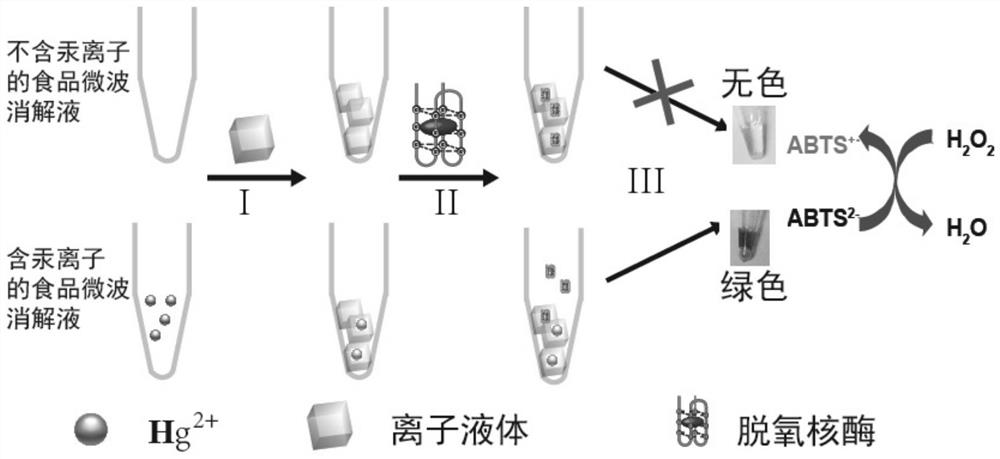
A method for rapid detection of mercury content in food based on ionic liquid
A technology of ionic liquid and food, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of combined use, no sensor, low extraction efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of less demand, simple operation and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
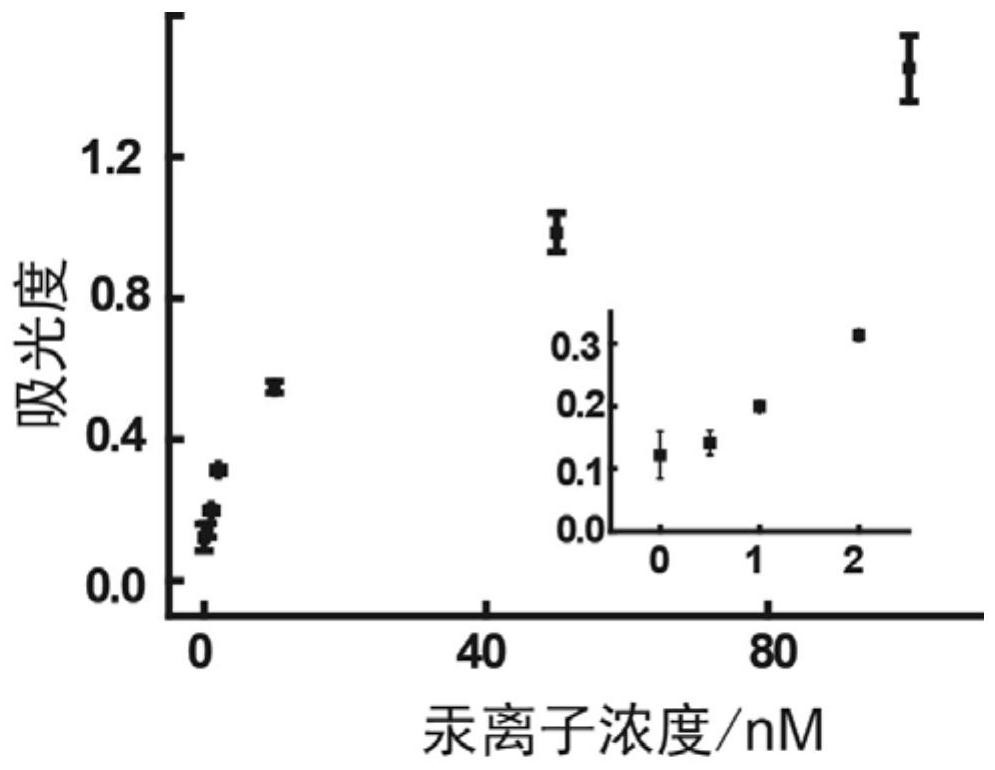
[0031] Example 1. Drawing of working curve.
[0032] Mercury solution, deoxyribozyme oligonucleotide EAD2 (5'-CTGGGAGGGAGGGAGGGA-3') solution, hemin solution, 2,2-azido-bis(3-ethyl) used in all the following examples - benzothiazole-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) and hydrogen peroxide solution, both in 4-hydroxyethylpiperazine ethanesulfonic acid buffer solution A (25mM HEPES, 20mM KNO 3 ,200mM NaNO 3 ,150mM NH 4 Cl, 0.025% (w / v) Triton X-100, and 1% (v / v) DMSO)) were dilution solvents.
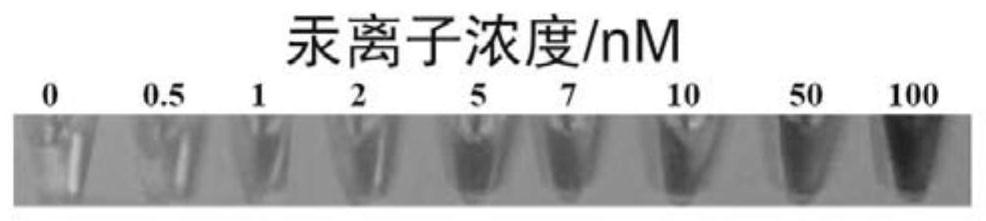
[0033] like figure 1 As shown, 10 μL of ionic liquid (N-octylpyridine tetrafluoroborate) was added to 1 mL of mercury ion solutions of different concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 50, 100 nM). Heated at 80 °C for 10 min, and then quenched in an ice bath for 10 min. After centrifugation at 8000 r / min for 10 min, the ionic liquid at the bottom of the centrifuge tube was taken out. Using buffer solution A as a dilution solvent, prepare 60 μL of 0.5 μM DNAzyme oligonucleotide ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2. Determination of selectivity:
[0036] Take 10 μL of N-octylpyridine tetrafluoroboric acid and add it to 1 mL of 100 nM solution of different metal ions (Hg 2+ , Cr 3+ , Ni 2 + , Ca 2+ , Pb 2+ , Cu 2+ , Fe 3+ , Fe 2+ , Cd 2+ , Zn 2+ , Mg 2+ )middle. Heated at 80°C for 10min and quenched in ice bath for 10min. Centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 10 min to separate and take out N-octylpyridine tetrafluoroboric acid at the bottom of the centrifuge tube. Prepare 60 μL of 0.5 μM DNAzyme oligonucleotide EAD2 solution, heat at 95°C for 6 minutes, and then slowly cool to 37°C. Hemin (15 μL, 20 μM) was added to the above EAD2 solution, and incubated at 25° C. for 90 min to form a DNAzyme complex. 2 μL of the ionic liquid obtained by centrifugation and 40 μL of DNAzyme complex were incubated at 25°C for 30 min. Centrifuge at 8000 r / min, take the upper 35 μL DNAzyme complex, add buffer solution A and dilute to 100 μL. Then 3.75 mM 10 μL of ABTS and 15 mM 5 μL o...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3. Determination of the extraction efficiency of ionic liquids enriched with different concentrations of mercury ions from buffer solutions and 20% nitric acid:
[0039] 10 μL of N-octylpyridine tetrafluoroborate was added to 1 mL of water containing different concentrations of mercury ions or 20% nitric acid solution (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 50, 100 nM). Heated at 80°C for 10min and quenched in ice bath for 10min. Centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 10 min to separate and take out N-octylpyridine tetrafluoroboric acid at the bottom of the centrifuge tube. The supernatant was collected, and the concentration of mercury ions in the supernatant was measured by atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer. Instrument conditions 270V, 25mA. Measure 15s, delay 0.5s. The carrier current is 5% HCl, and the reducing agent is 2% NaBH 4 , 0.5%NaOH, the extraction efficiency (1-(C 初始 *V 初始 -C 萃取后 *V 萃取后 ) / C 初始 *V 初始 )*100%.
[0040] The result is as Figure 4 As shown, N-oct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com