Two-stage error correction coding method and system applied to storage system in satellite severe environment
A storage system and error correction coding technology, applied in the field of on-board reliable storage systems, can solve problems such as difficult to guarantee the reliability of on-orbit systems, multiple single event flips, multiple bit errors, etc., to reduce the probability of irreparable, The effect of ensuring safe operation and reducing impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
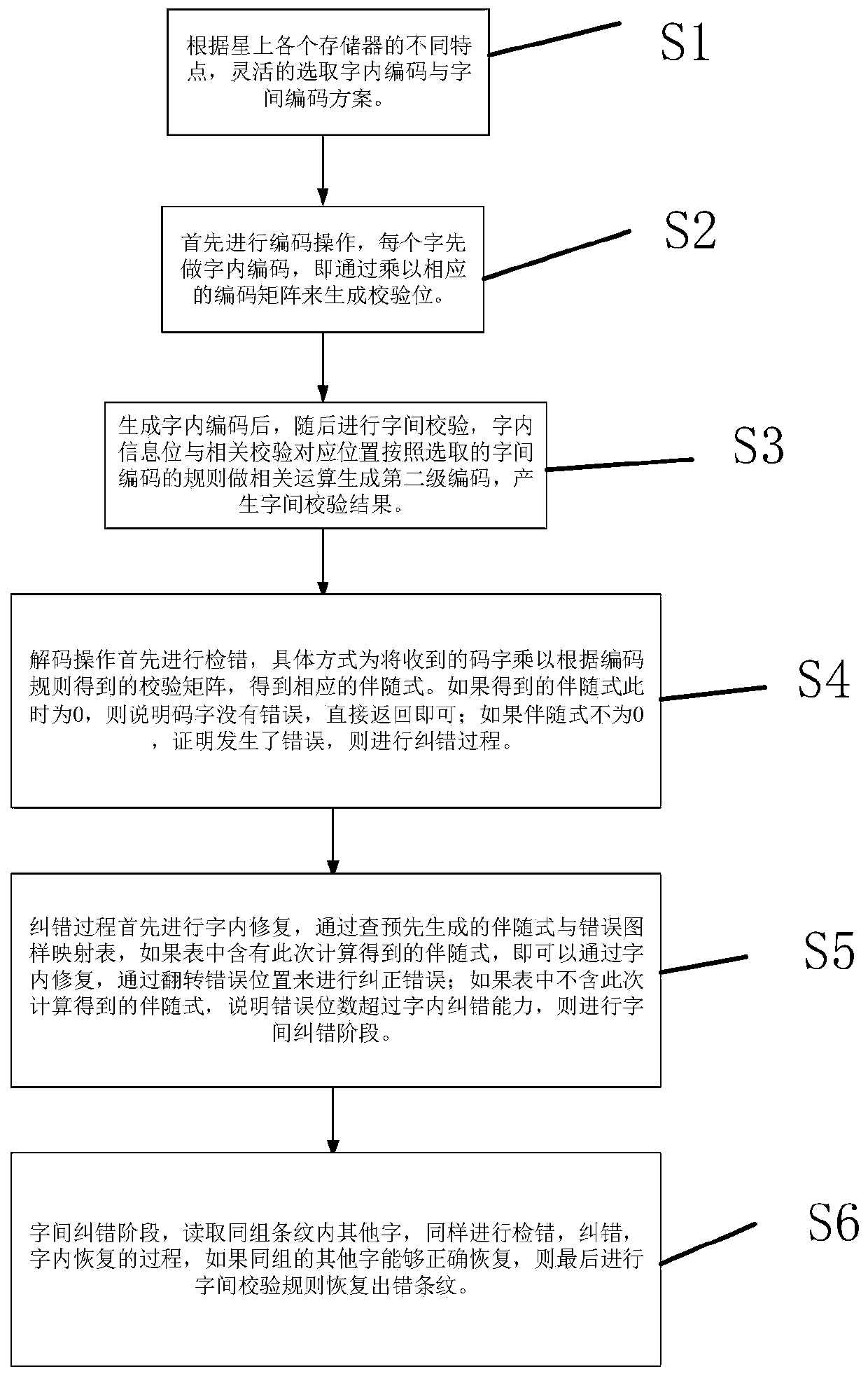
[0045] for figure 1 The different characteristics of the memory in step S1 will be described with reference to specific examples.
[0046] For example, the program memory PROM, NOR_FLASH itself is a read-only memory, and it is not easy to be affected by single events in the harsh environment of the space, that is, the reliability is high, so the EDAC (39,32) code with low error correction can still be used in the word, Parity code or high error correction code is used between words. For the data memory NAND_FLASH and the running memory SRAM, which have low reliability and more write operations, high error correction codes such as BCH double error correction codes can be used within words, and parity codes can be used between words. In this way, reliability, cost, and performance can be balanced according to the characteristics of different storage devices.
[0047] In the present invention, the original storage coding scheme BCH(44,32) is used for intra-word coding, and the ...
Embodiment 2
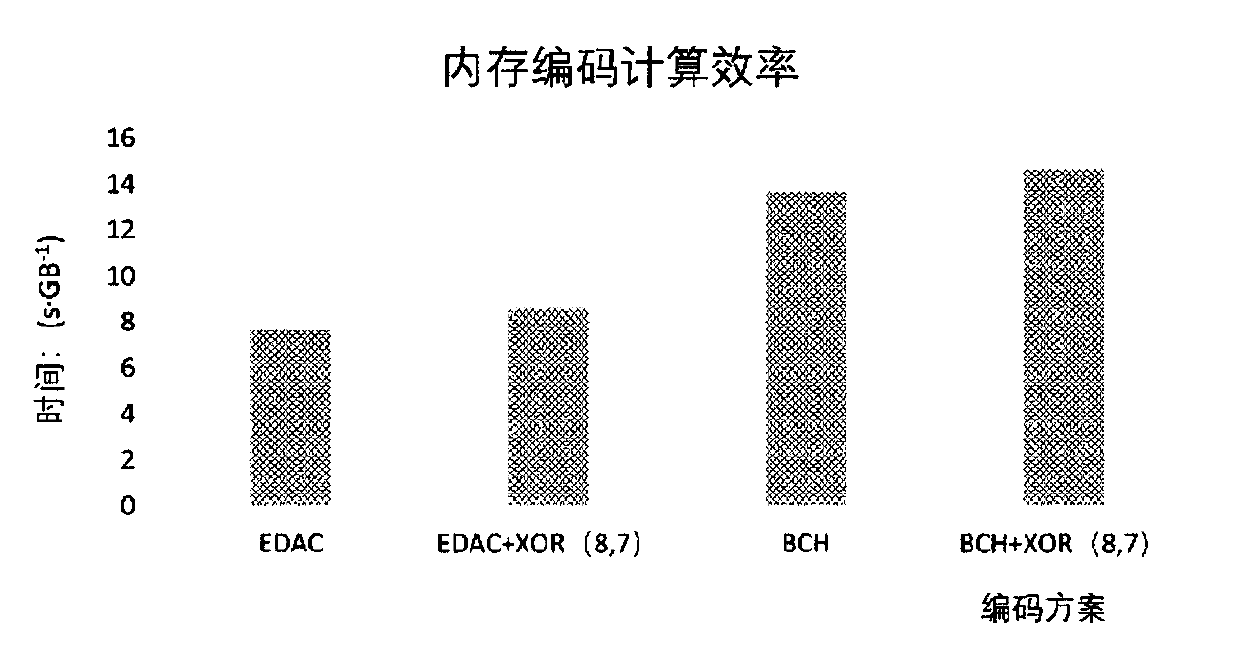
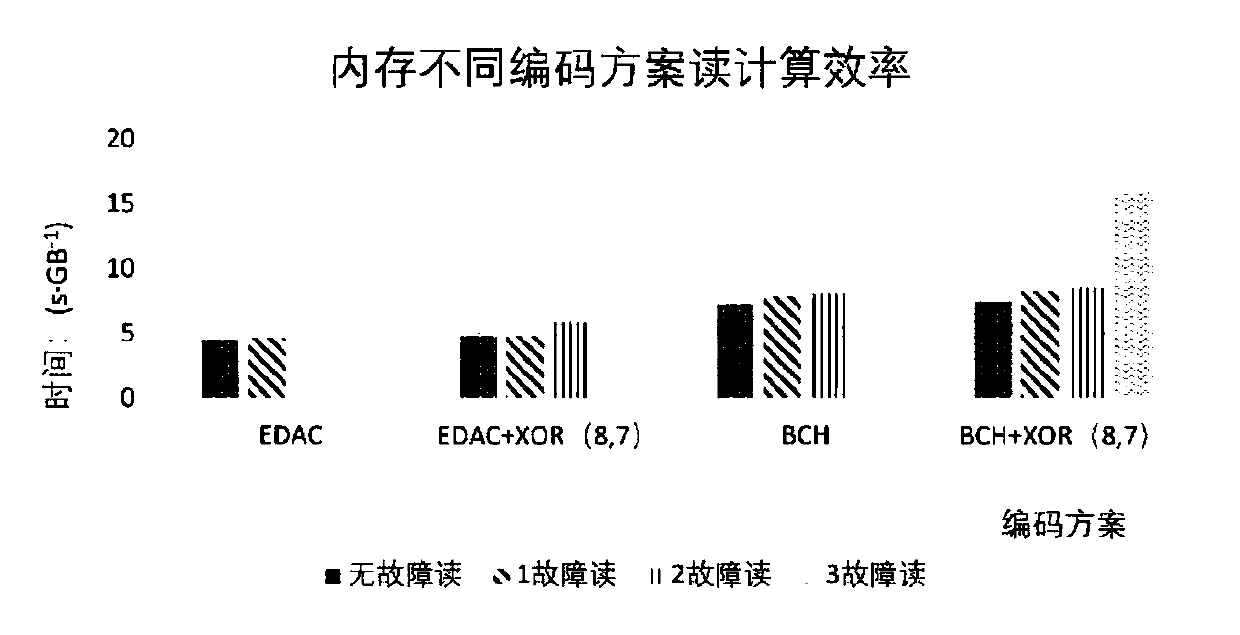
[0073] In this example, we mainly analyze the computing performance of encoding, error detection and error correction for the two possible intra-word coding schemes EDAC(39,32) and BCH(44,32) and the newly proposed two-level redundancy scheme. The experimental results are reflected in the relevant calculation process of encoding, and the inputs are the generation matrix required for different encodings, the parity check matrix required for decoding and the mapping table of syndromes and error patterns, the corresponding information generated randomly, and the random generated information in each stripe. wrong location. Taking encoding and decoding 1GB of data as an example, the preliminary test results of encoding and computing efficiency in two modes of internal memory and external storage are as follows: figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 Shown:
[0074] Depend on figure 2 , image 3 It can be seen that in the memory system, compared with the two-level redun...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The experimental part of Embodiment 2 mainly reflects the calculation results related to the encoding and decoding of the two-level redundancy scheme. In this embodiment, the two-level storage coding is applied to the codec simulation system mentioned above, and the situation of writing and updating single words by the system is described. Its input is the required encoding matrix and the updated stripe address. Still taking the two-level coding BCH(44,32) and XOR(8,7) as an example, the two-level redundant coding is applied to the external memory. The abscissa is the number of user write (update) requests, and the ordinate is the average time it takes for the storage system to complete the update of each request. The experimental results are as follows: Image 6 shown.
[0080] pass Image 6 It can be seen that the method of updating and delaying writing applied to the external memory system has obvious advantages compared with methods such as updating synchronously...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com