Efficient phosphorus-removing saccharomyces and application thereof in domestic sewage treatment
A technology of domestic sewage and yeast, applied in the field of environmental biology, can solve problems such as shortage of phosphorus resources, red tide, damage to water bodies and water ecological environment, etc., to improve treatment efficiency and stability, broaden application research ideas, and enhance practical application value Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
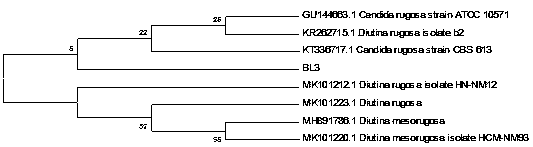
[0019] Example 1: Isolation, screening and identification of bacterial strains.
[0020] (1) Material preparation:
[0021] 1. Collect granular filter material from a well-run A / O alternate biofilm system, and make a bacterial suspension, and use the gradient dilution method to inoculate the diluted liquid onto the yeast screening medium for coating and separation of yeast; Use an inoculation loop to pick different types of yeast for streaking and purification; finally, the purified yeast is stored in a -86°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator;
[0022] 2. culture medium
[0023] Yeast screening medium (1L): 20 g peptone, 20 g glucose, 10 g yeast extract, 15~20 g agar powder, 15ug / ml streptomycin, 60 mg / L chloramphenicol, sterilized at 121 °C 15 minutes;
[0024] YPD solid medium (1L): 20 g peptone, 20 g glucose, 10 g yeast extract, 15-20 g agar powder, sterilized at 121 °C for 15 min;
[0025] YPD liquid medium (1L): 20 g peptone, 20 g glucose, 10 g yeast extract, steri...
example 2
[0048] Example 2 Bacterial strains in the present invention Candida rugosa Culture of BL3.
[0049] (1) Optimizing the culture conditions of bacterial strains in the present invention
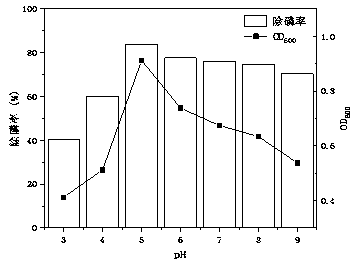
[0050] ①Different pH
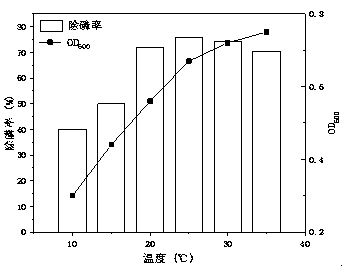
[0051] Use hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 (3 parallel samples) before the sterilization of the wastewater medium, take 16 mL of bacterial suspension to inoculate, and adjust the OD 600 =0.2±0.02, cultured on a shaker (28 ℃, 220 r / min) for 60 h, and measured OD 600 and PO in the supernatant 4 3- -P concentration, calculate the phosphorus removal rate, see the results figure 2 ;Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the bacterial strain of the present invention has an OD within the range of 3 to 9 at pH 600 , The phosphorus removal rate increases gradually. When the pH value is 3, the phosphate removal rate of the strain BL3 is only 40.6%; when the pH value is between 5 and 7, the phosphate removal rate of ...
example 3
[0060] Example 3 Bacterial strains in the present invention Candida rugosa Application of BL3 in sewage treatment: Take sewage from the regulating tank of a reclaimed water station in a university in Shandong (the concentration of COD is 400mg / L, the concentration of phosphorus is 11mg / L, and the concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 44 mg / L), and the test of phosphorus removal in wastewater is carried out. The specific steps As follows: Take 350 ml of actual sewage (sterilized) in a 500 ml Erlenmeyer flask, adjust the OD 600 =0.2±0.02, under the conditions of pH 5 and temperature 25 ℃, aerobic culture on a shaking table with a shaking frequency of 220 r / min; , 48 h, and 60 h to take test water samples, take the supernatant after centrifugation, and measure the concentration changes of orthophosphorus, ammonia nitrogen, and COD in the supernatant, and the results are shown in Figure 6 ;Depend on Figure 6 It can be seen that within 12 hours during the aerobic cultivation pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com