A laser electrochemical backside cooperative micromachining method and device for semiconductor materials
A semiconductor and electrochemical technology, applied in metal material coating process, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, liquid chemical plating, etc., can solve the problems that the technical applicability needs to be further expanded, and the localized processing of the back of the material has not been discussed. Achieve no residual stress, good surface quality, no thermal damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
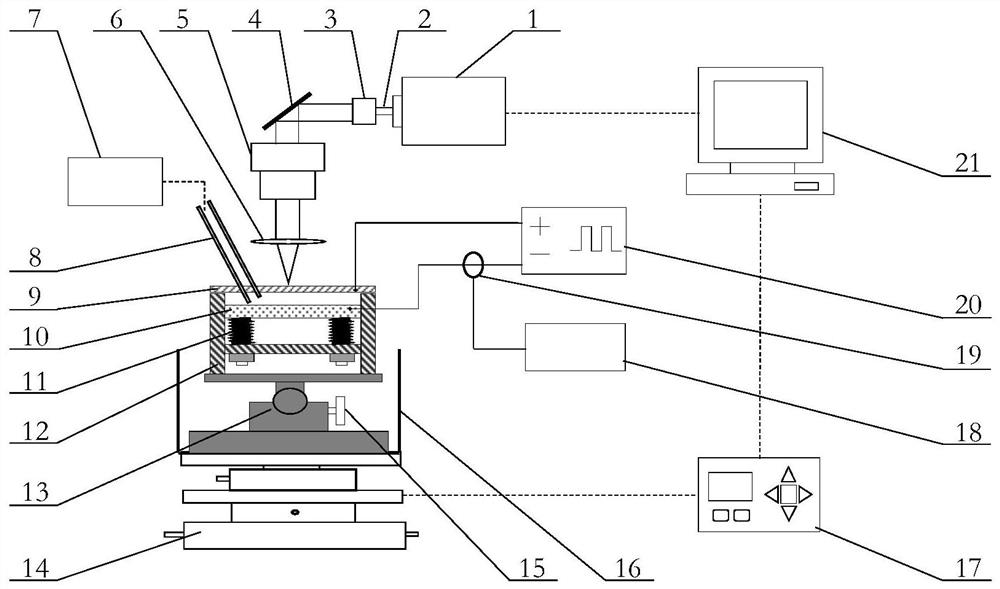
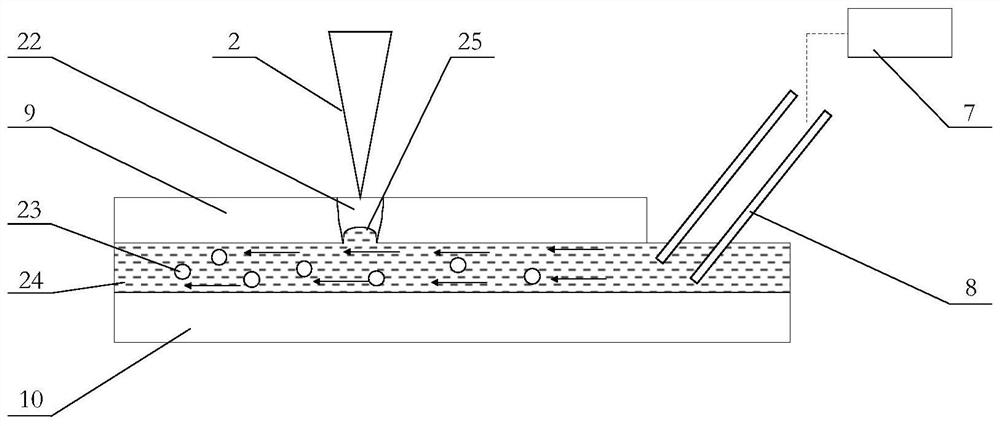
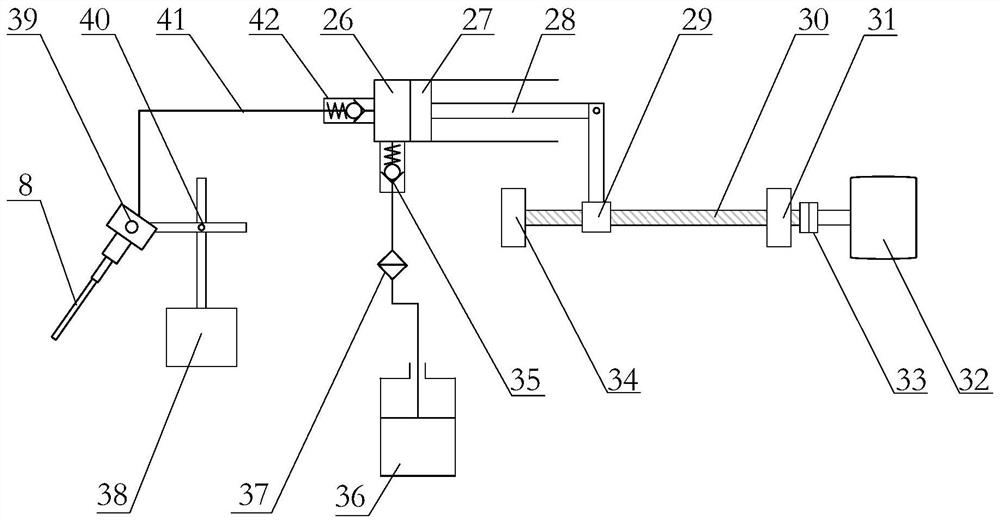
[0044] combined with figure 2 , this embodiment is a laser electrolysis backside collaborative micromachining method for semiconductor materials based on localized conductive channels. The laser beam 2 generated by the laser 1 is adjusted and transmitted by an external optical path and then focused on the surface of the semiconductor material 9, and the thermal effect of the laser is used to process high-efficiency materials. Removal, complete micro-hole, micro-groove processing. At the same time, the thermal effect of the laser generates a local temperature field around the irradiated area, which locally enhances the conductivity of semiconductor materials such as single crystal silicon. On this basis, using a stable low-voltage electrolyte beam generating device to introduce a low-voltage electrolyte beam on the back of the semiconductor material 9, in the region where the conductivity is enhanced, electrochemical anodic dissolution is introduced locally, and the laser-etch...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a semiconductor material laser electrolysis back-facing cooperative micromachining system based on a localized conductive channel, including an optical path system, a stable low-pressure jet flow generation system, and an electrolytic processing system; the optical path system includes a laser 1 and an external optical path, wherein the external The optical path includes a beam expander 3 , a mirror 4 , a vibrating mirror 5 and a lens 6 . The laser 1 outputs the laser beam 2, the diameter of the laser beam is enlarged by the beam expander 3, the direction is adjusted by the reflector 4, the movement form of the beam is controlled by the vibrating mirror 5, and finally after being focused by the lens 6, it is irradiated to the surface of the semiconductor material 9, and the A localized conductive channel 22 is formed in the semiconductor material 9 . The generation of the laser beam 2 and the movement of the vibrating mirror 5 are all co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com