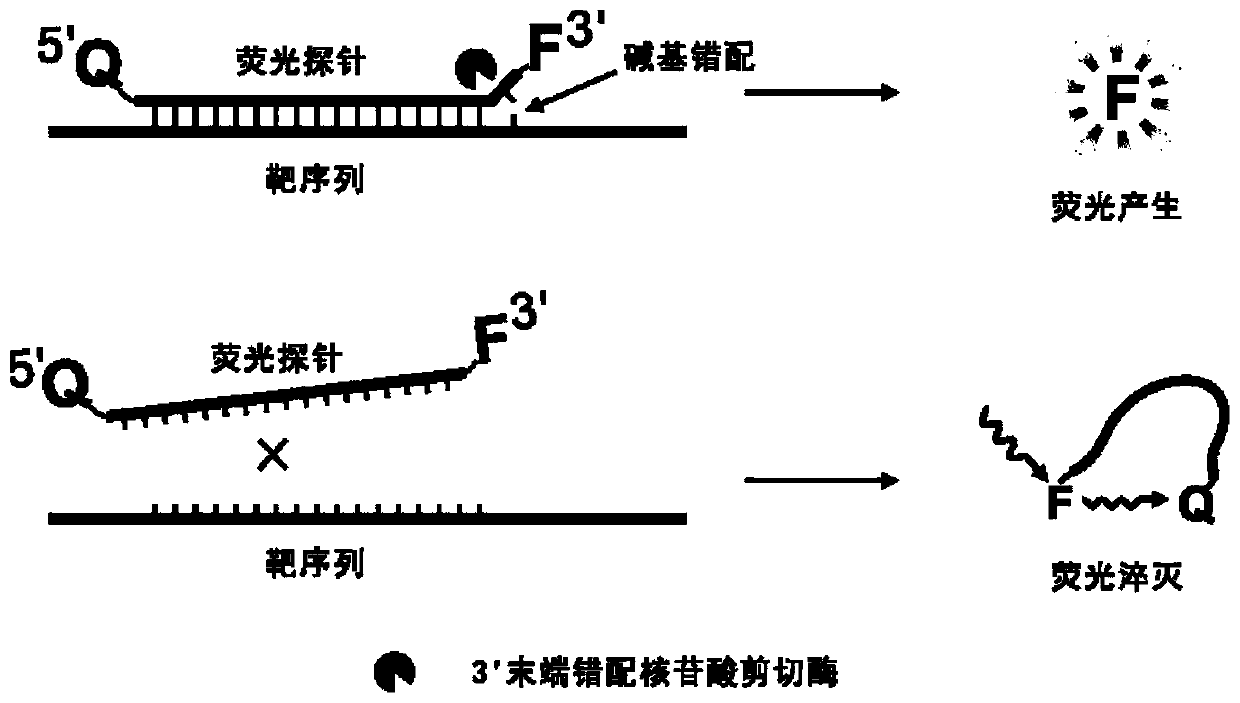
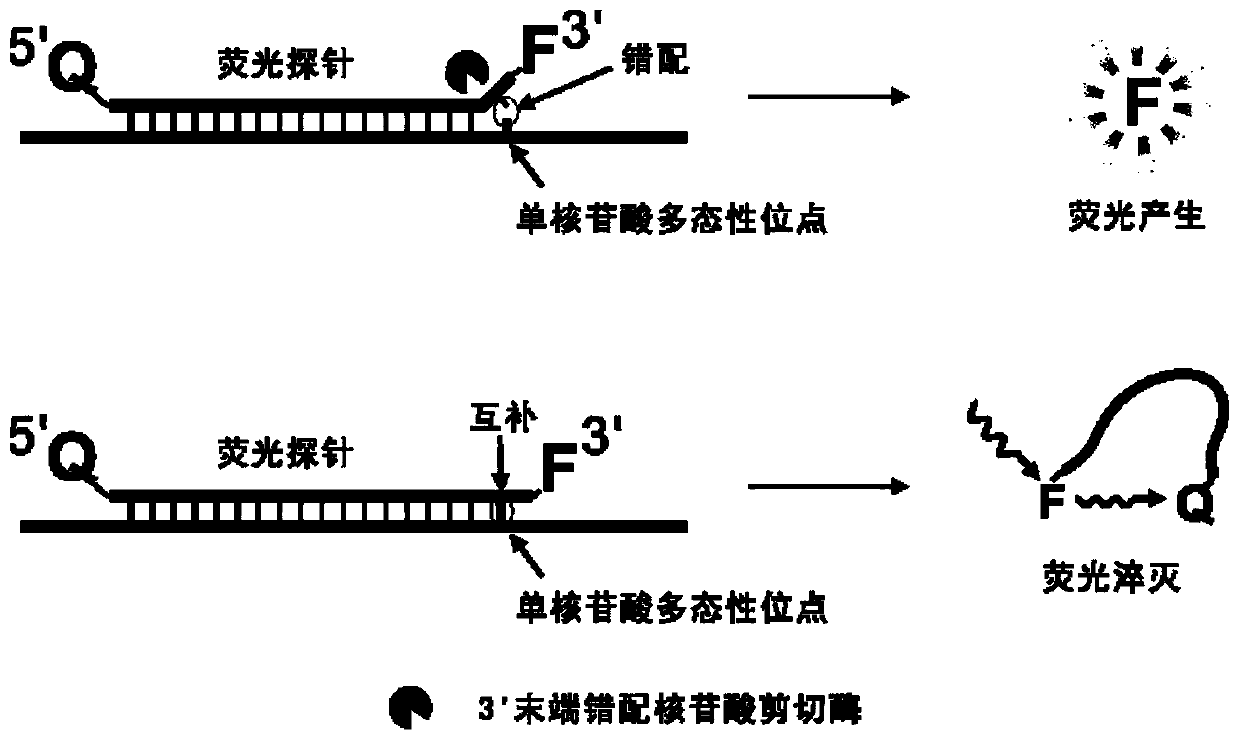
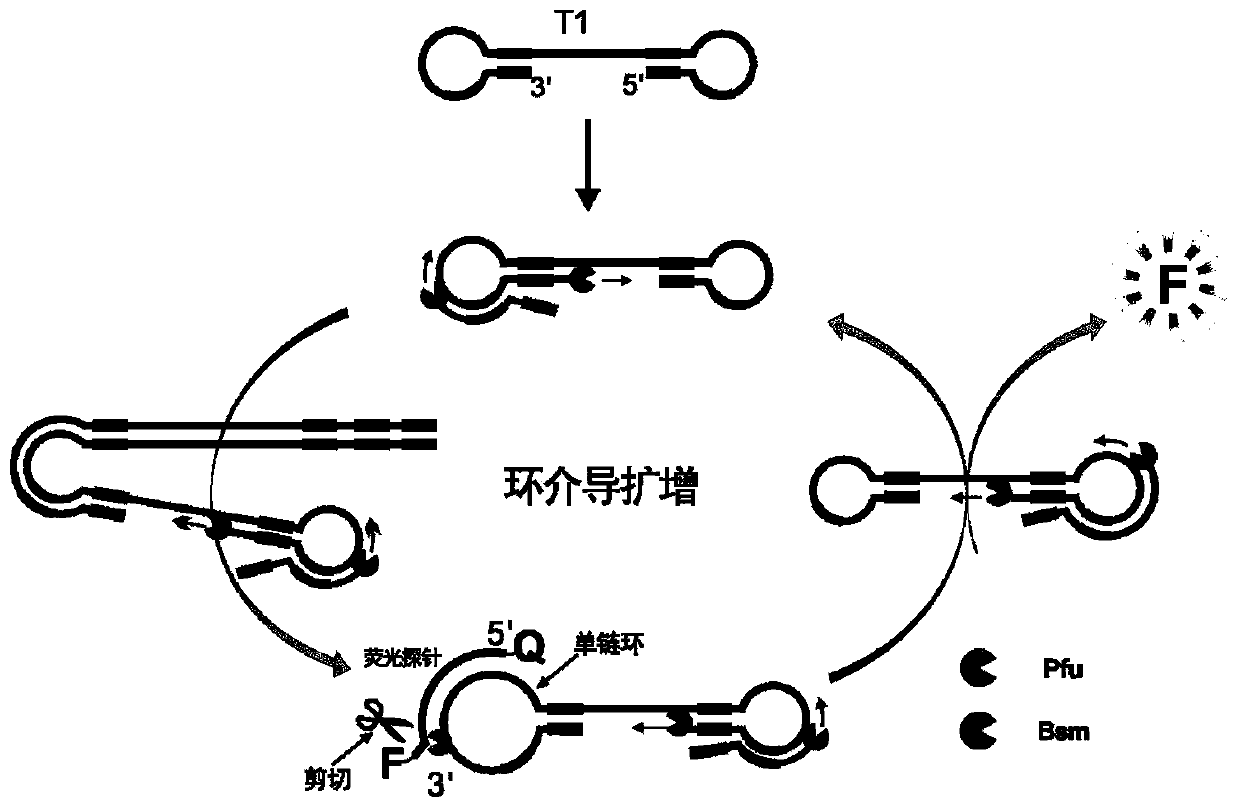
Fluorescent probe
A technology of fluorescent probes and probes, applied in DNA/RNA fragments, measurement/inspection of microorganisms, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as unsuitable polymerases, achieve great practical value, easy preparation, and wide application range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1. Examples of fluorescent probes applied to quantitative detection of loop-mediated amplification reactions
[0039] The fragment of the BRAF gene was cloned into the plasmid T1, and the recombinant plasmid was sequenced and verified to obtain the recombinant plasmid T1-BRAF as a template for the amplification reaction. Loop-mediated amplification primers and fluorescent probes were designed for the BRAF gene sequence.
[0040] BRAF gene fragment sequence:
[0041] 5'-TAAAAATAGGTGATTTTGGTCTAGCTACAGTGAAATCTCGATGGAGTGGGTCCCATCAGTTTGAACAGTTGTCTGGATCCATTTTGTGGATGGCACCAGAAGTCATCAGAATGCAAGATAAAAATCTACAGCTTTCAGTCAGATGTATATGC-3'
[0042] (1) Loop-mediated amplification primers and fluorescent probe sequences:
[0043] FIP: 5'-AGACAACTGTTCAAACTGATGGGTAAAAATAGGTGATTTTGGTCTAGC-3'
[0044] BIP: 5'-TCCATTTTGTGGATGGCACCGCATATACATCTGACTGAAAGC-3'
[0045] LB:5'-GCAAGATAAAAATCCATACA-3'
[0046] F3:5'-TATTTCTTCATGAAGACC-3'
[0047] B3:5'-CCAGTCATCAATTCATAC-3'
[0048] PM ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, single nucleotide polymorphism detection example
[0059] The recombinant plasmid in Example 1 was mutated to obtain a mutant plasmid corresponding to BRAF (V600E), and T1-BRAF and T1-BRAF-M were used as templates for detection respectively.
[0060] Mutation template sequence:
[0061] TAAAAATAGGTGATTTTGGTCTAGCTACAGAGAAATCTCGATGGAGTGGGTCCCATCAGTTTGAACAGTTGTCTGGATCCATTTTGTGGATGGCACCAGAAGTCATCAGAATGCAAGATAAAAATCCATACAGCTTTCAGTCAGATGTATATGC
[0062] The bases in italics indicate the mutation sites.
[0063] The primers and probes designed in Example 1 were used to distinguish between normal plasmids and mutant plasmids.
[0064] (1) Reaction system and reaction conditions
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] Finally, the reaction system was made up to 25 μL with sterilized deionized water.
[0068] The reaction conditions are: react at 60°C for 70 minutes.
[0069] (3) Detection method
[0070] Using a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument, set the FAM chan...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3, Fluorescent Probes Realize Specific Detection Example of Loop-Mediated Amplification Reaction
[0074] In Example 1, the sequence of the recombinant plasmid T1-BRAF and the complementary pairing of the fluorescent probe was replaced with any sequence, and the replaced sequence could not be complementary to the fluorescent probe to obtain a new plasmid T1-BRAF-N, respectively with T1-BRAF and T1-BRAF-N as templates for detection.
[0075] The template sequence after replacement is as follows:
[0076] TAAAAATAGGTGATTTTGGTCTAGCATGTCGCAACAATATTATGACTATACCCATCAGTTTGAACAGTTGTCTGGATCCATTTTGTGGATGGCACCAGAAGTCATCAGAATGCAAGATAAAAATCATACAGCTTTCAGTCAGATGTATATGC
[0077] The parts in italics are the replaced sequences.
[0078] (1) Reaction system and reaction conditions
[0079]
[0080]
[0081] Finally, the reaction system was made up to 25 μL with sterilized deionized water.
[0082] The reaction conditions are: react at 60°C for 90 minutes.
[0083] (3) D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com