Method for hydrodeoxidation upon lignin by using ruthenium-based catalyst under deep eutectic solvent condition
A low eutectic solvent, ruthenium-based catalyst technology, applied in molecular sieve catalysts, lignin derivatives, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of water consumption, large organic solvent consumption, difficulty in direct utilization, etc., and achieve wider application. The effect of surface, large pore size, and large specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0024] Weigh a certain amount of ChCl and acetic acid (the molar ratio of the two substances is 1:2), add it into a beaker, stir and heat in an oil bath at 80°C for 2h, and obtain a clear and transparent solution after cooling, which is the prepared ChCl: Acetic acid DES.
[0025] Add eucalyptus wood powder and deionized water (reaction solid-to-liquid ratio 1:12g / ml) into a high-pressure reactor, and react at 170°C for 1 hour under a nitrogen atmosphere. After the reaction, cool to room temperature, filter under reduced pressure, and filter the residue Dry at 105°C for 12h to obtain a hydrothermal residue.
[0026] Weigh 2g of hydrothermal residue and 40g of ChCl: acetic acid DES, add them to the Erlenmeyer flask, and react at 120°C for 4h. , the filter residue was dried at 105°C for 12 hours, weighed after cooling to room temperature, and the mass of lignin dissolved in the DES filtrate was obtained according to the subtraction method. The volume is 50ml.
[0027] Add 100...
Embodiment 5
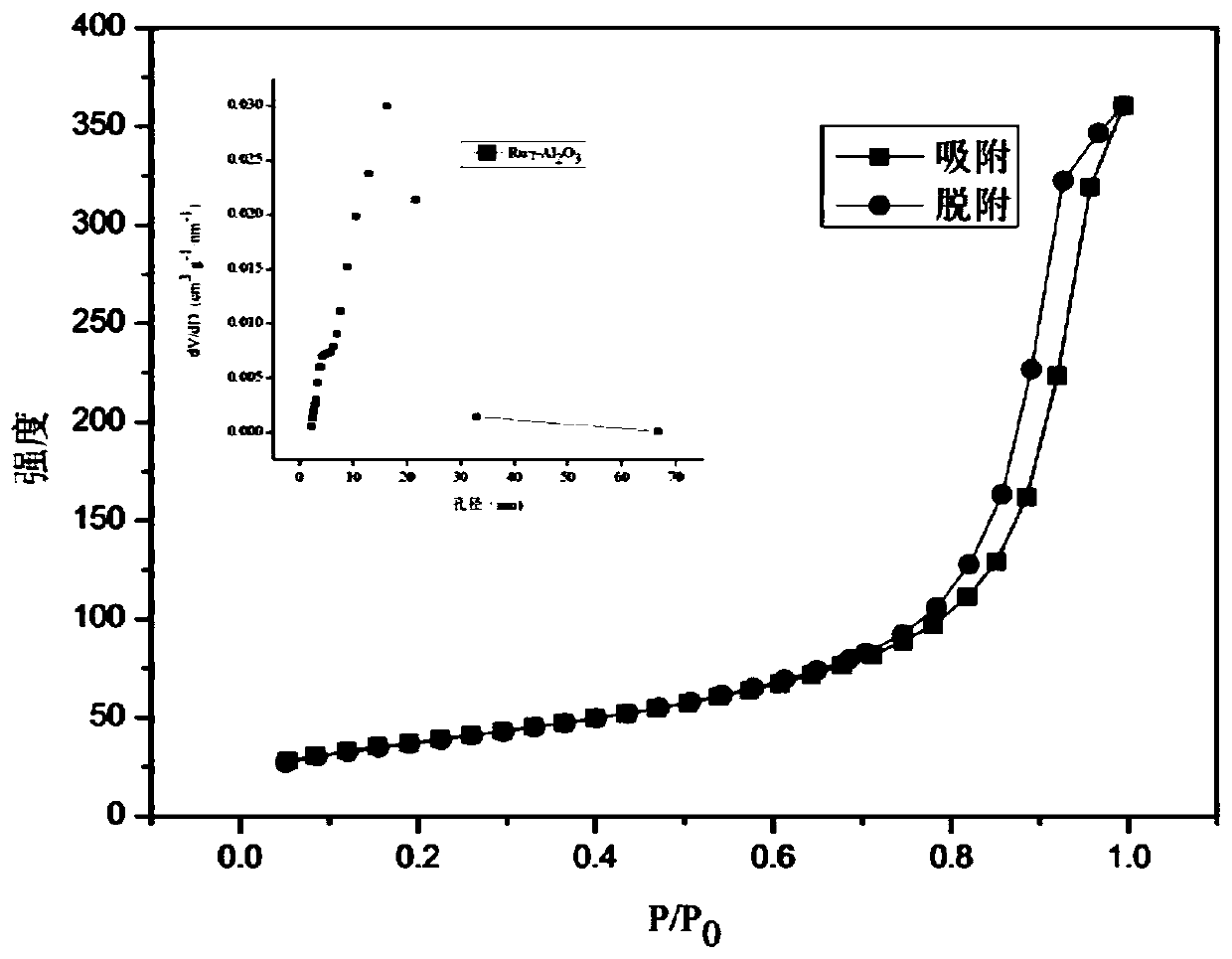
[0028] The adsorption-desorption curve and pore size distribution figure of the catalyst used in embodiment 5 are as follows figure 1 shown. according to figure 1 It can be seen that the catalyst has a V-type isotherm and a H3-type hysteresis loop. From the pore size distribution diagram, it can be seen that the pore size of the catalyst belongs to mesopores, the pore size distribution is narrow, and the pore size is large. It has better catalytic activity, and the yield of liquid products and phenolic products is higher.
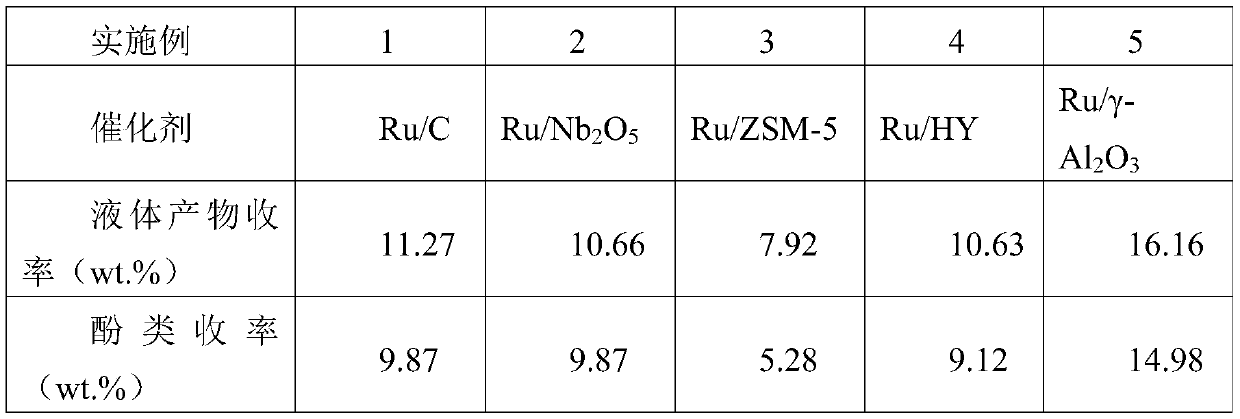
[0029] Table 1 Effect of different catalysts on lignin hydrodeoxygenation
[0030]
Embodiment 6-11
[0032] With reference to Example 5, the Ru / γ-Al of 100mg 2 o 3 The catalyst and 50ml of DES filtrate were added to the high-pressure reaction kettle, and the gas was repeatedly replaced by hydrogen for 3 times, and 1MPa H was filled after removing all the air. 2 ,React at 120-280°C for 4 hours. After the reaction, quickly cool down the reactor with cold water, collect the gas, filter it under reduced pressure, and extract it with ethyl acetate. See Table 2 for the yield of liquid products and phenols.
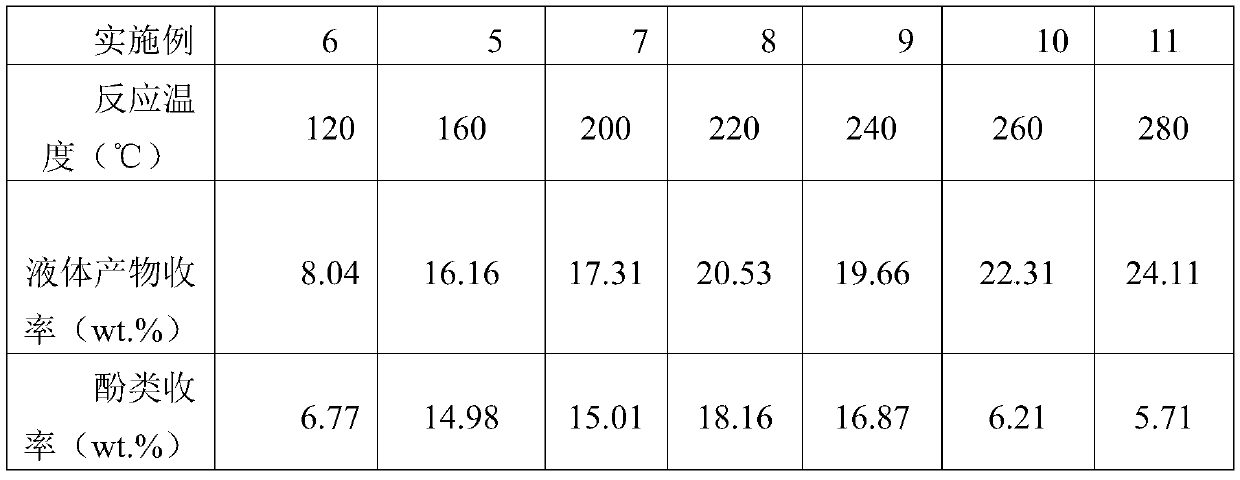
[0033] Table 2 Effect of temperature on lignin hydrodeoxygenation
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com