Drug for preventing and treating cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM)
A brain spongy and malformation technology, applied in the field of medicine for preventing and treating cerebral cavernous malformation lesions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
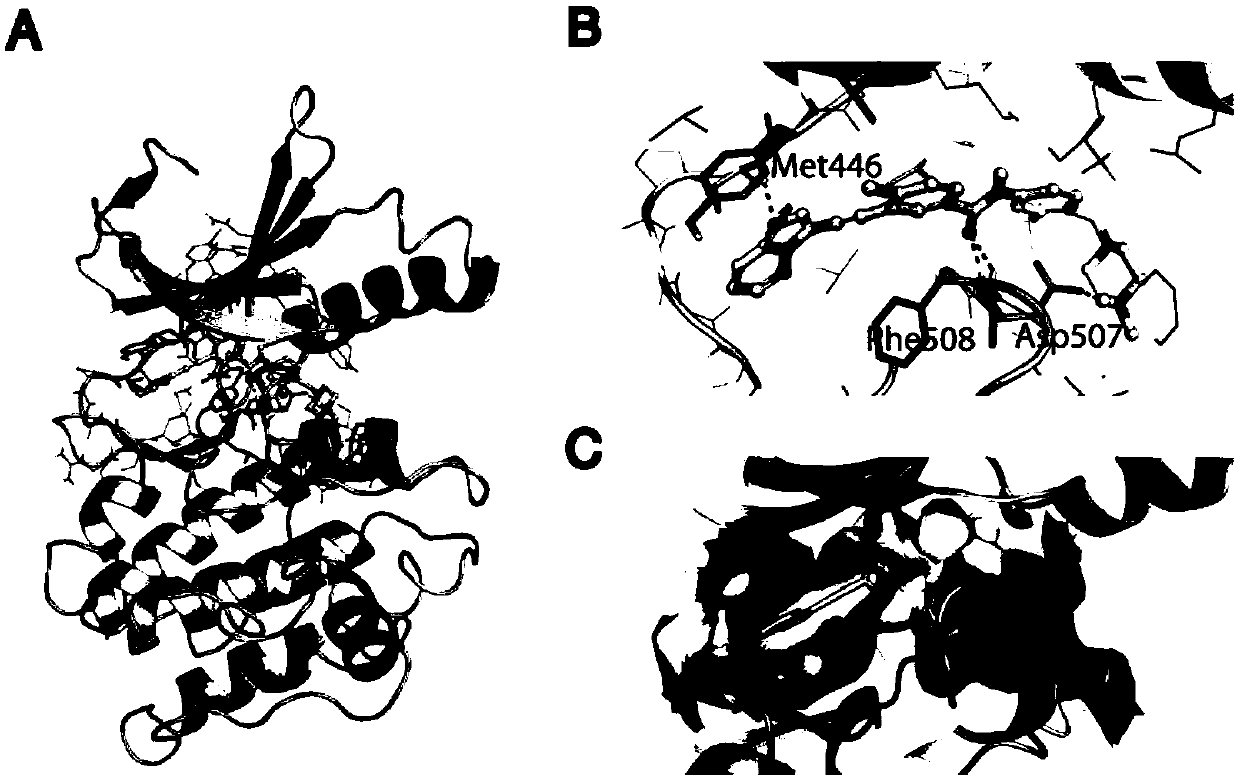
[0111] Example 1, Ponatinib directly inhibits MEKK3 kinase activity
[0112] The inventors performed complex protein modeling based on crystal structures and performed in vitro kinase assays using purified MEKK3 and its interacting substrates and its kinase substrate MEK5. Ponatinib is a type II kinase inhibitor that binds the kinase in the DFG-out conformation. Based on the previously solved crystal structure of the Ponatinib-FGFR4 complex, the Ponatinib-Abl complex and the structure-solved DFG-out kinase PAK1 with high homology to the MEKK3 kinase domain, computer modeling reveals that in the ATP-binding band, Ponatinib binds with hydrogen Bond and π-π bond (color) interactions with MEKK3 kinase domain binding ( figure 1 , A, B, C).
Embodiment 2
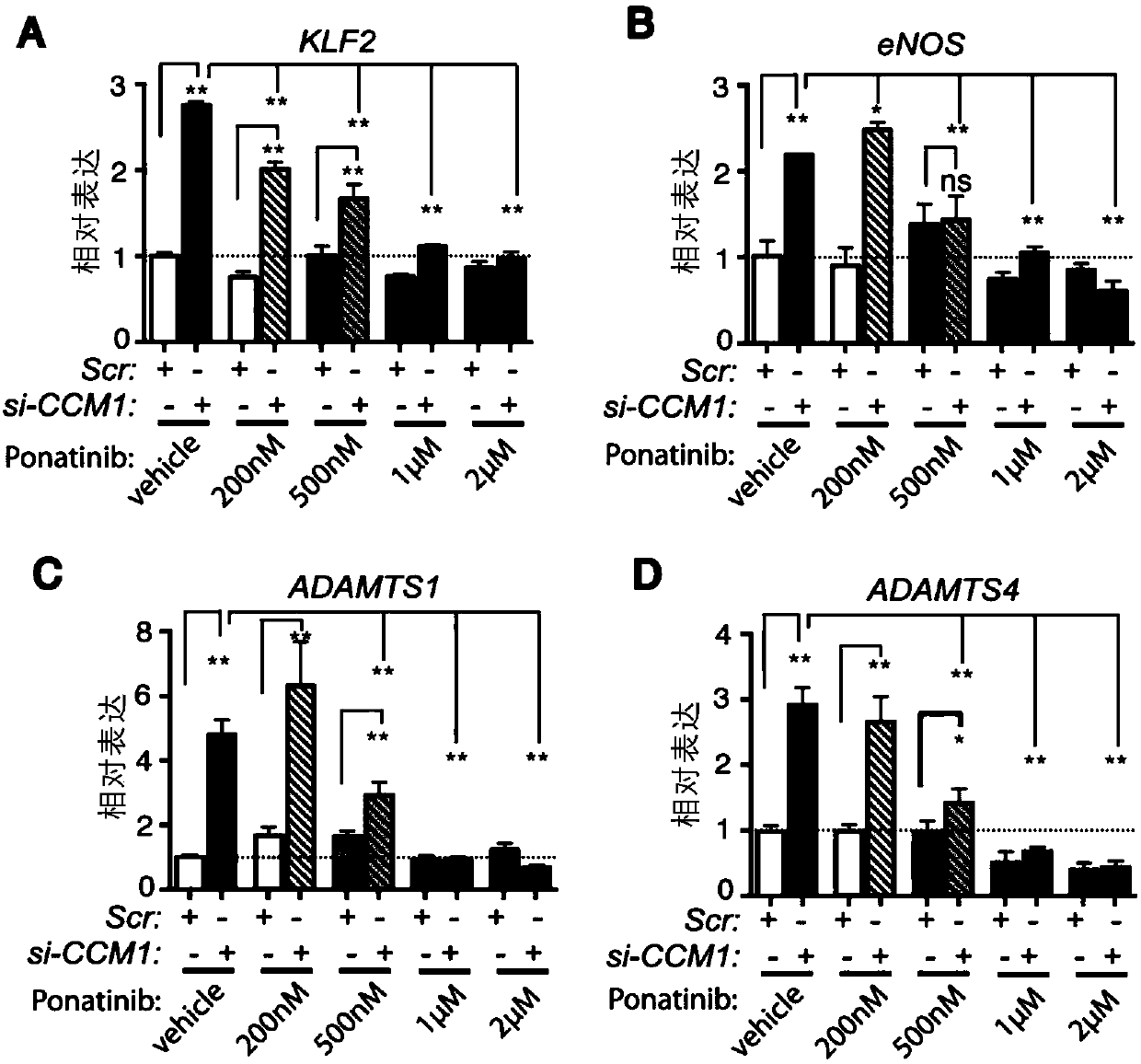
[0113] Example 2, Ponatinib inhibits the activity of MEKK3 signaling pathway in the CCM gene deletion cell model
[0114]Loss of CCM genes in endothelial cells causes upregulation of MEKK3 signaling. In order to demonstrate whether Ponatinib can correct CCM lesions by inhibiting abnormal MEKK3 activity, the inventors constructed a human umbilical vein endothelial cell system with siRNA knockout of the CCM1 (siRNA) gene, and administered different doses of Ponatinib. The obtained results showed that CCM1 gene deletion increased the expression level of MEKK3 downstream target genes. In cells treated with control siRNA, Ponatinib did not affect the expression of KLF2, eNOS, and ADAMTS1; while compared with the control group, high doses of Ponatinib decreased the expression of ADAMTS4 ( figure 2 A~D). More importantly, Ponatinib treatment group can reduce the high expression of these genes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, so that it can reach the same expression level...
Embodiment 3
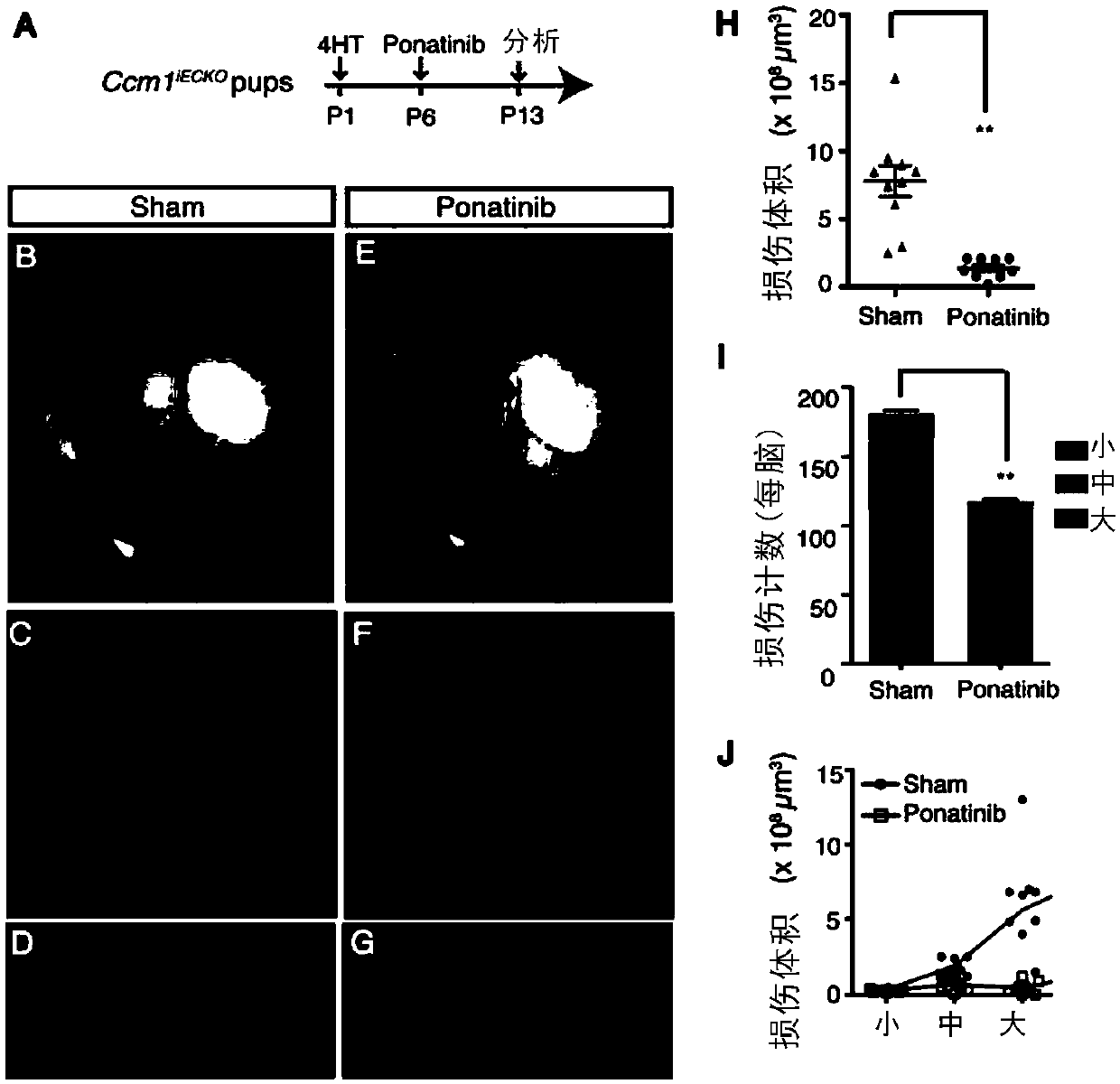
[0116] Example 3, Ponatinib inhibits the formation and expansion of CCM aberration in the disease model of CCM1 gene deletion
[0117] In vitro experiments have confirmed that Ponatinib can correct abnormal signaling changes in CCM1-deficient endothelial cells. In order to confirm whether Ponatinib can alleviate CCM lesions in an animal model of CCM1 gene deletion, the inventors specifically induced the knockout of the endothelial cell CCM1 gene in an animal model (Cdh5-CreERT2; Ccm1fl / fl, marked as Ccm1 iECKO Mice) were given Ponatinib (10mg / kg) by intragastric administration ( image 3 A). Neonatal mice were induced with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HT) to produce a CCM1 deletion disease model on the first day after birth, and tiny CCM lesions began to appear on the 6th day after birth, and on the 13th day, through Micro- Ccm1 can be seen on CT iECKO Mice with multiple vascular malformations ( image 3 B-D).
[0118] When the inventors in the newborn Ccm1 iECKO Ponatinib admi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com