A detection method for visual identification of microRNAs based on structural unwinding of G-quadruplex probes
A technology of quadruplexes and probes, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as high production costs, inability to fully meet application requirements, complex reaction process, etc., and achieve the effect of simple design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1, the design of probe and the establishment of detection method
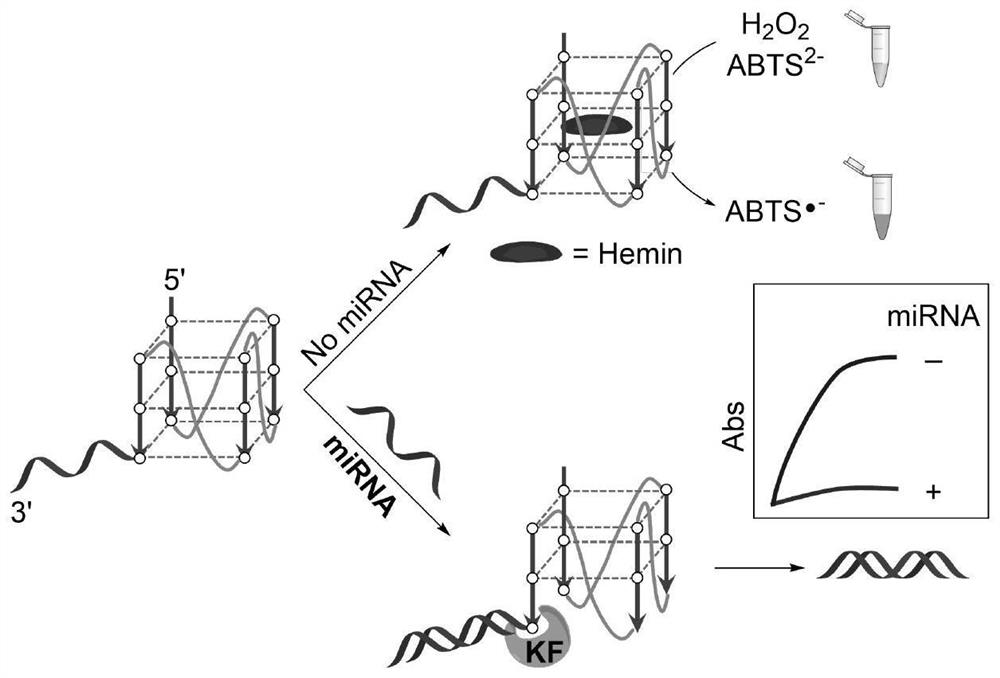
[0052] The G-quadruplex probe designed by the present invention includes a binding segment and a signal segment, and the binding segment is a DNA fragment that can specifically recognize and bind to the target miRNA (the binding segment is reversely complementary to the full-length sequence of the target miRNA) , the signal segment is a DNA segment that can form a G-quadruplex structure for outputting a signal.
[0053] The detection principle of the present invention sees figure 1 . When there is no target miRNA molecule, the G-quadruplex structure in the probe can combine with heme to form DNAzyme, which can catalyze H 2 o 2 Oxidation of ABTS [2,2′-hydrazine-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diamine salt] reaction, the color of the solution changes from colorless to obvious green, which is characteristic in the absorption spectrum The absorption peak is 420nm; in the presence of ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2, G-quadruplex probe design using miRNA21 as target molecule
[0074] The G-quadruplex probe MG41 was designed with miRNA21 as the target molecule, as shown in Table 1.
[0075] Table 1 The sequence of G-quadruplex probe and miR21
[0076]
[0077] In the probe MG41, the 1st to 19th positions from the 5' end are the signal segment, and the 20th to 41st positions are the binding segment.
Embodiment 3
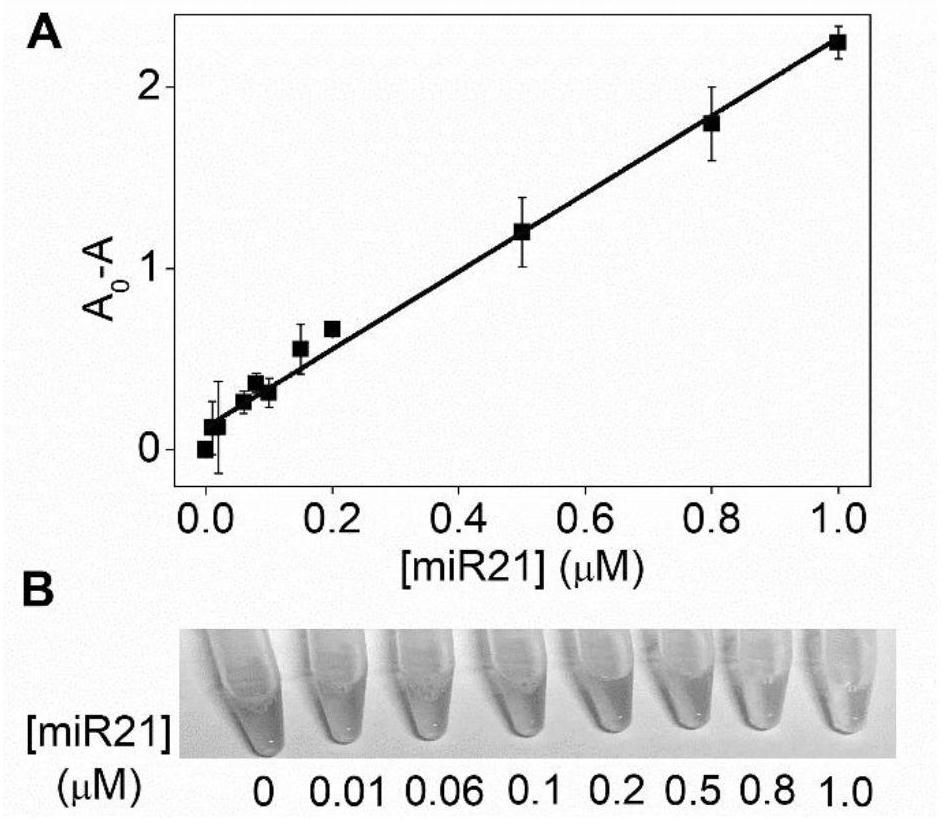
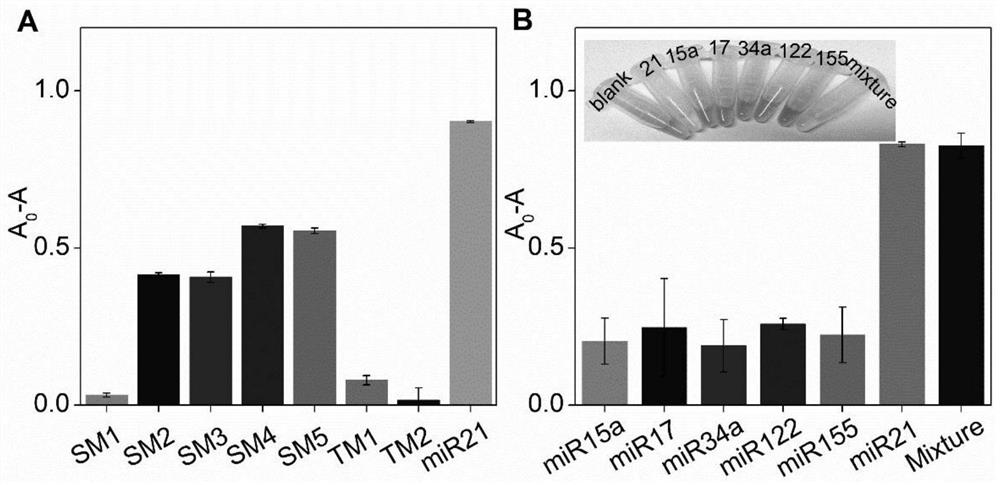
[0078] Embodiment 3, sensitivity
[0079] 1. Heat the MG41 probe prepared in Example 1 at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then place it on ice to anneal and cool down.
[0080] 2. Configure the reaction system as follows, and perform the hybridization reaction at 37°C for 80 minutes.
[0081] Reaction system: probe 8 μl, 10×KF reaction buffer 2 8 μl, dNTPs 4 μl, Tris-HCl buffer 44 μl, miRNA21 8 μl.
[0082] The concentration of the probe in the reaction system was 1 μmol / L.
[0083] Different gradients (0-1 μmol / L) are set for the concentration of the miRNA21 in the reaction system.
[0084] The concentration of dNTPs in the reaction system was 0.5mmol / L.
[0085] The concentration of Tris-HCl buffer in the reaction system was 10mmol / L.
[0086] 3. After completing step 2, add 8 μl DNA polymerase KF to the reaction system, incubate at 37°C for 50 minutes, and then incubate at 80°C for 10 minutes to inactivate KF.
[0087] The concentration of DNA polymerase KF in the reaction sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com