Non-peptidic polymeric linker compound, conjugate comprising same linker compound, and methods for preparing same linker compound and conjugate
A technology of non-peptidyl polymers and compounds, applied in the direction of medical preparations and pharmaceutical formulations of non-active ingredients, can solve the problems of reduced stability of reactive groups and reduced yield of conjugates, and achieve high yield and stable sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0135] The preparation method may include: 1) introducing an amino group (-NH 2 ), introducing R at one end of the non-peptidyl polymer through an amide bond with the amino group; and
[0136] 2) introducing an aliphatic hydrocarbon group comprising a functional group selected from the group consisting of: 2,5-dioxapyrrolidinyl, 2,5-dioxapyrrolyl, Aldehydes, maleimides, C 6 -C 20 Aryl disulfide, C 5 -C 20 Heteroaryl disulfides, vinyl sulfones, mercaptans, haloacetamides, succinimides, p-nitrophenyl carbonate and derivatives thereof, wherein R2 is the same as defined in formula 1 or 1a.
[0137] In a specific embodiment, the non-peptidyl polymer of 1) may be polyethylene glycol.
[0138] In a specific embodiment, the molecular weight of the non-peptidyl polymer of 1) may be in the range of 0.1 kDa to 100 kDa, especially 0.1 kDa to 50 kDa, and more specifically 0.3 kDa to 10 kDa, but is not limited thereto.
[0139] In a specific embodiment, 2) a C including an aldehyde gr...
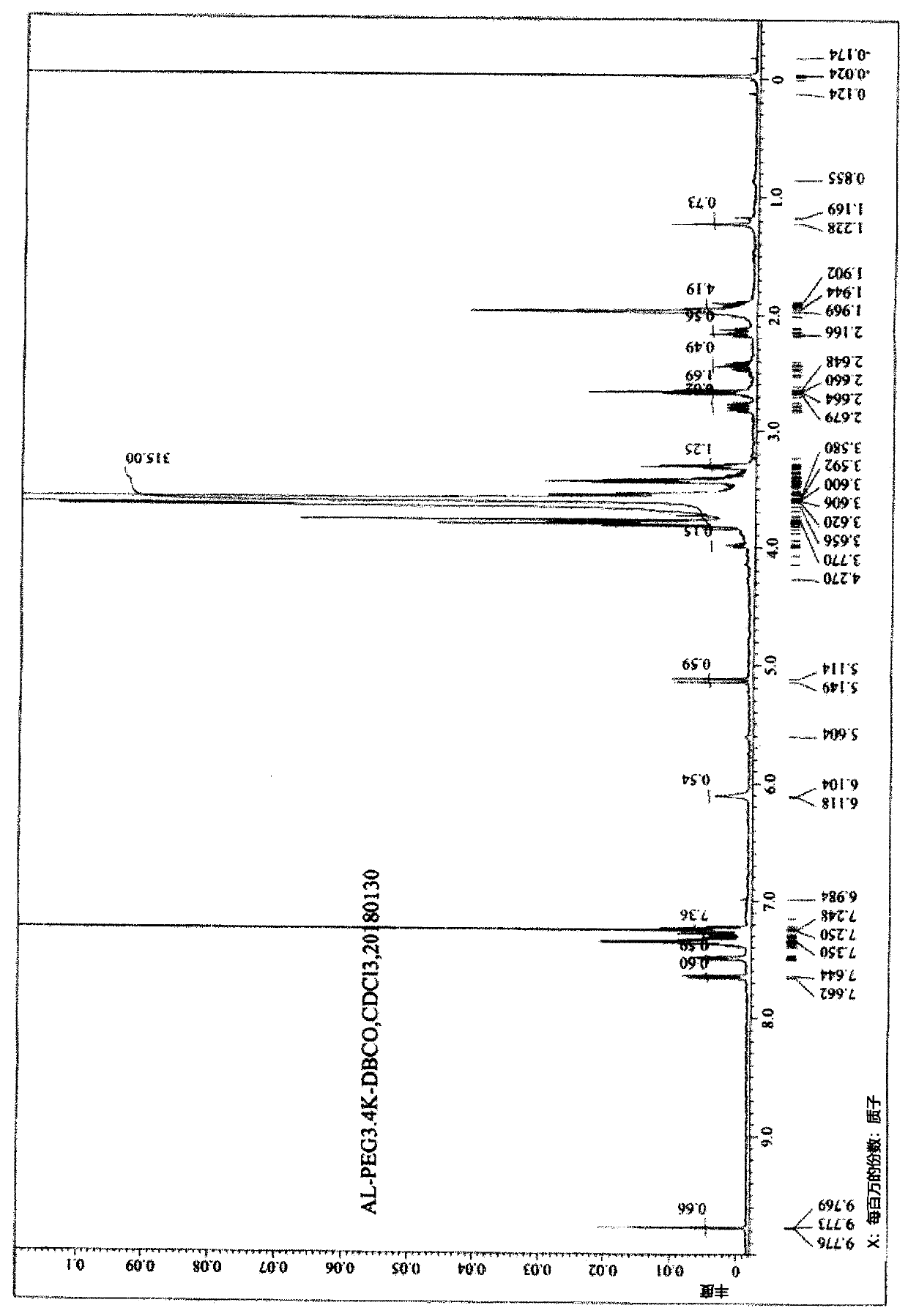
Embodiment 1
[0335] Embodiment 1: Preparation of linker compound (1)
[0336]
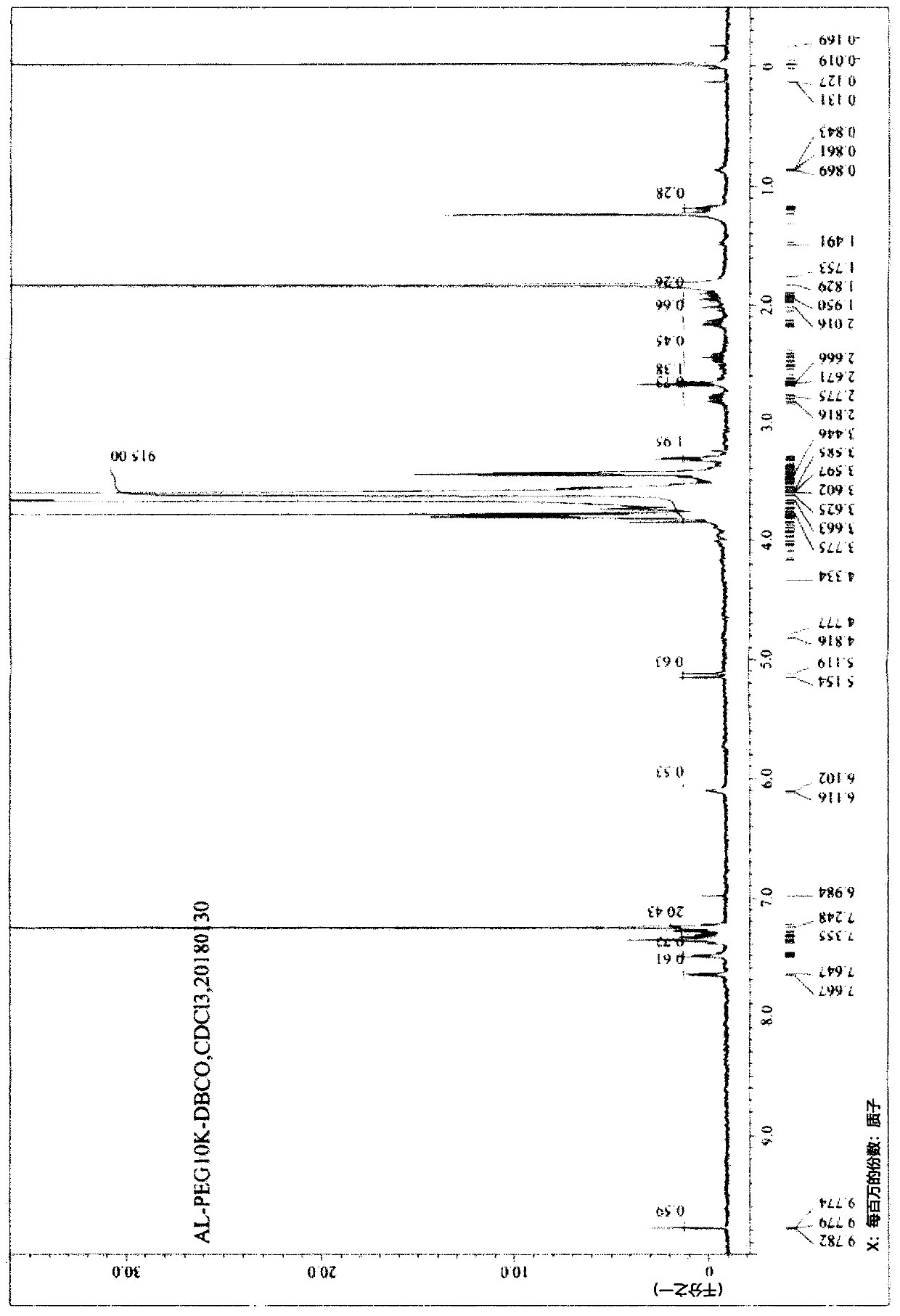
[0337] 1-1: Preparation of Compound 2 (MW=10000)
[0338] 20 g of Compound 1 (MW=10000) and 60 mL of dichloromethane were introduced into the reactor. While keeping the reaction temperature below 10°C, 1.11 g of triethylamine and 1.15 g of methanesulfonyl chloride were added thereto, followed by stirring at room temperature for 3 hours. After the reaction was completed, 100 mL of water and 40 mL of dichloromethane were added, followed by stirring for 5 minutes. The obtained organic layer was separated, and then 100 mL of dichloromethane was added to the aqueous layer for further extraction. The organic layer was collected, washed with 100 mL of water, and dried over magnesium sulfate. Filtration was performed, and the remaining filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure. 20 mL of dichloromethane was added to the concentrate, which was then dissolved, and 300 mL of methyl tert-butyl ether was added dro...
Embodiment 2
[0345] Embodiment 2: Preparation of linker compound (2)
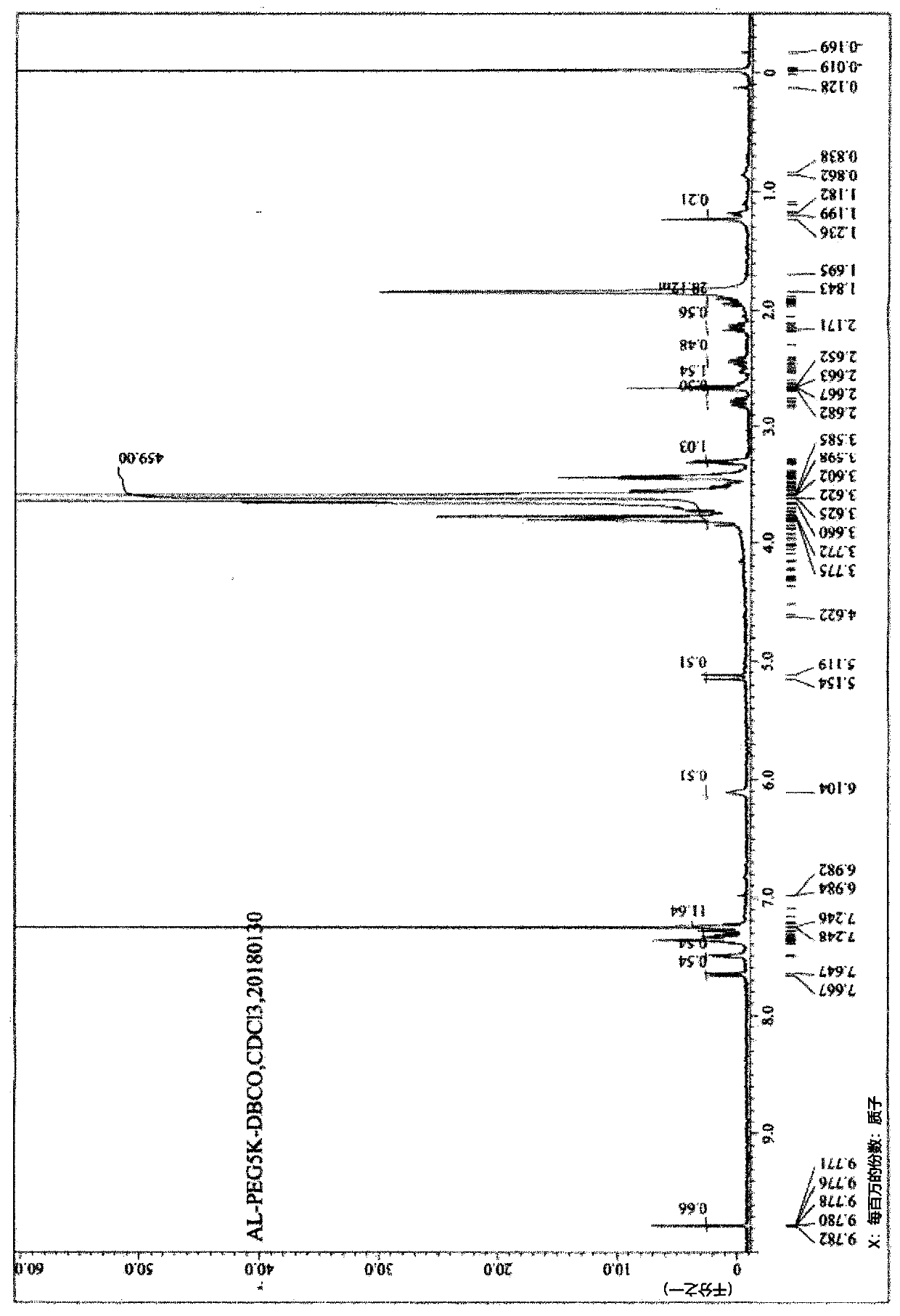
[0346] 2-1: Preparation of Compound 2 (MW=5000)
[0347] 20 g of Compound 1 (MW=5000) and 60 mL of dichloromethane were introduced into the reactor. While keeping the reaction temperature below 10°C, 2.23 g of triethylamine and 2.29 g of methanesulfonyl chloride were added, followed by stirring at room temperature for 3 hours. After the reaction was completed, 100 mL of water and 40 mL of dichloromethane were added, followed by stirring for 5 minutes. The obtained organic layer was separated, and then 100 mL of dichloromethane was added to the aqueous layer for further extraction. The organic layer was collected, washed with 100 mL of water, and dried over magnesium sulfate. Filtration was performed, and the remaining filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure. 20 mL of dichloromethane was added to the concentrate, which was then dissolved, and 300 mL of methyl tert-butyl ether was added dropwise over 20 minutes....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com