Anthropogenic lysozyme encoding gene and expressing method and application thereof in pichia pastoris
A technology encoding a gene, lysozyme, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, applications, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of low expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
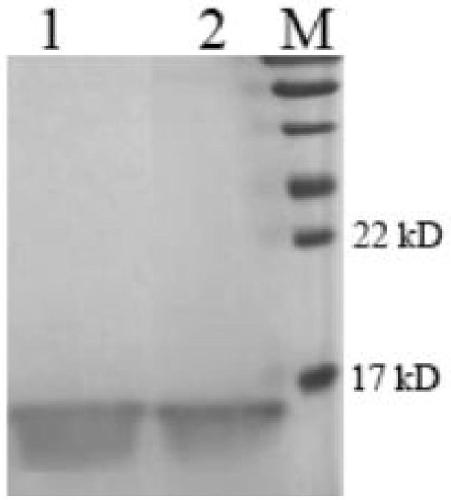
[0022] Embodiment 1, human source lysozyme gene sequence codon optimization
[0023] The sequence derived from the human lysozyme gene was codon-optimized to a certain extent: a. Reduce the occurrence probability of continuous A / T / G / C bases and avoid the generation of stem-loop structure; b. In the entire gene sequence, increase Some rare codons, especially during translation initiation, reduce the rate of ribosome elongation. The optimized human lysozyme gene sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and the optimization rate of the entire sequence is 23.2% compared with the original sequence.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2, construction of expression vector and protein expression
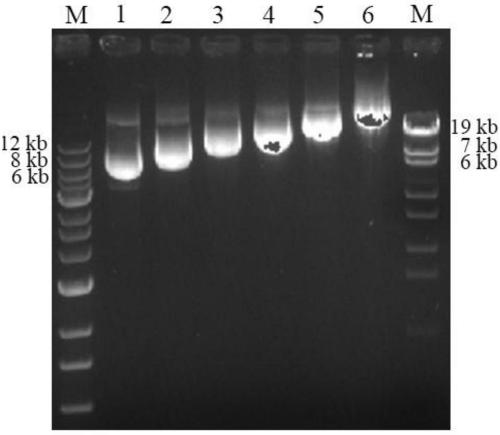
[0025] 1. Artificial synthesis of gene sequence
[0026] The nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 was entrusted to Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. to artificially synthesize the gene according to the conventional technology in the field, and the gene was inserted into the plasmid vector pUC57, and stored for future use.
[0027] 2. Gene sequence amplification
[0028] Design primer pair (hLYZ-F, hLYZ-R) according to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2
[0029] The underlined part of the forward primer is the Cpo I restriction site, and the underlined part of the reverse primer is the Not I restriction site. The sequence design of this site conforms to the sticky end produced by the method of cutting with T4 DNA polymerase.
[0030] PCR reaction system:
[0031]
[0032] PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 57°C...
Embodiment 3
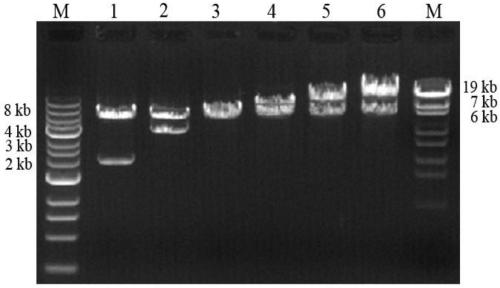
[0045] Example 3, construction of cofactor genes and related vectors
[0046] 1. Cofactor gene amplification
[0047] Through the website https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / , search for the Bip, Ero1 and Pdi1 gene sequences derived from Pichia pastoris GS115 and design primers for gene amplification (primer list), these genes were respectively constructed in the pGAPZB vector between the EcoR I and Age I restriction sites. The underlined part of the forward primer is the restriction site of EcoR I and its homologous sequence at the left end of the vector, and the underlined part of the reverse primer is the restriction site of Age I and its homologous sequence at the right end of the vector. The sequence design conforms to the method of T5 exonuclease construction vector.
[0048] PCR reaction system:
[0049]
[0050] PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 6min, denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 57°C for 30s, extension at 72°C (1kb / 30s), 30 cycles, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com