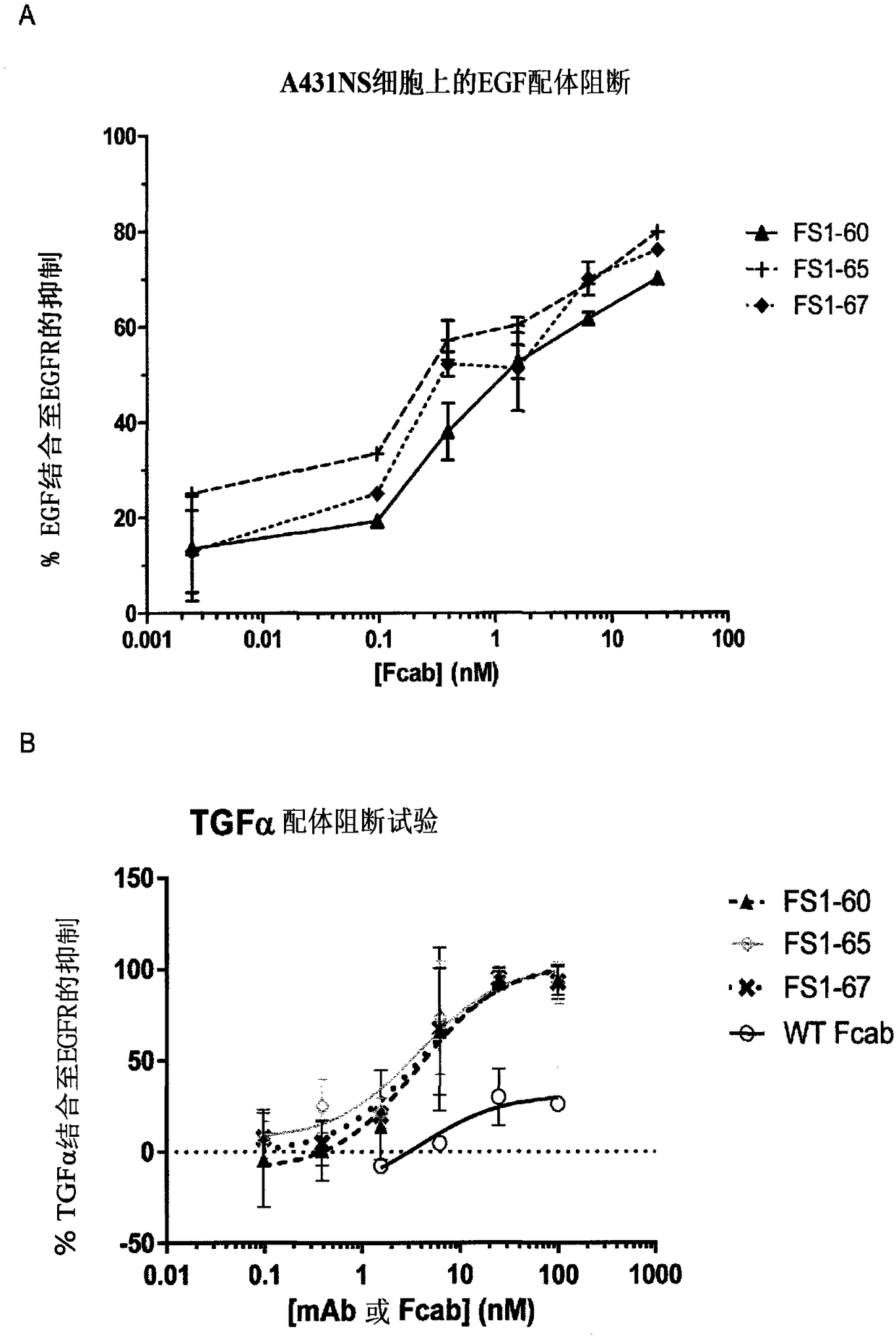
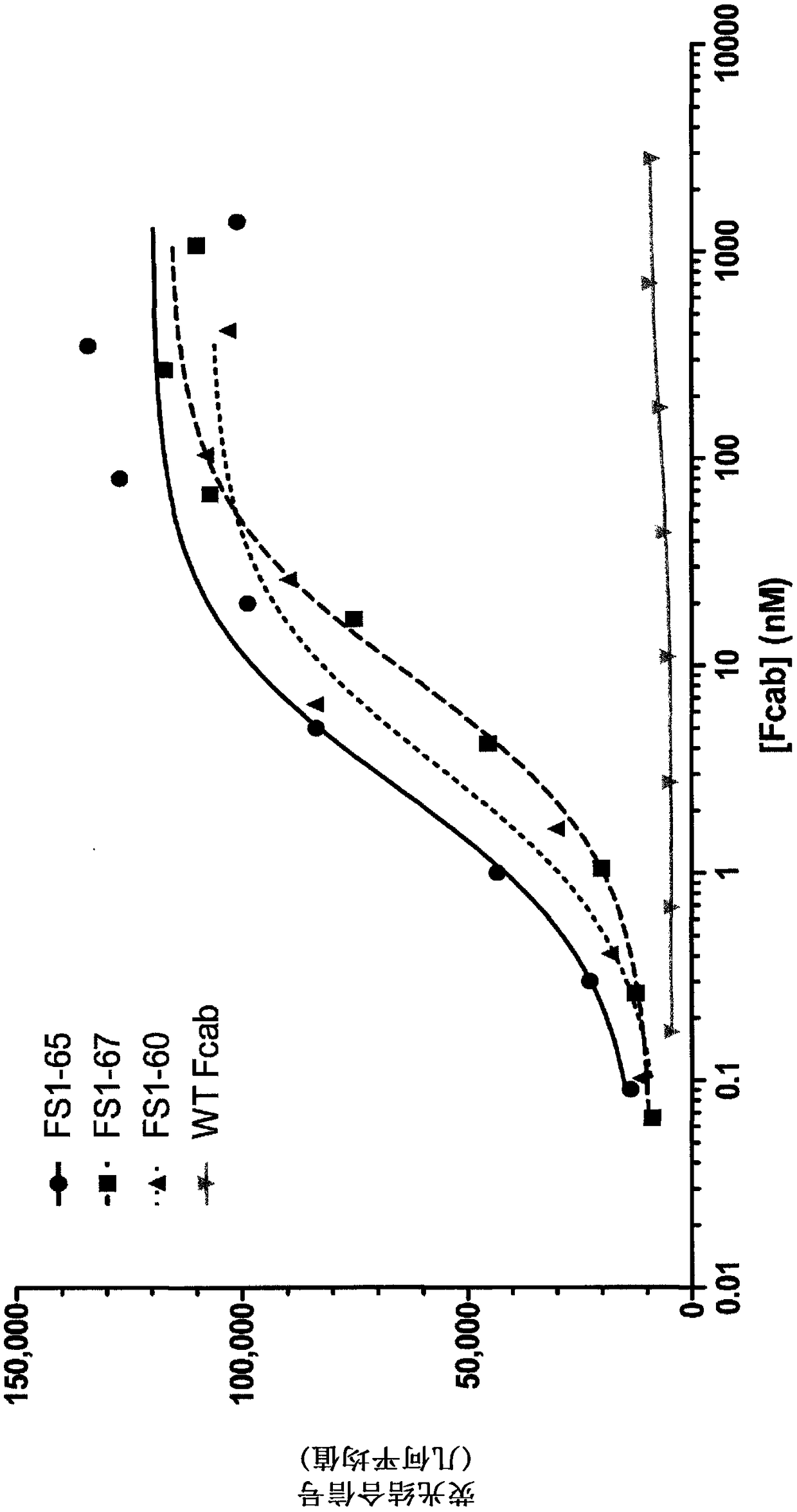
EGFR binding molecules
A technology of binding sites and antibody molecules, applied in drug combinations, organic active ingredients, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as overall survival and progression-free survival
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0160] Example 1 - Preparation of Anti-EGFR Antigen Binding Fcs (Fcab)
[0161] EGFR-specific Fcabs were selected from yeast-displayed Fcab libraries by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and from phage-displayed Fcab libraries by magnetic bead capture as described below.
[0162] Primary selection of anti-EGFR Fcabs from a yeast library using FACS
[0163] A method for selecting antigen-specific Fcabs by FACS from a yeast display Fcab library is described in WO 2009 / 132876. A library of clones expressing Fcabs on the surface of yeast cells was incubated with 300 nM biotinylated EGFR extracellular domain. Cells were then stained with Streptavidin-Allophycocyanin (APC) (BD Bioscience, 349024) to separate antigen-binding yeast cells based on fluorescent signal using a high-speed cell sorter (BD Bioscience, FACSAria). This selection procedure was repeated several times to enrich for a sufficiently pure population of antigen-binding yeast cells. Streptavidin-APC and a...
Embodiment 3
[0176] Example 3 - EGFR-specific Fcabs bind to epitopes on EGFR other than cetuximab
[0177] Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to determine whether EGFR-specific Fcabs FS1-60, FS1-65 and FS1-67 competed with a known anti-EGFR antibody, cetuximab (Merck), for binding to EGFR.
[0178] BIAcore 3000 (GE healthcare) was used to determine whether EGFR-specific Fcabs FS1-60, FS1-65 and FS1-67 were likely to bind to human EGFR-coated chips saturated with cetuximab (CX) and vice versa.
[0179]A streptavidin chip (SA chip) (GE Healthcare BR-1000-32) was coated with 200RU of biotinylated human EGFR extracellular domain (ECD). Experiments were performed in HBS-P buffer using a flow rate of 20 μl / min (GE Healthcare) and the EGFR surface was regenerated by passing 50 mM NaOH three times at 50 μl / min for 12 s. The first EGFR-binding compound (EGFR-specific Fcab or cetuximab) was injected at 20 μl / min for 4 minutes, followed by the second EGFR-binding compound (cetuximab or EGFR-...
Embodiment 4-E
[0183] Example 4 - Binding affinity of EGFR-specific Fcabs to human and mouse EGFR
[0184] The binding affinity of EGFR-specific Fcabs to human and mouse EGFR was determined using SPR. For affinity measurement, a BIAcore 3000 instrument (GE healthcare) was used and the SA chip was coated with 200 or 1000 RU of biotinylated human (in-house) or mouse (Sino Biological) EGFR extracellular domain. A serial concentration of Fcab (1-1000 nM) in HBS-P buffer (GE Healthcare) was injected at 20 μl / min for 2.5 minutes to measure association rates. HBS-P buffer was then injected for 15 minutes to measure the off-rate. 50 mM NaOH was used twice at 50 μl / min for 10 seconds to regenerate the EGFR surface. Binding affinities (K D ). The results show that EGFR-specific Fcabs bind to human and mouse EGFR with binding affinities between 0.7–6.0 nM (see Table 3).
[0185] Table 3: Binding affinity of EGFR-specific Fcabs to human and mouse EGFR (K D )
[0186] Fcab
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com