A kind of maize bm1 gene mutant and the molecular marker and application of the gene
A molecular marker, corn technology, applied in the field of plant molecular biology, can solve problems such as brown pigmentation, and achieve the effect of huge economic value and improvement of corn germplasm resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Identification of Mutant Genes of Maize Brown Leaf Midrib Mutants
[0042] 1. BSR-seq mapping of brown leaf midrib mutant gene in maize
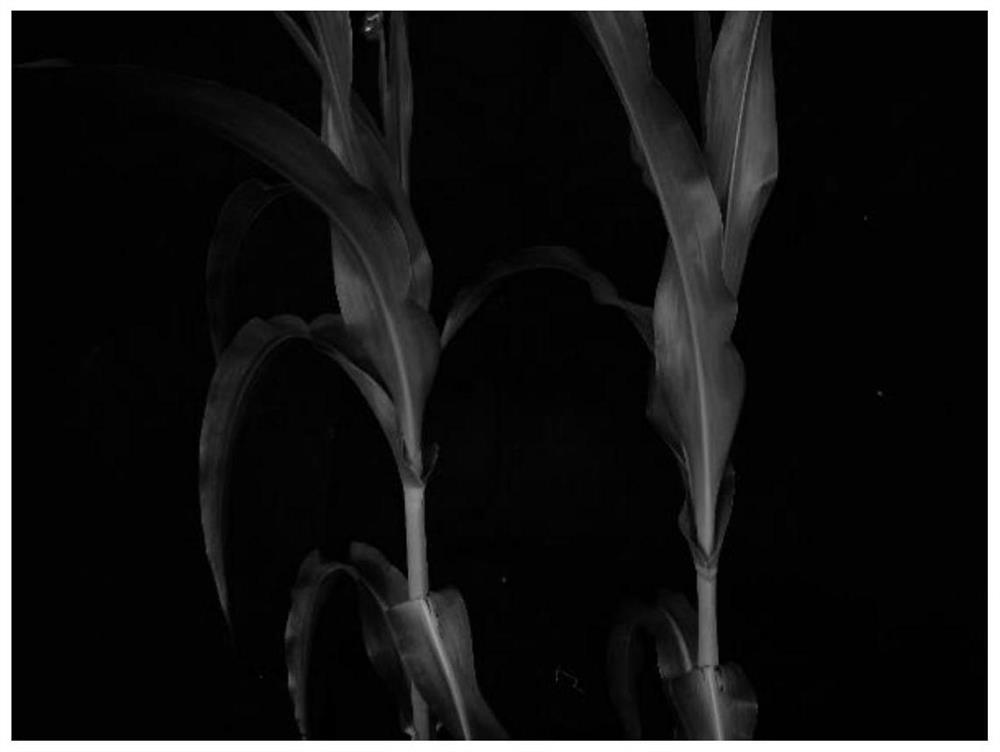
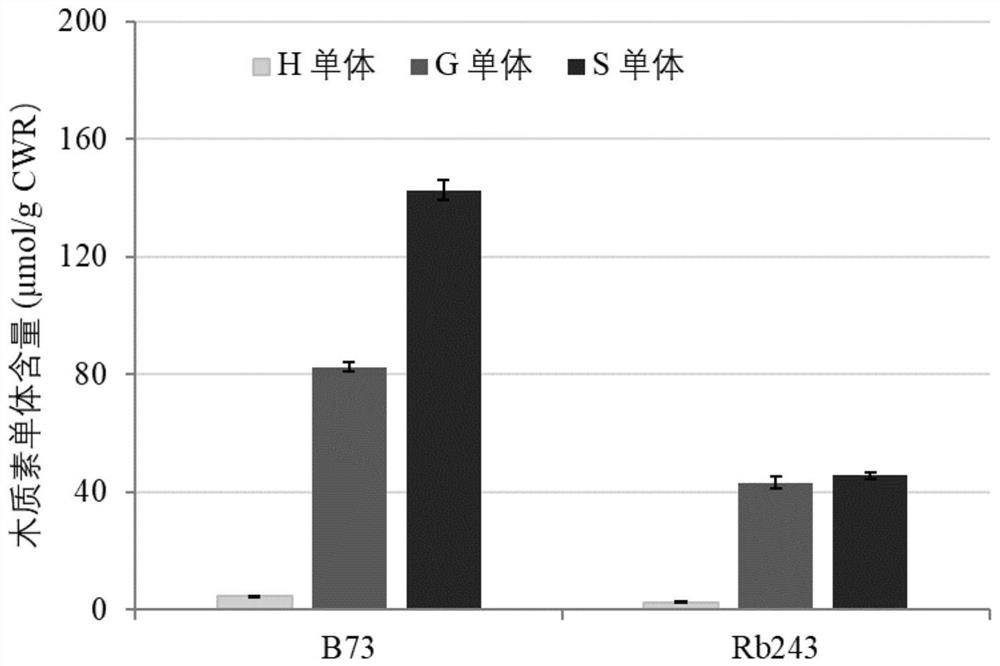
[0043] During the corn planting process, the inventors have discovered a natural mutant Rb243 in the brown leaf midrib of corn ( figure 1 ), the contents of H, G, and S lignin types in vein cell wall residues (CWR) were 2.54±0.12, 43.21±1.84, 45.50±1.30 μmol / g, respectively, which were significantly lower than those of normal maize B73 (H, G , S-type lignin contents were 4.37±0.02, 82.49±1.41, 142.42±3.39μmol / g)( figure 2 ). After the maize brown leaf midrib mutant Rb243 was crossed with normal maize B73, the F1 hybrids had normal leaf veins, and among the 591 F2 individuals, there were 152 brown leaf midrib individuals and 439 normal leaf vein individuals, which conformed to the 1:3 segregation ( x 2 1:3 =0.16, P=0.69), indicating that the midrib trait of maize brown leaf is controlled by a recessive single gene.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Development of Functional Molecular Markers of Brown Leaf Midrib Mutant bm1 Mutant Gene
[0056] Based on the sequence difference between brown leaf midrib mutant Rb243 and normal maize B73 in the first exon of bm1 gene, the present invention develops a PCR functional molecular marker PCR-Zmbm1 for detecting the mutant. The amplification primers for the functional molecular marker PCR-Zmbm1 are shown in Table 1. The PCR amplification program is: 94°C pre-denaturation for 4 minutes; 94°C denaturation for 20 s, 60°C annealing for 20 s, 72°C extension for 20 s, 34 cycles; 72°C ℃ extension 10min. 141F, -193F and 394R primers were used to amplify the bm1 gene, and the amplified products were detected by agarose electrophoresis. The size of the amplified fragment in the brown leaf midrib mutant Rb243 was 588bp, and that in normal maize B73 was 254bp, Rb243× The amplified fragment sizes in B73 hybrids were 254bp and 588bp ( Figure 7 ). Adopt the molecular marker ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Application of Functional Molecular Marker PCR-Zmbm1 in Molecular Marker-Assisted Breeding Jingke 968 is a maize hybrid widely promoted in China. Its female parent is Jing 724 and its male parent is C92. None of these materials have brown leaf midribs Phenotype. Using PCR-Zmbm1 functional molecular marker-assisted selection, the leaf midrib traits of Jing 724 and C92 were improved, and the improved Jingke 968 with brown leaf midrib phenotype was obtained ( Figure 9 ).
[0058] The specific implementation method is as follows: the brown midrib maize mutant Rb243 is used as the non-recurrent parent, and Jing 724 and C92 are used as the recurrent parent. Rb243 was crossed with Jing 724 and C92 respectively, and then backcrossed with Jing 724 and C92 for 5 times, and all of them were self-crossed once, that is, BC5F2. A single plant with a brown leaf midrib phenotype was selected from the BC5F2 generation, and the single maize plant was Jing 724 and C92, which ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com