Micro acoustic sensor based on diffraction grating structure
An acoustic sensor and diffraction grating technology, which is applied to instruments, utilizes wave/particle radiation, and measures ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic waves, etc. It can solve the problems of low signal-to-noise ratio and high noise of MEMS acoustic sensors, and achieve low cost and increased perforation rate, reducing the effect of damping
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
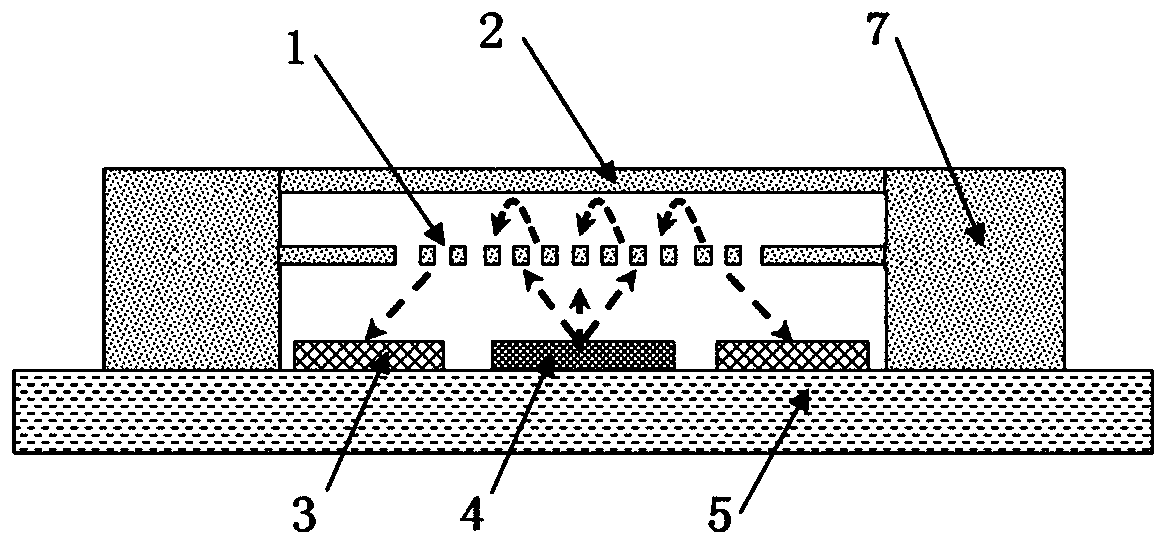
[0038] A miniature acoustic sensor based on a diffraction grating structure, such as figure 1As shown, it includes MEMS chip, VCSEL4, PD3 and substrate 5; both VCSEL4 and PD3 are fixedly installed on substrate 5, VCSEL4 is located in the center of substrate 5, PD3 is distributed on both sides of VCSEL4, and the distance d between PD3 and VCSEL4 is not less than 10μm;
[0039] The MEMS chip, VCSEL4 and PD3 are located in a closed cavity. The MEMS chip includes a diffraction grating 1 and a thin film mirror 2. The thin film mirror 2 is located above the diffraction grating 1. An upper cavity is formed between the thin film mirror 2 and the diffraction grating 1. The diffraction grating A lower cavity is formed between the grating 1 and the substrate 5; the distance h between the thin film mirror 2 and the diffraction grating 1 is 0.5-4 μm.
[0040] In the micro-acoustic sensor, an upper cavity is formed between the thin film mirror 2 and the diffraction grating 1, and the sound...
Embodiment 2
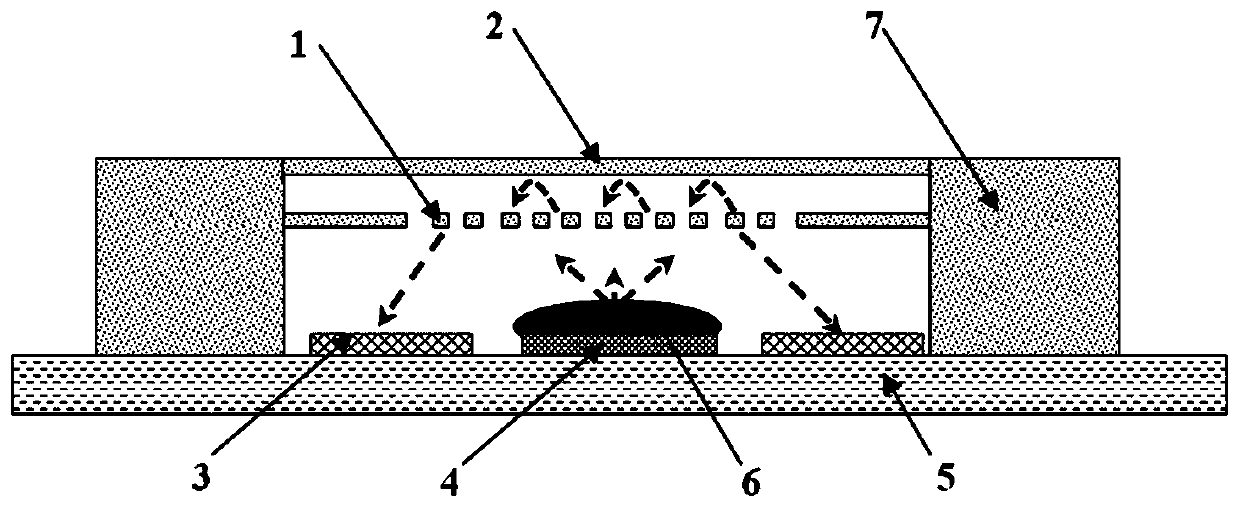
[0053] A kind of microacoustic sensor based on the diffraction grating structure provided according to embodiment 1, its difference is:
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, a collimating lens 6 is installed on the VCSEL4. The function of the collimating lens 6 is to collimate the light spot emitted by the VCSEL4, increase the light intensity of the + / - 1st order diffracted light of the diffraction grating to the PD3, and improve the sensitivity of the sensor. figure 2 The direction of the arrow in the middle is the path that the light passes through.
Embodiment 3
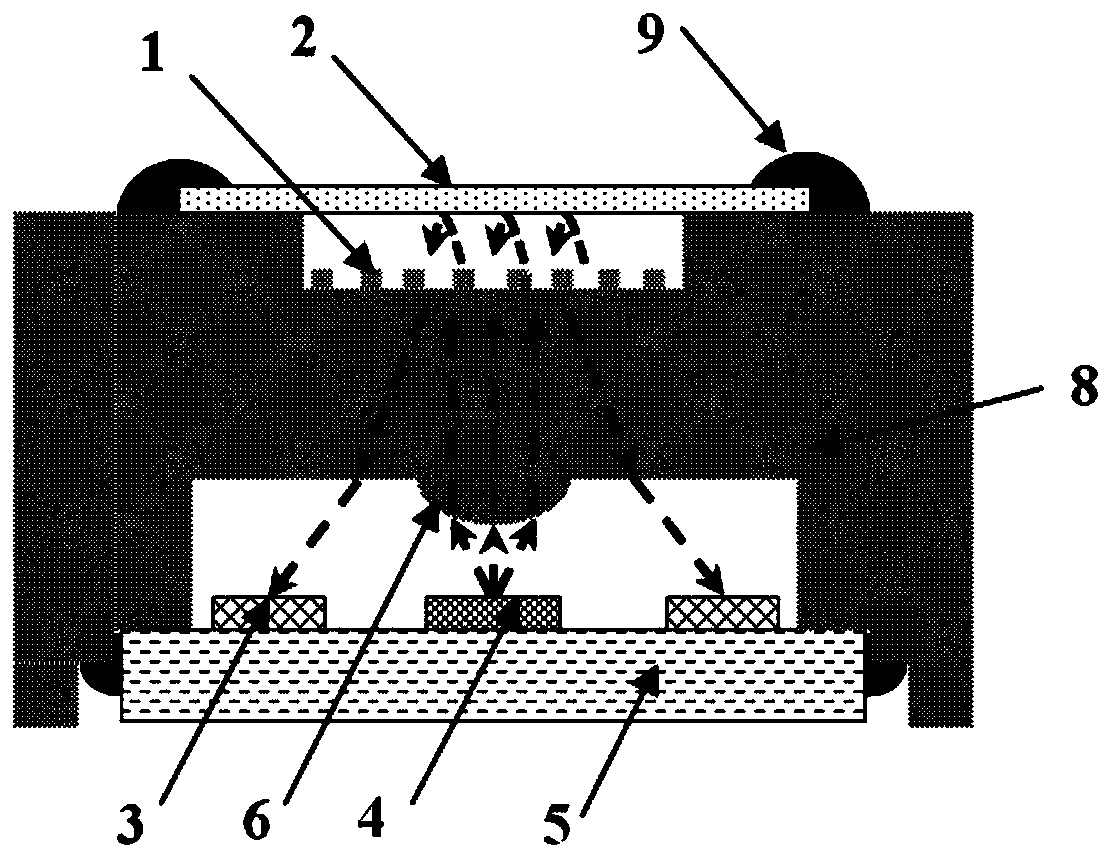
[0056] A kind of microacoustic sensor based on the diffraction grating structure provided according to embodiment 1, its difference is:
[0057] Such as image 3 As shown, an optical collimator structure 8 is arranged between the substrate 5 and the MEMS chip, the upper part of the optical collimator structure 8 is an upper groove structure, the lower part of the optical collimator structure 8 is a lower groove structure, and the diffraction grating in the MEMS chip 1 is arranged on the groove bottom surface of the upper groove, and the film reflector 2 is connected to the upper edge of the optical collimator structure 8 through the fixing glue 9, and the film reflector 2 forms an upper cavity for light reflection with the grating and the upper groove. The lower groove is connected to the substrate 5 through a fixing glue 9; the groove bottom of the lower groove is an inverted collimator lens 6, and the inverted collimator lens 6 is located directly above the VCSEL4. When the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com