Efficient cordyceps sinensis ascospore separating method
A technology for spore separation and ascospores, which is applied in the field of ascospore separation of Cordyceps sinensis, which can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-consuming, fragile ascospores, and easy contamination, and achieve the effects of low cost, high success rate and strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1, germination culture of Cordyceps sinensis ascospores.
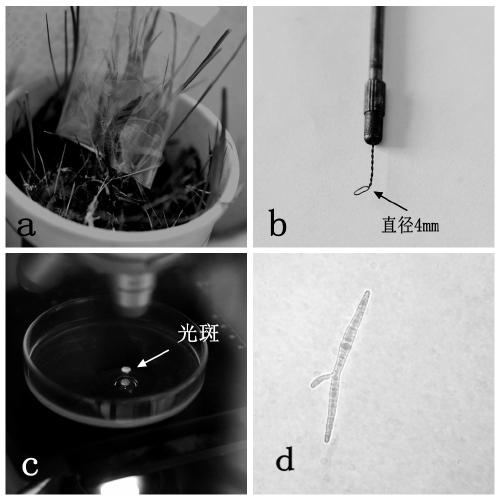
[0029] The Cordyceps sinensis used in the present invention is the fresh Cordyceps sinensis of the ascospore ejection period in Tianzhu area, Gansu Province. Its main steps are: 1. Cover the sterilized cellophane bag on the fruiting body of Cordyceps sinensis during the ascospore ejection period to collect ascospores ( figure 1 a). 2. Dilute the collected ascospores with a small amount of sterile water. After calculating the ascospore density with a hemocytometer, dilute the ascospore suspension to 45 / ml. 3. Pipette gun to quantitatively draw 1ml of ascospore dilution on a 90mm germination medium plate, spread it evenly with a middle coating rod, and then transfer it to a 15°C constant temperature incubator for germination culture. During this period, continuously observe the ascospore germination with a microscope.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2, the isolation and cultivation of Cordyceps sinensis ascospores
[0031] After 3-5 days of germination and culture, the ascospores will begin to germinate and can enter the stage of isolation and culture. The main steps are: 1. Transfer the 90mm germination medium plate into the ultra-clean workbench, and observe the germination of ascospores with an ordinary optical microscope. 2. After finding a single ascospore, confirm it repeatedly with a high-power lens to ensure that the ascospore in the field of view is a germinated single spore ( figure 1 d). 3. Turn off the fluorescent lamp of the ultra-clean workbench and all ambient light sources to create a dark environment. 4. Use a self-made ring sampler ( figure 1 b) Aim at the bright circular spot formed by the light path of the microscope on the surface of the germination medium in a dark environment ( figure 1 c) Hole sampling. 4. Inoculate the sampling blocks containing germinated monospores one ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3, the vegetative growth cultivation of Cordyceps sinensis
[0033] When isolated and cultured for about 30 days, the Cordyceps sinensis fungus developed from a single germinated ascospore in the petri dish began to produce signs of growth visible to the naked eye ( figure 2 a), the colony morphology was obvious at 60 days ( figure 2 b), the diameter of the colony is about 1cm, and the diameter of the colony further increases after 90 days, and the pigment is obvious ( figure 2 c) At this time, the Cordyceps sinensis fungus developed from a single ascospore has been successfully obtained. If further research and identification is required, the vegetative growth link can be carried out first. The main steps are: 1. The Cordyceps sinensis obtained through isolation and culture Army, use a 5mm puncher to punch a sample, and inoculate it on a 70mm nutrient medium plate. 2. After the sealing film is sealed, transfer them to a constant temperature incubator at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com