Quantum dot conductive ink and quantum dot film
A technology of conductive ink and quantum dot film, which is applied in the field of printing, can solve the problems of poor stability of quantum dot ink, uneven film formation, and failure to meet the requirements of use, and achieve the effect of improved film formation, high stability, and smooth process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This embodiment provides a quantum dot conductive ink, including: CdSe quantum dots with a mass ratio of 6%; diethylene glycol monobutyl ether (a first solvent with a boiling point of about 230°C) with a mass ratio of 42.3%; The mass ratio is 12.5% n-octanol (the second solvent, the boiling point is about 196°C); the mass ratio is 20% 2,4-pentanediol (the second solvent, the boiling point is about 193°C); the mass ratio is The ratio is 14.2% isoamyl isovalerate (the third solvent, the boiling point is about 193 ° C); is 174°C). The preparation of the quantum dot conductive ink in Example 1 can be accomplished by simply mixing and stirring all the raw materials.
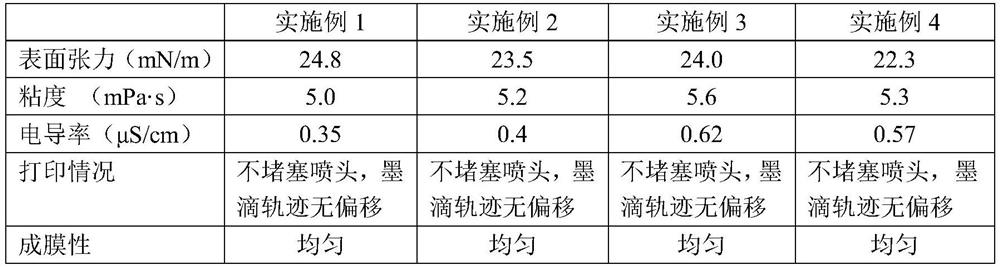
[0039] The quantum dot conductive ink in Example 1 remains stable after being placed for 30 days, and no agglomeration or precipitation will occur. At 25°C, the viscosity, surface tension and conductivity properties of the quantum dot conductive ink were tested, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This embodiment provides a quantum dot conductive ink, including: CdSeS quantum dots with a mass ratio of 5%; diethylene glycol monopentyl ether (a first solvent with a boiling point of about 255°C) with a mass ratio of 45%; 13.9% of 3-methyl-2-heptanol (second solvent, boiling point is about 166°C); 22% of 1,6-hexanediol (second solvent, boiling point of about 250°C); 12.1% by mass of isoamyl butyrate (the third solvent, with a boiling point of about 179°C); 2% by mass of 1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctyl alcohol (surface tension regulator, the boiling point is about 174°C). The preparation of the quantum dot conductive ink in Example 2 can be achieved by simply mixing and stirring all the raw materials.
[0043] In Example 2, the quantum dot conductive ink remains stable after being placed for 30 days, without agglomeration or precipitation. At 25°C, the viscosity, surface tension and conductivity properties of the quantum dot conductive ink were tested, and the results ar...
Embodiment 3
[0046] This embodiment provides a quantum dot conductive ink, comprising: CdSe / ZnS quantum dots with a mass ratio of 4%; triethylene glycol monomethyl ether (the first solvent, with a boiling point of about 249° C.) with a mass ratio of 46.3% ); mass proportion is 15% 3-methyl-2-heptanol (second solvent, boiling point is about 166 ℃); mass proportion is 20.8% isononyl alcohol (second solvent, boiling point is about 178 ℃ ); the mass ratio is 10.9% isoamyl butyrate (the third solvent, the boiling point is about 179 ° C); the mass ratio is 3% 1H, 1H, 11H-perfluoro-1-undecanol (surface tension regulator, the boiling point is about 180°C). The preparation of the quantum dot conductive ink in Example 3 can be achieved by simply mixing and stirring all the raw materials.
[0047] In Example 3, the quantum dot conductive ink remains stable after being placed for 30 days, without agglomeration or precipitation. At 25°C, the viscosity, surface tension and conductivity properties of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com