Two-phase direct-current bias current vernier reluctance motor
A reluctance motor and DC bias technology, which is applied in the direction of AC motor control, magnetic circuit, electromechanical device, etc., can solve the problems of large torque pulsation, high vibration noise, weak magnetic field, etc., to improve strength, reduce switching devices, short end effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
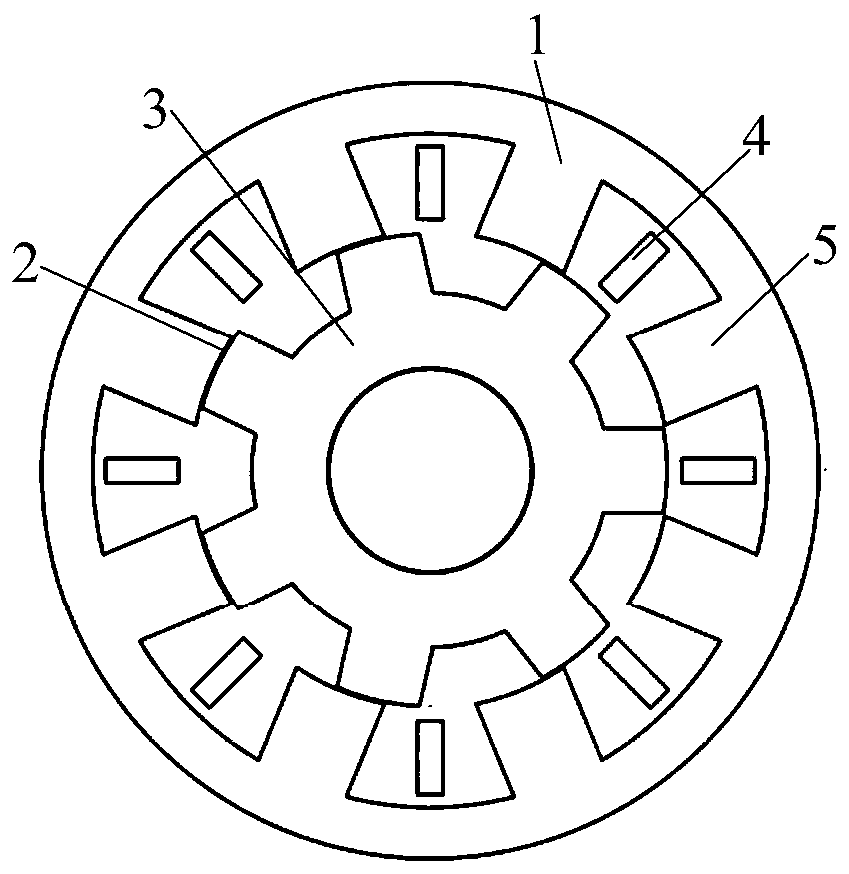
[0040] like figure 1 as shown, figure 1 It is the two-phase DC bias current vernier reluctance motor of embodiment 1, comprising a stator 1, an air gap 2, and a rotor 3, the stator 1 is sleeved on the periphery of the rotor 3, and an air gap 2 is arranged between the two, and the stator and the rotor are both A double-salient pole structure is adopted; the stator 1 includes a stator yoke, a stator end and a stator winding 4. The stator end is composed of a number of evenly distributed stator teeth 5, and the stator winding 4 is connected in a non-overlapping and centralized manner with fractional slots, alternately It is connected to half of the stator teeth 5; the air gap 2 has a great influence on the performance of the motor, and an appropriate air gap length is required. Here, 0.3mm is selected through optimization. In Embodiment 1, the stator has 8 slots, the rotor has 7 slots, the stator winding has 5 pairs of poles, and the number of DC excitation pole pairs is 2.
[...
Embodiment 2
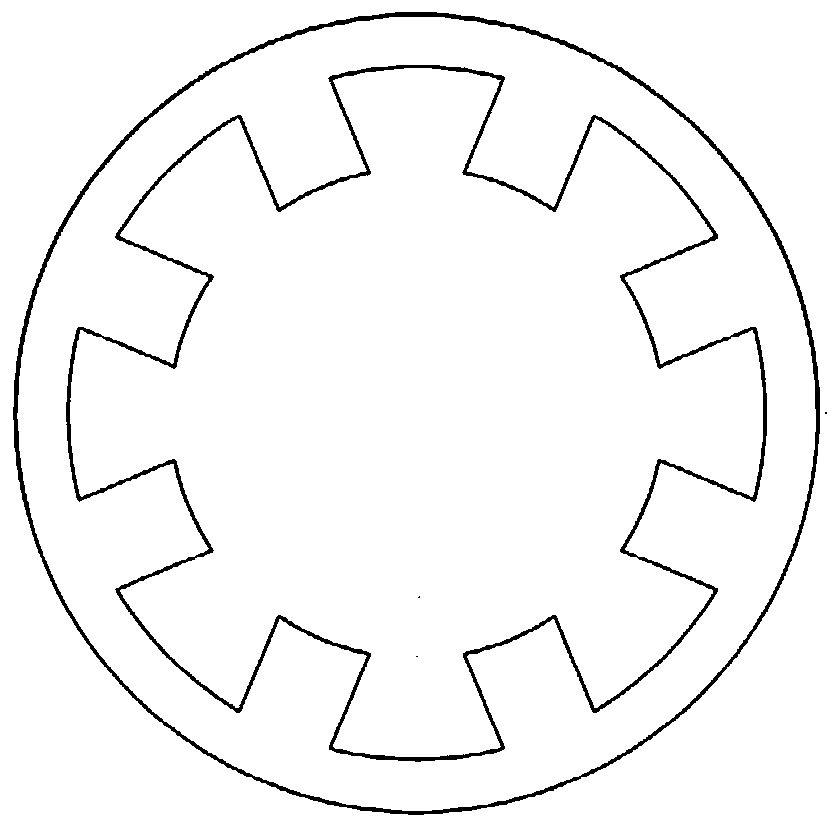
[0052] The motor of embodiment 2 is as Figure 5 As shown, the structure of the motor is basically the same, the only difference is that the slots and poles match and the direction of the direct current is different. like Figure 5 As shown, the motor also belongs to the two-phase DC bias current vernier reluctance motor, the stator has 8 slots, the rotor has 9 slots, the stator winding 4 has 5 pairs of poles, and the number of DC excitation pole pairs is 4. Structurally than figure 1 The embodiment adds 2 rotor slots; according to the counterclockwise or clockwise direction, the currents of the stator winding 4 are i A+ i B+ i A- and i B- , the purpose of doing this is to reconstruct the direction of the DC current so that it meets the slot-to-pole fit.
[0053] The use of this arrangement ensures on the one hand the number of pole pairs of the expected rotating fundamental magnetic field generated by the AC current, and on the other hand ensures the number of pole pair...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com