Fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and application of fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method
A chemical sensor and internal oxidation technology, which is applied in the field of biological detection and molecular biology, can solve problems such as difficult to quantify 8-oxoG damage, and achieve the effect of improving detection sensitivity, improving sensitivity, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
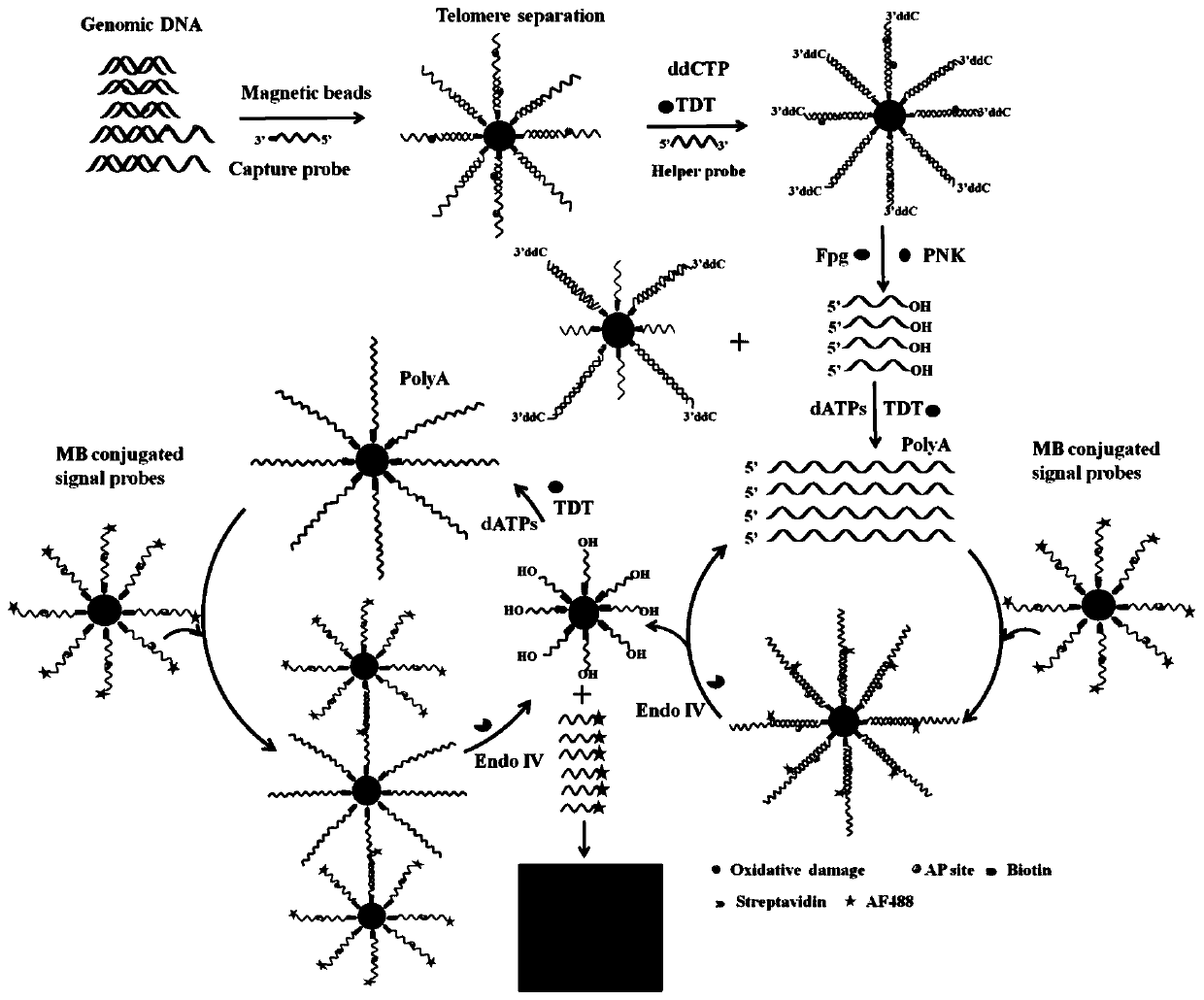
[0072] 1. Detection principle and method steps of the present invention:
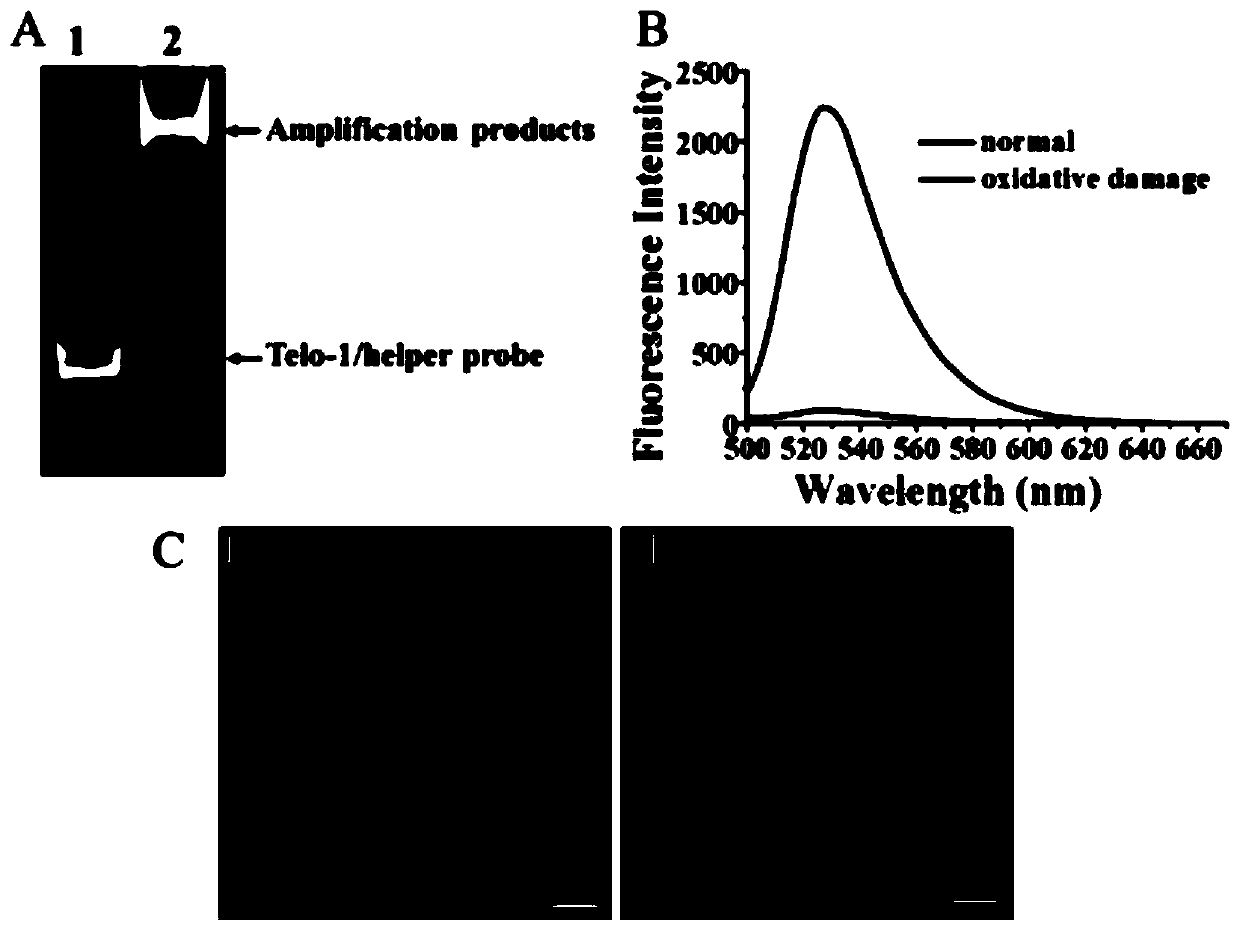
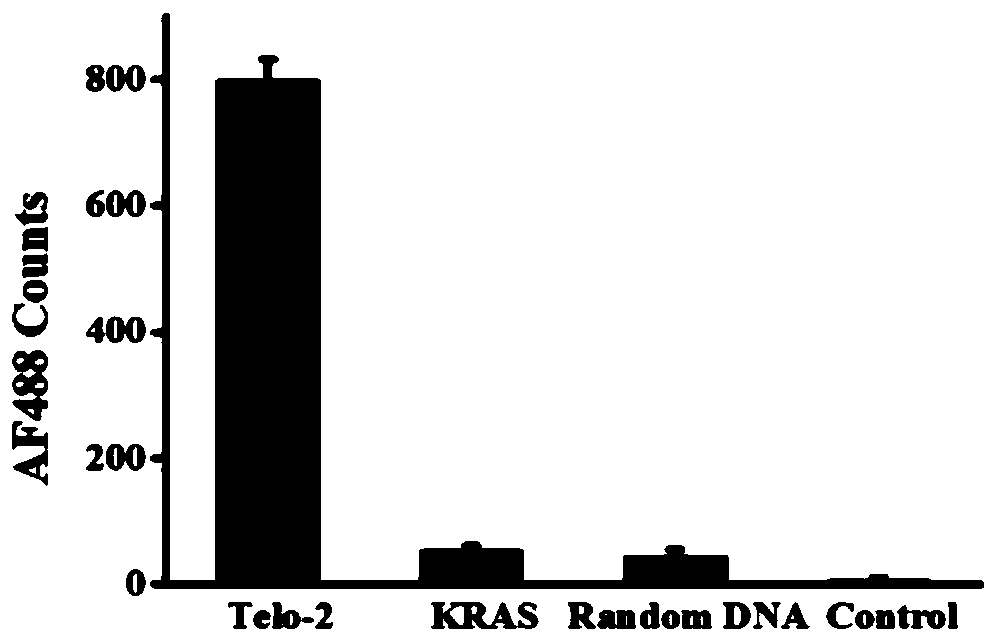
[0073] Genomic DNA was first extracted by digestion with dsDNA fragmentase to obtain DNA with 50-200 bp. In the human genome, telomeres are composed of repetitive sequences (TTAGGG) n Composition, which forms long regions of double-stranded DNA terminating in single-stranded 3'G-rich overhangs. To enrich telomeres, 3'-biotinylated capture probes were designed to hybridize to telomeres and streptavidin-coated magnetic beads were used to separate telomeres from genomic DNA. All isolated telomeres were end-labeled with ddCTP by polymerization using TdT to prevent non-specific amplification. Subsequently, in order to improve the efficiency of the base excision repair reaction, an auxiliary probe modified with ddC at the 3' end was also designed to hybridize to single-stranded telomeres to form formamide pyrimidine [fapy]-DNA glycosylase (Fpg) dsDNA substrate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com