Method for improving toughness of high-carbon equivalent steel plate welding heat affected zone through rare earth
A welding heat-affected zone and high carbon equivalent technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency and manufacturing converters, can solve problems such as easy aggregation and growth, and achieve the effect of inhibiting grain growth and improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment.
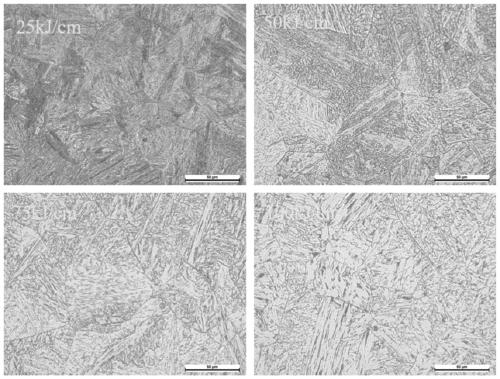
[0033] The invention discloses a method for improving the toughness of a welding heat-affected zone of a high carbon equivalent steel plate by using rare earth. Among them, the LF+vacuum degassing / RH process route is adopted for refining outside the furnace, and rare earth alloys are added in the RH refining process, so that fine and dispersed inclusions containing rare earth Ce and original inclusions modified by rare earth are newly generated in molten steel . These inclusions inhibit the growth of the original austenite grains in the heat-affected zone during the welding process, and the addition of rare earths also delays the bainite transformation in the heat-affected zone of welding and inhibits the formation of upper bainite, thus greatly improving the welding process. Toughness in the weld heat-affected zone of carbon-equivalent thick plates.
[0034] The study on improving...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com