Method for identifying lycium ruthenicum based on DNA bar code and application thereof
A black fruit wolfberry, barcode technology, applied in the field of biotechnology identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] 1. Extraction of DNA
[0047] Take 0.5g of clean and mildew-free fruit and fruit powder samples respectively, mark them, put them into liquid nitrogen quickly, and store them in a -80°C refrigerator for later use.
[0048] Genomic DNA of samples was extracted by CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) method with slight modifications. The specific method is as follows:
[0049] (1) The mortar was precooled with liquid nitrogen, the CTAB extract was preheated at 65°C, and the sterilized 2mL centrifuge tube was placed on ice for later use.
[0050] (2) Put the sample in a mortar, add 0.01g of PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone), add liquid nitrogen and grind to powder, and add liquid nitrogen while grinding.
[0051] (3) Transfer the powder into a 2 mL centrifuge tube, add 800 μL preheated CTAB extract and 1 μL mercaptoethanol (2‰) into the centrifuge tube, place in a water bath at 65°C for 1 hour, and shake gently every 10 minutes to mix.
[0052] (4) After the water bath, add t...
Embodiment 2
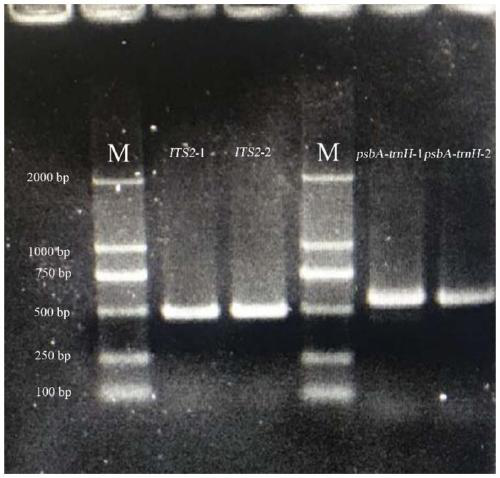
[0076] 1. DNA extraction and PCR amplification method are the same as in Example 1
[0077] 2. Sequencing
[0078] The amplified products were directly sent to Shanghai Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for bidirectional sequencing. The DNA barcode sequence after sequencing was proofread and spliced with the software DNAMAN 5.0, and some sites were manually corrected.
[0079] 3. Verification of sequencing results
[0080] The sequencing results were verified according to The nearest distance (minimum genetic distance) method:
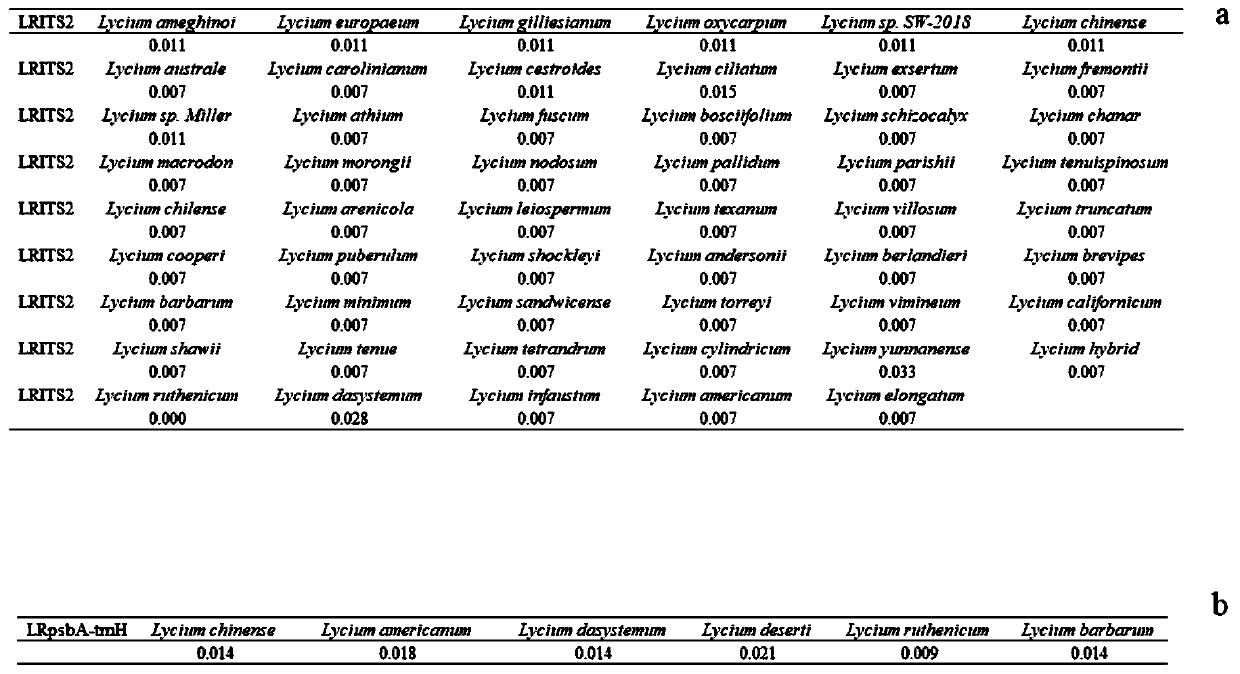
[0081] Download the ITS2 sequences and psbA-trnH sequences of Lycium barbarum plants uploaded by researchers from the NCBI GENEBANK website, including 53 ITS2 sequences and 6 psbA-trnH sequences. Sequences were aligned with MEGA 7.0, and the genetic distances of LRITS2, LRpsbA-trnH and the control sequence (Lycium barbarum) were calculated respectively. The calculation results show that the genetic distance between LRITS2 and the control sequence is...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The sequencing results of the samples were verified according to the method of phylogenetic evolution:
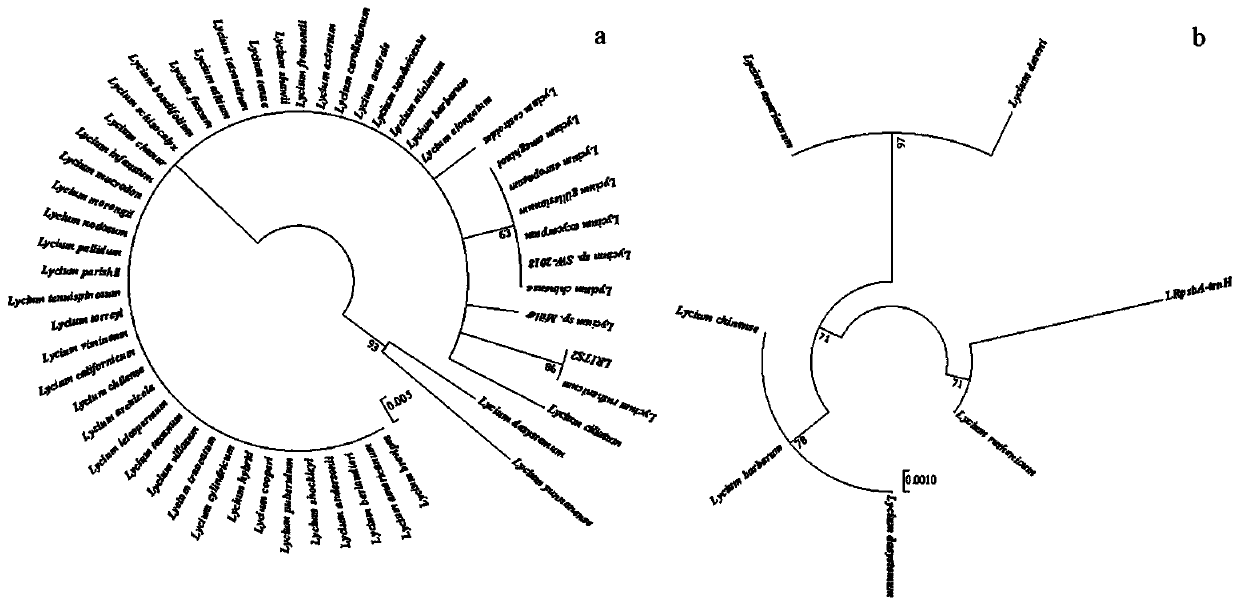
[0085] After comparing the sequences downloaded in Example 3 with MEGA 7.0, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Maximum Likelihood method (maximum likelihood method). The results of the study showed that LRITS2 clustered with the control sequence of Lycium barbarum, and the bootstrap value was 86, indicating that the evolution of the system was reliable ( image 3 a); LRpsbA-trnH is clustered with the control sequence, and the bootstrap is 71, indicating that the evolution of the system is reliable ( image 3 b). Therefore, the two DNA barcodes disclosed in the present invention can effectively identify Lycium barbarum.
[0086] image 3 Phylogenetic tree analysis of LRITS2 and ITS2 (a) and LRpsbA-trnH and psbA-trnH (b) sequences.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com