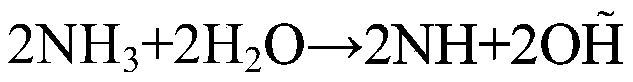Method for improving microbial cemented sand
A technology of microbial glue and sand, which is applied in the field of geotechnical engineering, can solve problems such as hidden safety hazards and loss of strength, and achieve the effects of improving toughness, increasing toughness, increasing unconfined compressive strength and residual strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A kind of method of improving microbial cemented sand of the present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Select the appropriate chemo-heterotrophic Gram-positive bacteria, prepare the corresponding medium to cultivate them, and then test the OD of the bacterial solution 600 Value and activity value, store the bacterial solution in a low temperature environment, and activate it regularly to maintain its activity;
[0038] (2) configure the cementing fluid matched with the selected chemo-heterotrophic Gram-positive bacteria;
[0039] (3) preparing soil by mixing cohesive soil, sand and stone in a weight ratio of 2:3:5;
[0040] (4) In parts by weight, mix 2 to 7 parts of sulfuric acid amide, 3 to 8 parts of triisopropanolamine, 10 to 20 parts of talcum powder, and 3 to 10 parts of carbolic acid, and adjust the pH value of the resulting mixture to make it The pH value is 7-9, and the modifying agent is obtained and set aside;
[0041] (5) Add the prep...
Embodiment 2
[0046] In this embodiment, on the basis of the foregoing embodiments, the microorganisms selected for use are further limited, and the chemoheterotrophic Gram-positive bacteria selected in the step (1) is Bacillus sarcina. The bacterial strain was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection, numbered ATCC11859, and the bacterium was a chemoheterotrophic Gram-positive bacterium. The individuals of Bacillus sarcina are oval, with a length of about 2-3 μm. This bacterium is currently the most commonly used bacterium for MICP in the field of geotechnical engineering, and its activity of secreting urease is relatively strong, which is representative to a certain extent. Other parts of this embodiment are the same as those of the foregoing embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0048] On the basis of the above-mentioned examples, the present embodiment further defines the medium components for cultivating microorganisms, the medium components configured in the step (1), in parts by weight, are 20 parts of yeast extract , 10 parts of ammonium sulfate, and 16 parts of Trisbase. The specific process of culturing microorganisms is as follows:
[0049] Use a constant temperature shaker incubator to carry out aerobic culture of bacteria at 30°C and 120rpm for 24 hours, and then use a microplate reader to measure the OD of the bacterial solution 600 (per unit OD 600 The value corresponds to about 108 bacteria) and the value is about 1.10. Using a conductivity meter to measure its activity is about 2.79mMureahydrolysed min -1 ·OD -1 . The strains were stored in a refrigerator at 4°C and activated regularly to maintain their activity. Other parts of this embodiment are the same as those of the foregoing embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com