Marker set and composition for comprehensively screening genetically modified ingredients and application
A technology of markers and compositions, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as the lack of comprehensive evaluation of transgenic components or transgenic strain methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Design and screening of embodiment 1, primers and probes
[0093] According to a large amount of market research data, first determine all the commercially grown transgenic strains on the market, and then determine the following seven screening elements as screening elements covering the strains except maize DAS40278, soybean DP305423 and soybean CV127: PCAMV35S, TCAMV35S, TNOS, PRbcS4, TPINII, TE9 and PAT; finally, query and determine the line-specific sequences of three transgenic lines: maize DAS40278, soybean DP305423 and soybean CV127.
[0094] Based on the above-mentioned 7 kinds of screening element sequences and the specific sequences of the above-mentioned three kinds of transgenic lines (10 kinds of sequences in total), the insertion sequence information of commercialized transgenic lines was collected, and based on this, each group (each screening element or Strain-specific sequences are grouped into one group, a total of 10 groups) and multiple pairs of prim...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Embodiment 2, the method for using digital PCR to detect genetically modified components
[0118] In this embodiment, it is judged whether the biological sample contains genetically modified components according to the result of digital PCR amplification. The method uses the 10 primers and probe combinations screened in Example 1 to carry out.
[0119] With the genome of the sample to be tested as a template, each sample to be tested is set in three parallels, and the combination of primers and probes (SEQ ID No.1-30) obtained by screening in Example 1 is used for digital PCR amplification, and negative Control and blank control, wherein negative control: use negative genome (ie, genomic DNA of non-transgenic sample) as template, and blank control: use water as template.
[0120] The specific steps of digital PCR amplification are as follows:
[0121] (1) Prime step: Remove the blue protective film from the digital PCR chip, inject Control Line Fluid into the holes on ...
Embodiment 3
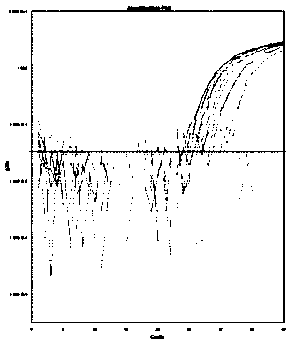
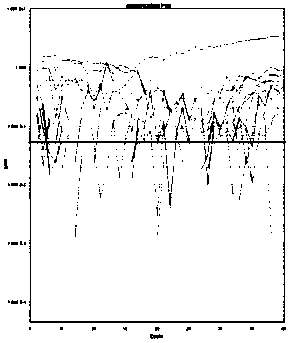
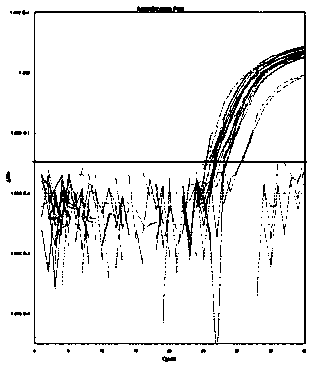
[0135] Embodiment 3, sensitivity detection
[0136] Sensitivity verification was performed according to the method established in Example 2 for detecting transgenic components using digital PCR. The sensitivity of the detection system is defined as the lowest copy number that the detection system can perform stable detection. In this example, seven screening elements PCAMV35S, TCAMV35S, TNOS, PRbcS4, TPINII, TE9, PAT and corn DAS40278, soybean DP305423, soybean CV127 were used The transgenic samples of the strain-specific sequences of the above-mentioned strains were artificially diluted to prepare homogeneous samples containing transgenic components of different mass percentages, and then digital PCR amplification was carried out according to the method of Example 2, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0137] (1) Test samples: select transgenic samples: corn MON87427 (as a sample for detection and screening element "PCAMV35S"), corn 59122 (as a sample for detection and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com