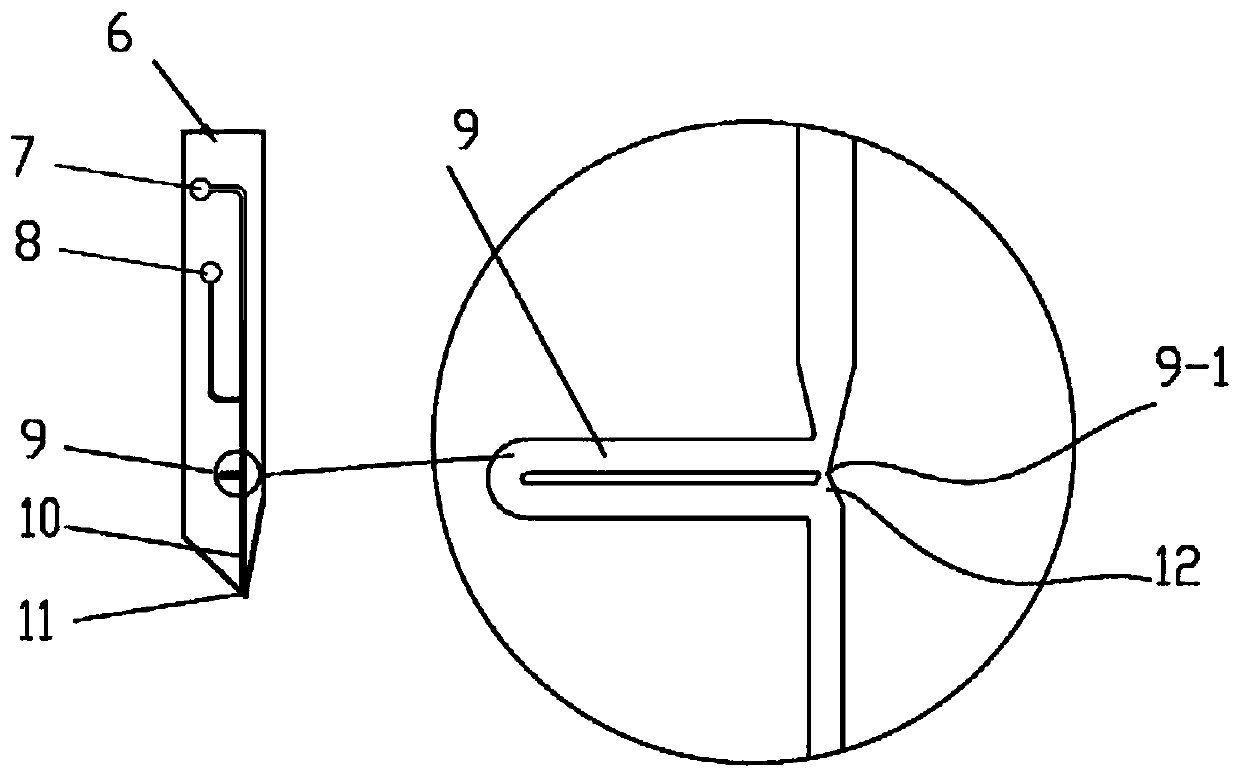
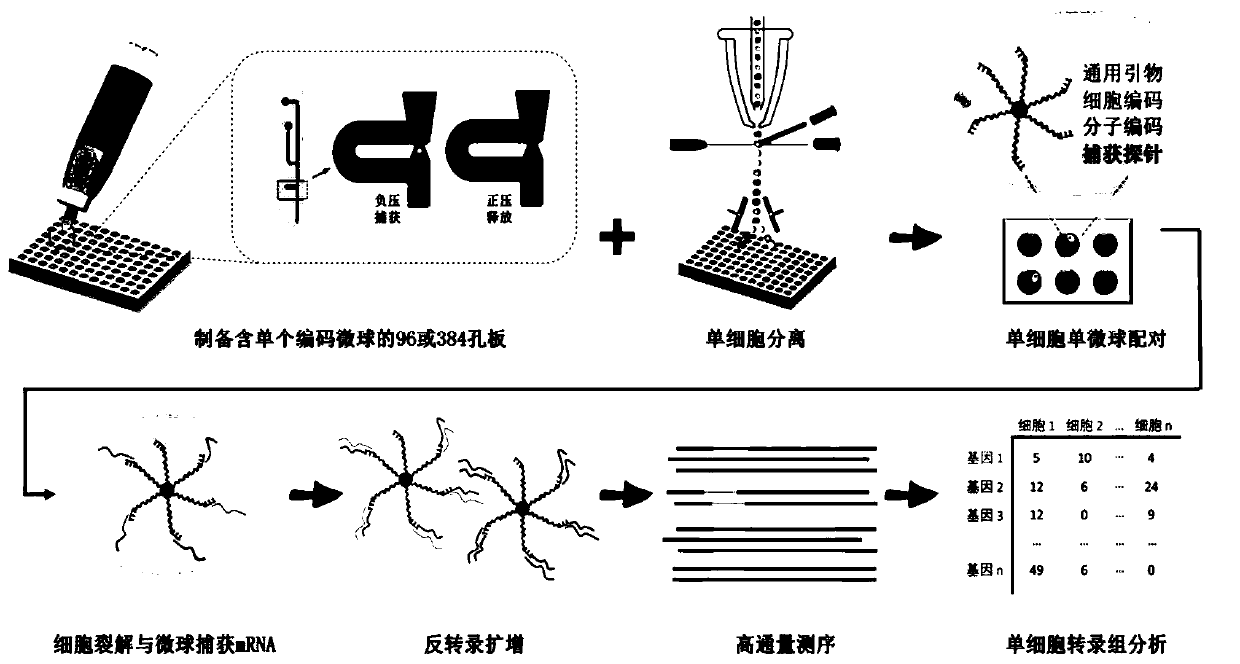
Method for analyzing unicellular inclusion
An inclusion, single-cell technology, applied in the field of single-cell sequencing, can solve the problems of high technical threshold, consumption, information deviation, etc., and achieve the effects of a wide range of analysis targets, high capture and release efficiency, and simple and convenient use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 High-throughput single-cell transcriptome sequencing
[0054] As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the selected cells are 3T3 and K562 cells, the cell diameter is 7-15 microns, the size of the coded microspheres used is 30-40 microns, and the single-coded microsphere pipette and fluorescence activated flow Sequencing sample preparation with formula sorting single cells is taken as an example, and the specific working process of this embodiment is introduced:
[0055] 1. Immerse the end of the chip of the portable single particle pipette with the solution inlet and outlet in the coded microsphere suspension, and use the syringe connected to the negative pressure port to generate negative pressure to absorb the sample of the coded microsphere suspension;
[0056] 2. Transfer the portable single-particle pipette to the cleaning solution, generate negative pressure through the syringe connected to the negative pressure port again, and draw the clean...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2 Transcriptome sequencing analysis of rare cells
[0075] Taking LnCap cells as an example, the cell diameter is 18-25 microns, and the specific process of Example 2 is introduced:
[0076] 1. After preparing the single microsphere microwell plate in the same process as in Example 1, prepare for the addition of single cells.
[0077] 2. Repeat the operation from step 2 to step 3 in Example 1, change the microsphere suspension to cell suspension, and add a single cell to the 96 or 384-well plate with a single particle pipette to realize a pair of cells and microspheres a pair.
[0078] 3. Add cell lysate to the 96-well plate or 384-well plate containing single cells and single microspheres, centrifuge at room temperature, and incubate.
[0079] 4. Repeat steps 5 to 9 in Example 1.
[0080] The single particle pipette developed by the present invention has extremely high single microsphere capture and release efficiency, and can directly add a single coded mic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com