Application of robenidine hydrochloride in preparation of medicine for treating fungal infection
A technology of prohexidine hydrochloride and fungal infection, which is applied in the direction of antifungal agents, drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulas, etc., to achieve the effects of low toxicity, good killing effect, and remarkable antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
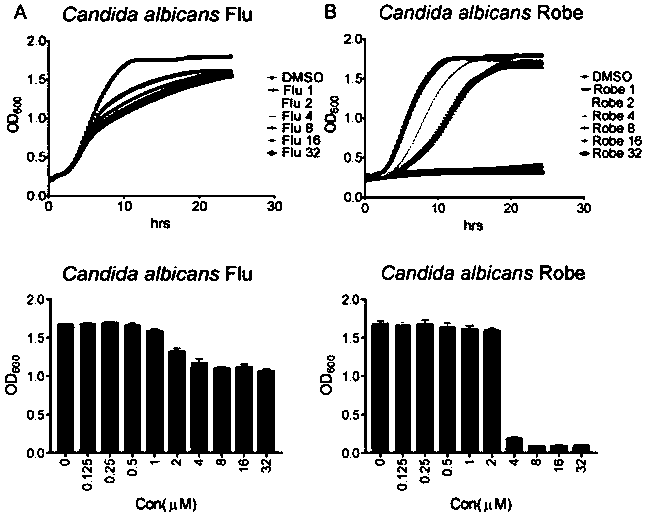
[0038] Experimental situation of the growth of Candida albicans after being treated with fluconazole and chlorhexidine hydrochloride respectively.
[0039] Use a sterile inoculation loop to take a small piece of strain from the frozen Candida albicans strain and inoculate it into a solid medium containing YPD, and incubate overnight (15 hours) in a 30°C incubator; after incubation overnight, wash with sterile PBS Twice; use a microplate reader to measure the concentration of the bacterial solution, and insert it into the YPD medium to make it OD 600 =0.4; Dissolve the prohexidine hydrochloride and fluconazole dissolved in DMSO in fresh YPD medium respectively, and configure to the required concentration, make 2-fold dilution in a 96-well plate, and then add 100 μl before Add 200μl to each well of the culture medium containing the bacteria solution, so that the concentration of the bacteria solution is OD 600 =0.2, the drug concentration from low to high is 1μM, 2μM, 4μM, 8μM,...
Embodiment 2
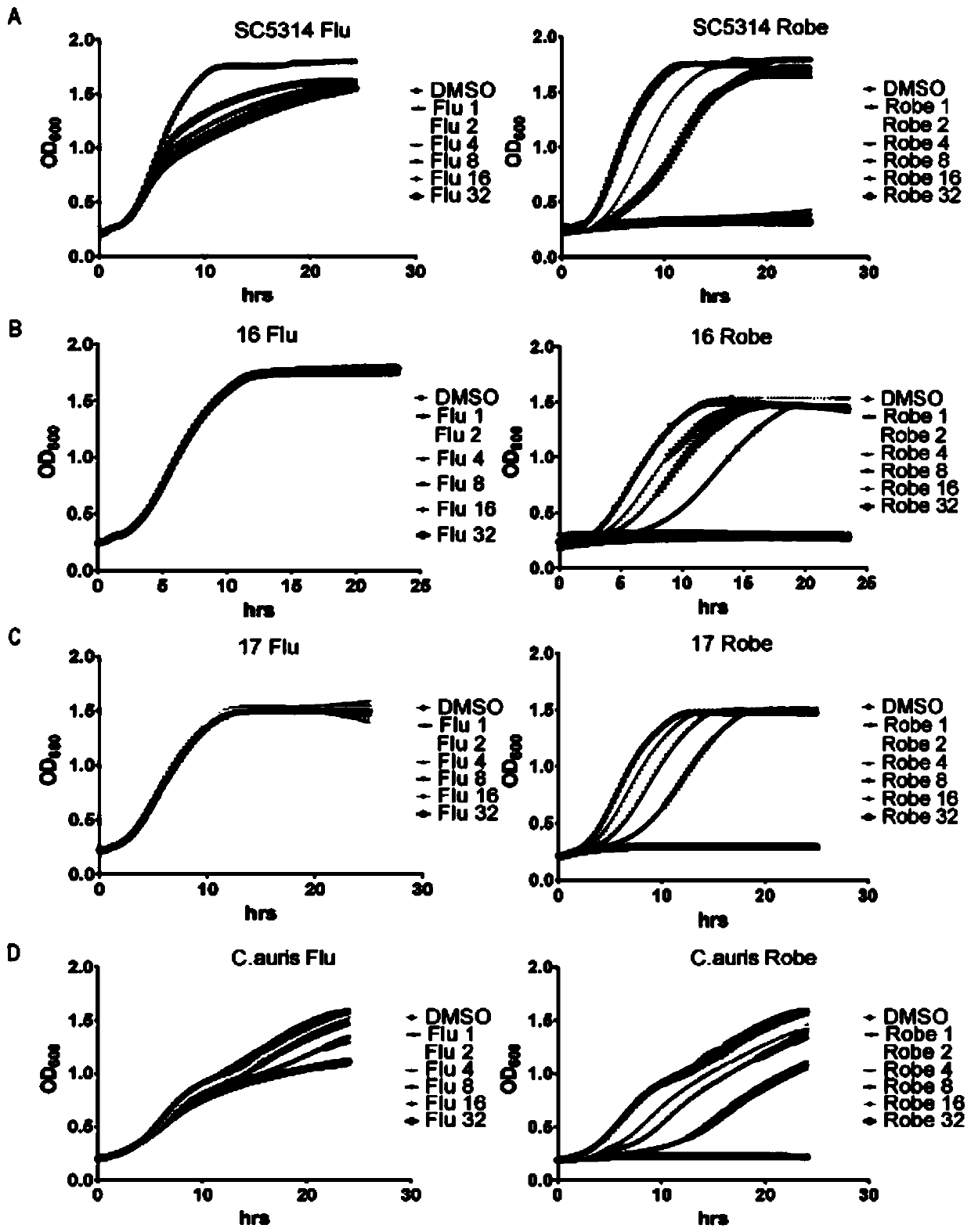
[0042] Antibacterial effect of prohexidine hydrochloride on clinical fluconazole-resistant strains and Candida auris
[0043] The experiment process is the same as in Example 1, except that the test strains are replaced by drug-resistant strains and Candida auris.
[0044] Experimental results such as figure 2 As shown, compared with the fluconazole control group, Chlorhexidine hydrochloride showed a significant effect on two drug-resistant bacteria #16 and #17 (Candida albicans drug-resistant strains extracted from clinically treated tumor patients). Obvious antibacterial effect, and in cells treated with different concentrations, prohexidine hydrochloride has a dose-dependent effect, and the inhibitory effect on cells is gradually enhanced from low to high. In addition, this experiment also added Candida auris, by figure 2 D in D can be obtained, and prohexidine hydrochloride also has a strong inhibitory effect on Candida auris, which has good clinical significance for t...
Embodiment 3
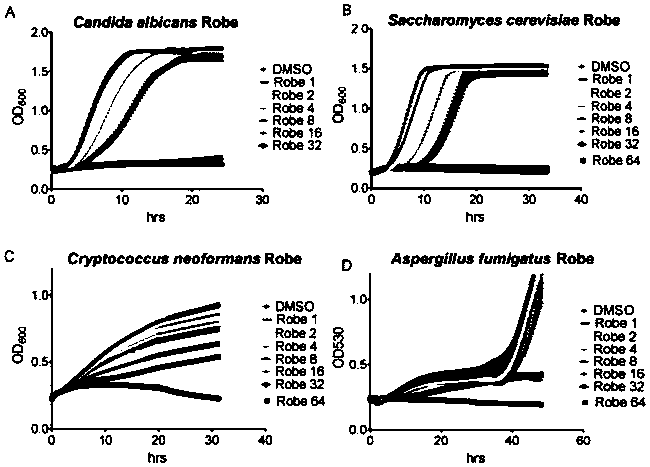
[0047] Chlorhexidine hydrochloride has significant antibacterial effect on several common human pathogenic fungi such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus fumigatus.
[0048] The experimental process is the same as in Example 1, except that the test strains are replaced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cryptococcus neoformans, and Aspergillus fumigatus.
[0049] Experimental results such as image 3 As shown, the growth curves of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans are very similar, and the minimum inhibitory concentration is 4 μM; the dose-effect relationship between Aspergillus fumigatus and Cryptococcus neoformans is obvious, and the growth of Candida albicans can be completely inhibited at the concentration of 32 μM (growth curve levels within 48 hours). Through the above experiments, it can be shown that prohexidine hydrochloride has a good inhibitory effect on these common clinical pathogenic fungi.
[0050] image 3 A is the anti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com