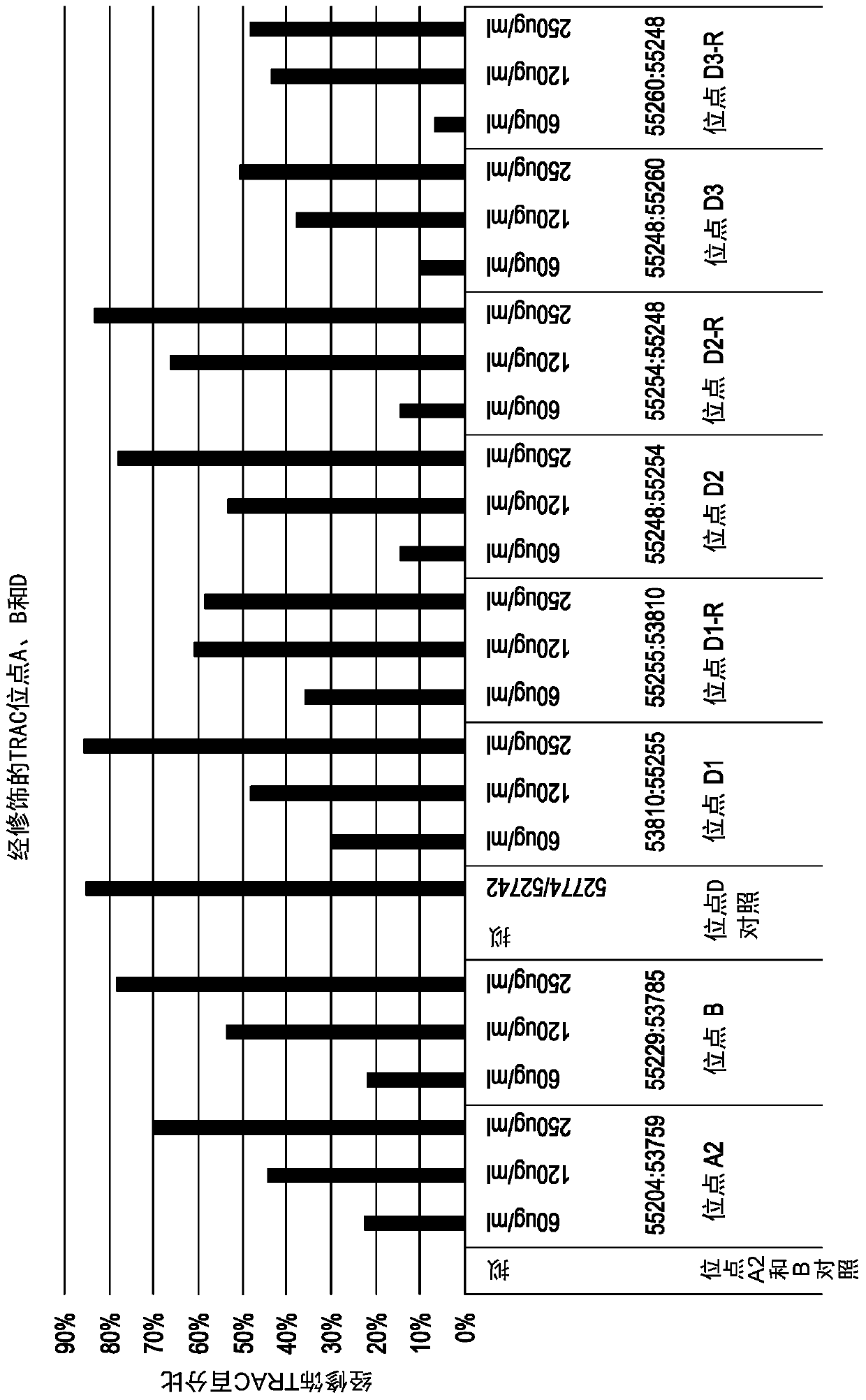
[0240] Example 3: TCRA-specific ZFN activity in T cells
[0241] The nuclease activity of TCRA-specific ZFN pairs was also tested in human T cells. ZFN-encoding mRNAs were transfected into purified T cells. Briefly, T cells were obtained from leukopheresis products and purified using Miltenyi's CliniMACS system (CD4 and CD8 dual selection). These cells were then activated using Dynabeads (ThermoFisher) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Three days after activation, cells were transfected with three doses of mRNA (60, 120, and 250 μg / mL) using a Maxcyte electroporator (Maxcyte), OC-100, 30e6 cells / mL, and a volume of 0.1 mL. On day 10 after transfection, cells were analyzed for on target TCRA modification using deep sequencing (Miseq, Illumina). Cell viability and cell growth (total cell doublings) were measured throughout 13-14 days of culture. In addition, at day 10 of culture for CD3 staining, TCR was measured on the cell surface of treated cells using standard FA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com