Anaerobic electrogenesis strain capable of degrading phenol and application thereof
A strain and phenol technology, applied in bacteria, biochemical fuel cells, microbial-based methods, etc., can solve the problem of low Coulombic efficiency of MFC
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
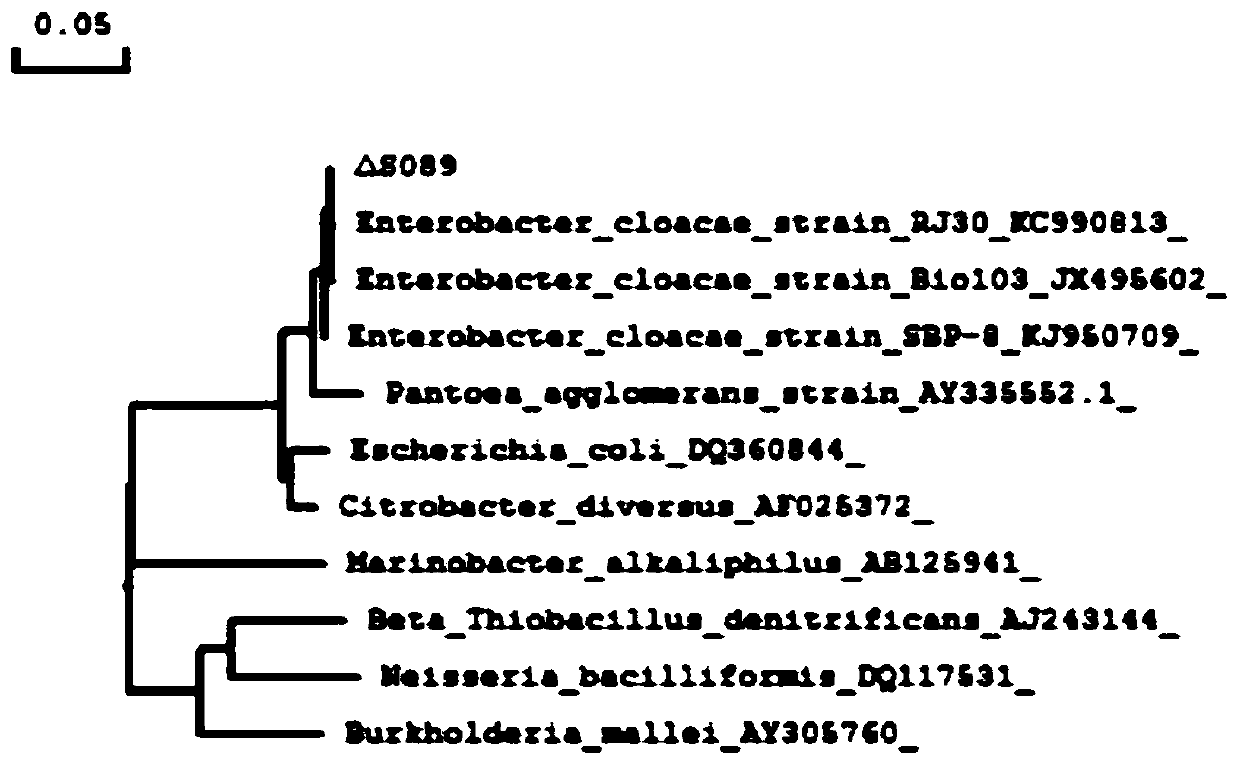
[0037] Specific embodiment 1: The anaerobic electrogenic strain that can degrade phenol in this embodiment is Enterobacter sp.A4, which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, and the preservation date is April 2019 On March 11, the deposit number is CCTCC No: M 2019249.
[0038] The Enterobacter sp.A4 of this embodiment is a Gram-negative bacterium, straight rod-shaped, with a cell size of (1.1-1.5 μm)×(2.0-6.0 μm), single or in pairs, moving with perinatal flagella or Non-motile, non-spore-free, non-capsulated, facultatively anaerobic, forming larger red colonies on MacConkey plates.
[0039] Enterobacter sp.A4 of this embodiment can decompose glucose and lactose to produce acid and gas, and acetate can be used as the only carbon source, but citrate cannot be used. h 2 The S test was negative, the indole test was negative, the methyl red test was negative, the V-P test was positive, and ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Specific embodiment two: the screening method of Enterobacter sp.A4 of the present embodiment is:
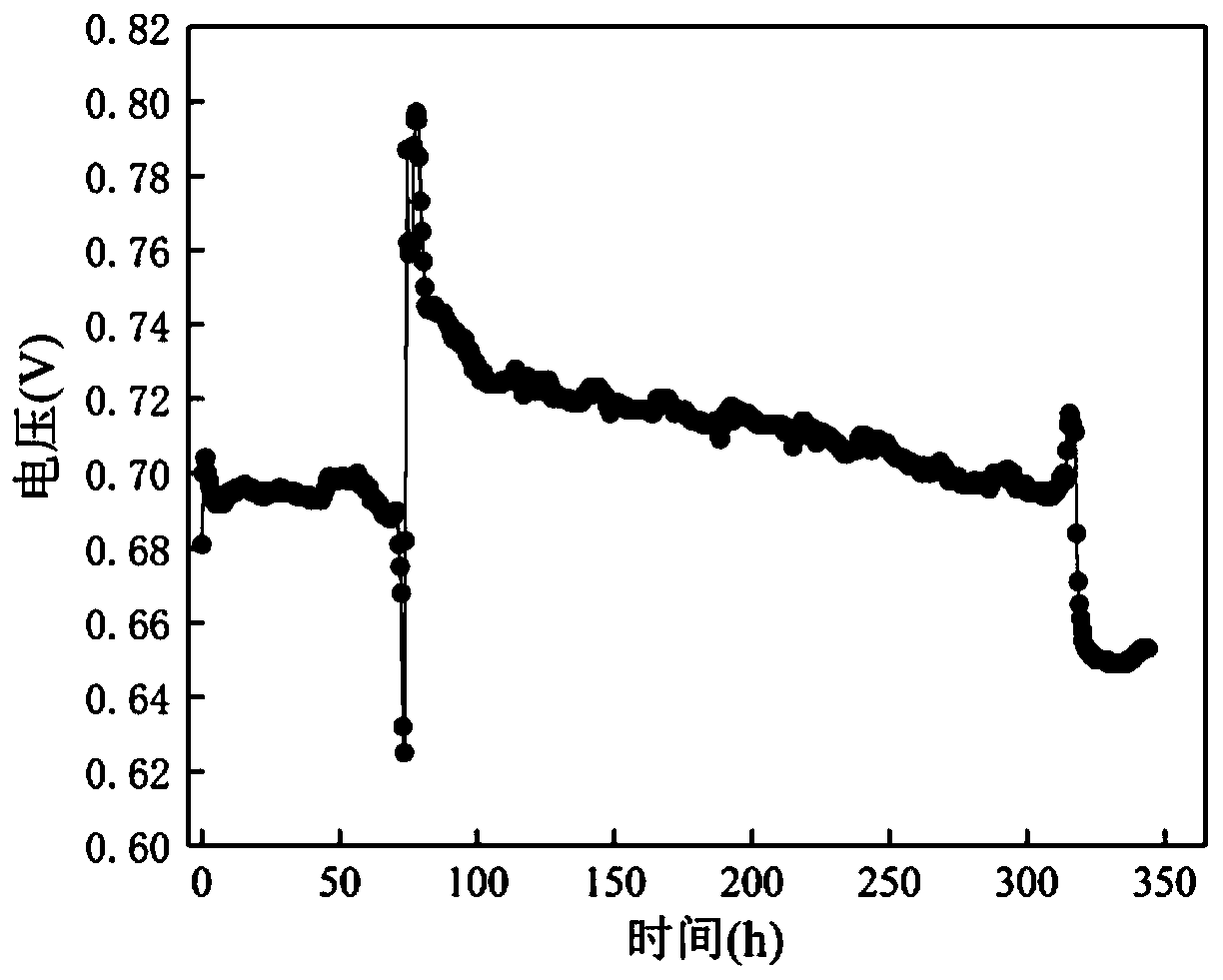
[0042] The microbial fuel cell is selected as a double-chamber MFC, and the volume of the two chambers is 600mL. The anode electrode is made of ferric chloride modified carbon felt (5cm×5cm, effective area 12.56cm 2 ), the cathode electrode uses a carbon brush, and the carbon brush is soaked with 1mol / L HCl and 1mol / L NaCl for 24 hours before use. The cathode chamber and the anode chamber are connected by a salt bridge, and the interface is insulated. The external rheostat box (0-9999Ω) in the circuit adopts a resistance of 1000Ω. The voltage generated during the experiment is directly recorded by the dual-channel voltage acquisition system (PISO813), and the data is measured every 60s.
[0043]Into 20min N before starting the battery 2 , to ensure anaerobic conditions. First, the sewage from the aeration tank and the sewage from the anaerobic tank are mixed at a vol...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific implementation mode 3: Optimization of growth of phenol-degradable anaerobic electrogenic bacteria and phenol degradation conditions
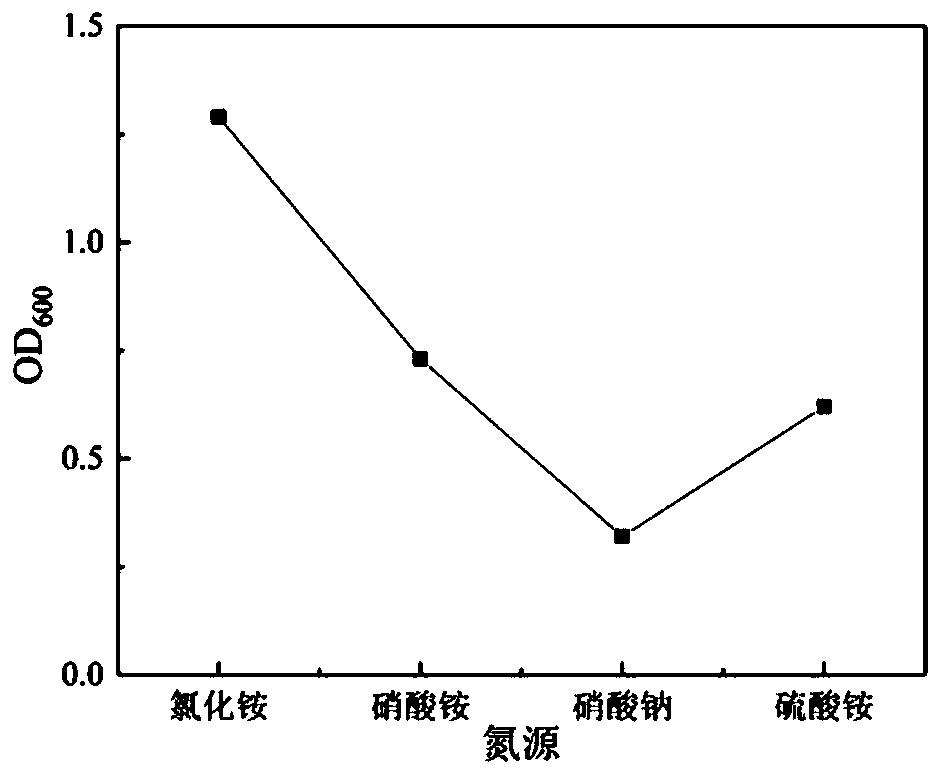
[0052] On the anaerobic operation platform, inoculate the strain on a shaker of separation medium at 30°C and 160r / min for 48h, take 3mL of the culture solution and put it in a centrifuge tube for 3 times of centrifugation (8000r / min), and the bacteria Put into 50mL physiological saline to make bacterial suspension. The bacterial suspension was inoculated into inorganic salt medium and cultured for 48 hours to study the effects of different biological characteristics (nitrogen source, carbon source, pH value, inoculum size, initial phenol concentration, temperature and metal ions) on the growth of the strain and the degradation of phenol . Do 2 repetitions when the strains are inserted into the shake flask, and 3 repetitions when measuring the growth amount and phenol degradation rate, and then take the average value.
[0053]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com