Low-energy-consumption rapid biochemical sewage denitrification process
A low-energy-consumption, sewage technology, applied in the fields of oxidized water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, flotation water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, low denitrification efficiency, etc. The effect of small, short total hydraulic retention time and less aeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
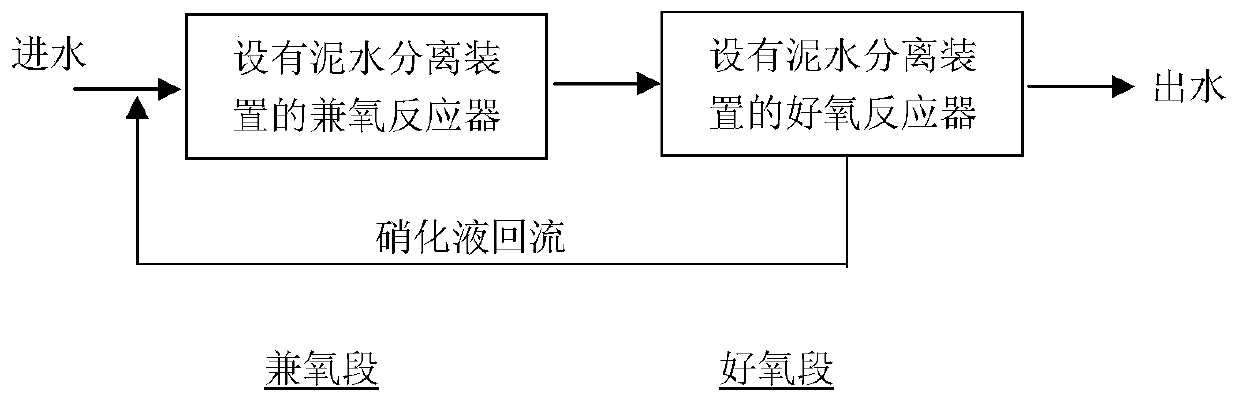
[0020] like figure 1 , a low-energy rapid biochemical sewage denitrification process, including a facultative section and an aerobic section, the aerobic section adopts a reaction-sedimentation integrated rectangular air-lift circulation bioreactor, and the aerobic section adopts an aerated biological filter. After the following procedures: Step 1, the sewage enters the aerobic section, and the sewage undergoes denitrification and short-range nitrification and denitrification reactions with the aerobic microorganisms in the aerobic section. A mud-water separation device is also arranged in the aerobic section. The sludge after mud-water separation continues to stay in the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the next step; process 2, the supernatant separated from the aerobic section enters the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the aerobic section. The aerobic microorganisms carry out the nitrification reaction, and then part of the physica...
Embodiment 2
[0022] like figure 1 , a low-energy rapid denitrification process for biochemical sewage, including a facultative section and an aerobic section. Coagulation and precipitation. After the following procedures: Step 1, the sewage enters the aerobic section, and the sewage undergoes denitrification and short-range nitrification and denitrification reactions with the aerobic microorganisms in the aerobic section. A mud-water separation device is also arranged in the aerobic section. The sludge after mud-water separation continues to stay in the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the next step; process 2, the supernatant separated from the aerobic section enters the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the aerobic section. The aerobic microorganisms carry out the nitrification reaction, and then part of the physically separated clear water is used as the nitrification liquid to return to the facultative section, and the other part is used as the...
Embodiment 3
[0024] like figure 1 , a low-energy rapid biochemical sewage denitrification process, comprising a facultative section and an aerobic section, the aerobic section adopts a facultative membrane bioreactor, and the aerobic section adopts an aerated biological filter. After the following procedures: Step 1, the sewage enters the aerobic section, and the sewage undergoes denitrification and short-range nitrification and denitrification reactions with the aerobic microorganisms in the aerobic section. A mud-water separation device is also arranged in the aerobic section. The sludge after mud-water separation continues to stay in the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the next step; process 2, the supernatant separated from the aerobic section enters the aerobic section, and the separated supernatant enters the aerobic section. The aerobic microorganisms carry out the nitrification reaction, and then part of the physically separated clear water is used as the nitr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com