Working layer refractory brick piling structure restraining splashing and nodulation of RH vacuum tank
A vacuum tank and working layer technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgical refining, can solve the problems of affecting the cleanliness of molten steel, matching the production rhythm of shadow refining, and poor sealing of vacuum tanks, so as to improve the efficiency of RH refining and reduce internal nodules , The effect of prolonging the continuous processing time of RH
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
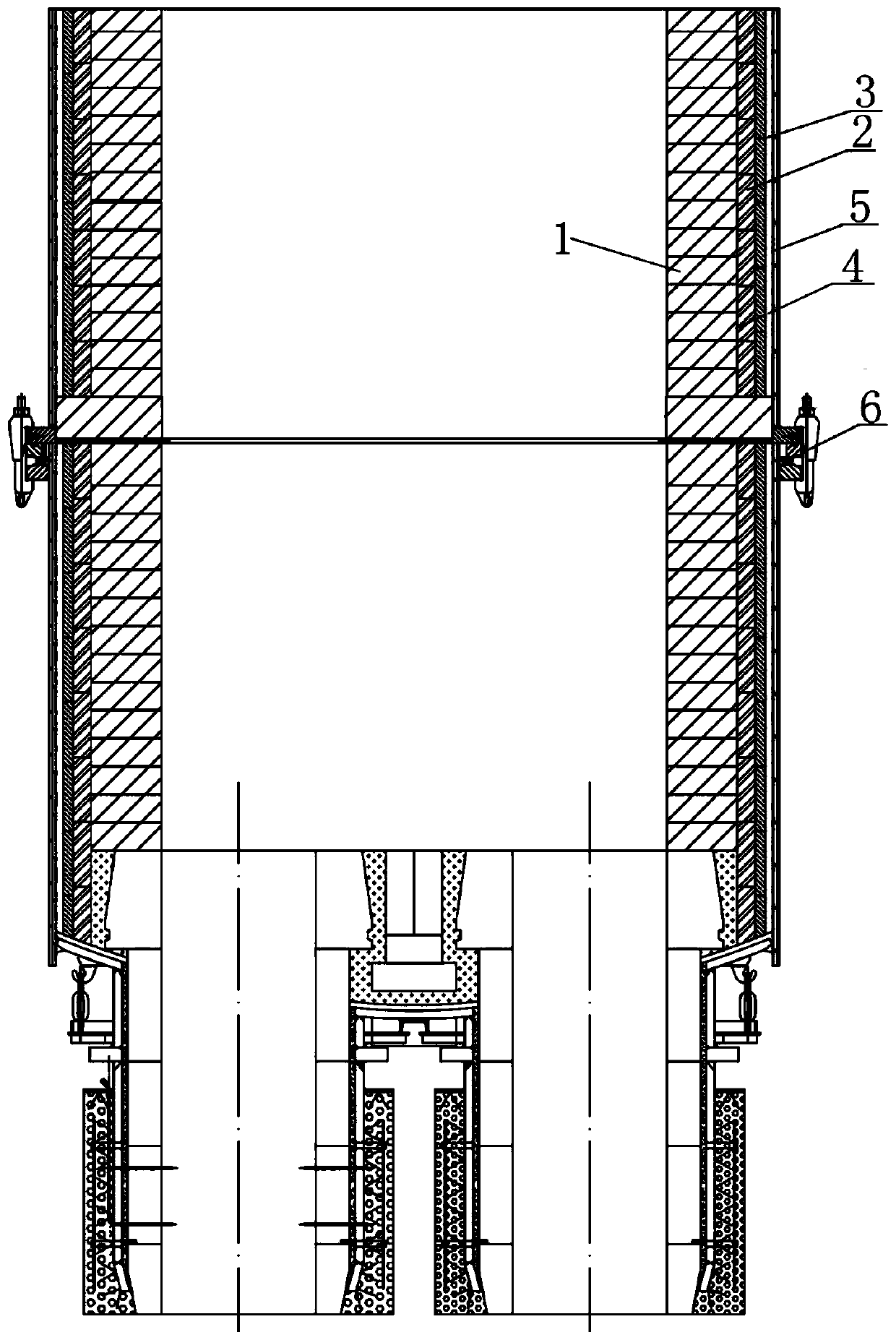
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the inner side of the refractory bricks in the working layer in the prior art is a smooth and straight stacked structure, and the connection position between the upper tank body and the lower tank body of the RH vacuum tank needs to be connected by a flange, because the flange is a steel product Long-term exposure to high temperature will lead to deformation of the flange, making the sealing of the vacuum tank not strong. It is necessary to add a circle of water cooling devices around to avoid deformation of the flange. However, in actual production, the temperature of the joint position is low due to water cooling, and the spray The splashed molten steel adheres to the upper and lower positions of the seam due to intense cooling. As the service life of RH increases, the cold steel at the seam becomes thicker and thicker, and there is a risk of falling off at any time. In the actual on-site production, there are seams The cold steel falls off ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The refractory brick stacking structure of the working layer that suppresses the splashing and nodulation of the RH vacuum tank body in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, except that:
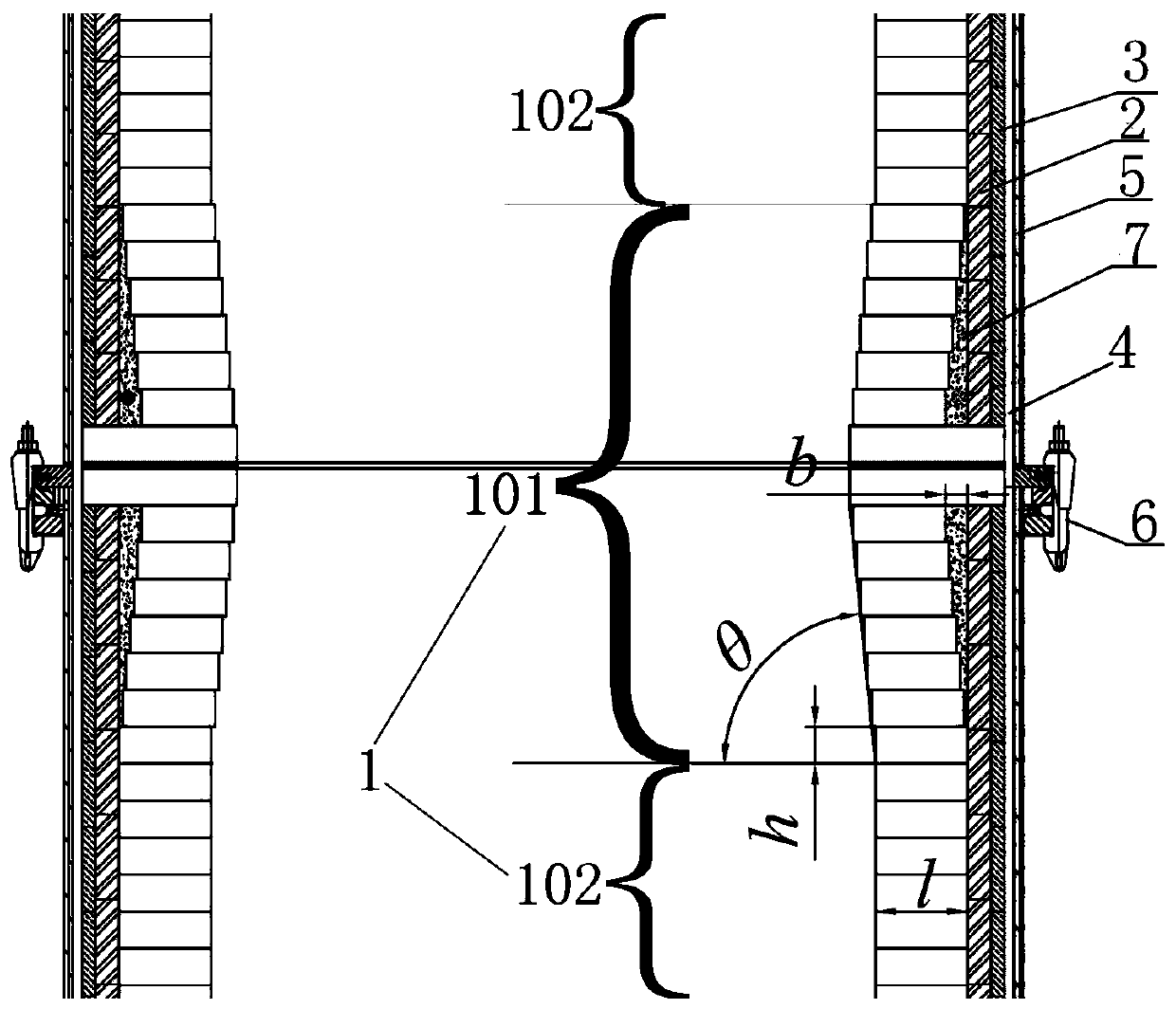
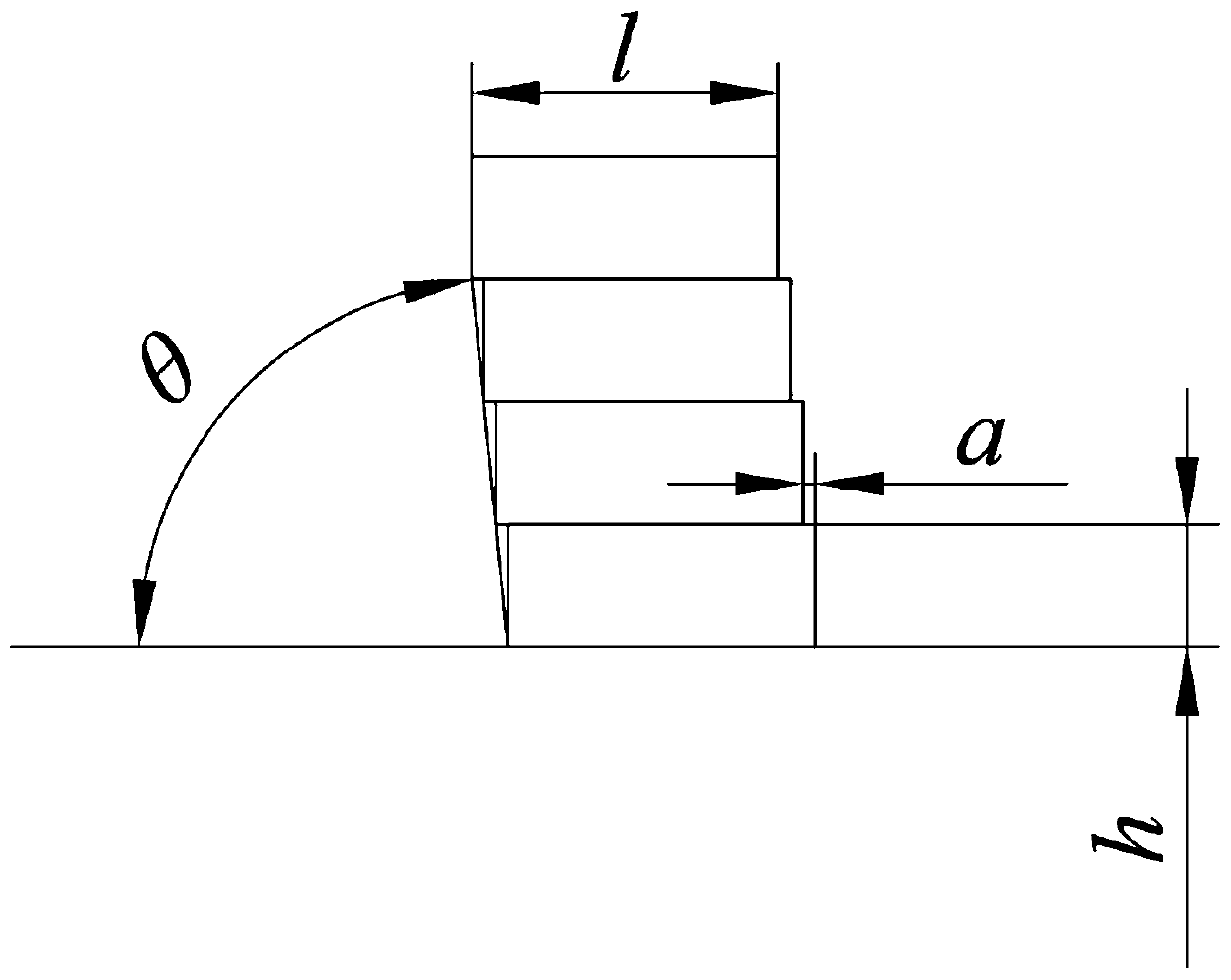
[0066] The included angle between the raised portion and the horizontal line is not more than 86° and not less than 80°. This range of included angles can effectively suppress the splashing and nodulation of the RH vacuum tank body. If the angle is less than 80°, it will cause damage to the refractory bricks. For the safety of stacking, when the angle is greater than 86°, the effect of suppressing the splashing and nodulation of the RH vacuum tank will be reduced or even not suppressed.
Embodiment 3
[0068] The refractory brick stacking structure of the working layer that suppresses the splashing and nodulation of the RH vacuum tank body in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 2, except that:
[0069] The thickness b of the thickest part of the heat insulating material (that is, the maximum offset of the refractory brick in the vertical direction) is 50 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com