Purifying method for coking residual ammonia water
A technology for coking residual ammonia water and ammonia water, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as activated carbon removal of ammonia and the effect of ammonia removal, high equipment requirements, and ozone leakage, etc., to achieve Simple and reliable regeneration operation, low equipment investment and short process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
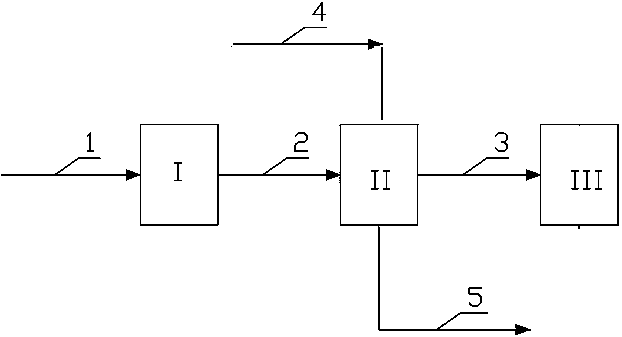
[0037] The specific implementation is as figure 1As shown in the device process, the tar concentration is 180mg / L, the volatile ammonia content is 3g / L (ammonium bicarbonate, free ammonia), and the remaining ammonia water with a COD (chemical oxygen demand) of 8000 mg / L is fed into the dust removal equipment. Ash pretreatment adsorbent adsorption tower, the remaining ammonia water after adsorption enters the deammonization adsorption tower, wherein the attached agent is molecular sieve adsorbent, and the adsorbent adopts hydrophobic ZSM-5 molecular sieve; the adsorbed waste water is sent to the storage Pool; the tar content in the treated wastewater is 2.2 mg / L, the ammonia nitrogen content is 80 mg / L, and the COD content is 2000 mg / L.
[0038] After the pretreatment adsorbent is adsorbed and saturated, the dedusted dust is filtered and sent to the coal blending station for coal blending. After the adsorbent in the deamination adsorption tower is saturated, it is regenerated ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The specific implementation is as figure 1 In the device process shown, the remaining ammonia water with a tar concentration of 200mg / L is sent to an adsorption tower filled with an adsorbent, wherein the adsorbent is a molecular sieve adsorbent, and the adsorbent adopts a TS-1 molecular sieve; the remaining ammonia water after adsorption Send it to the storage tank; part of the wastewater in the storage tank is reused as cooling water, and part of it is discharged. The remaining ammonia water before treatment contains a tar concentration of 200 mg / L, a volatile ammonia content of 3 g / L, and a COD of 8000 mg / L. In the remaining ammonia water after treatment, the tar content is 3 mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen content is 60 mg / L. The COD content is 1500 mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The specific implementation is as figure 1 In the device process shown, the remaining ammonia water with a tar concentration of 220mg / L is sent to the adsorption tower filled with adsorbents, wherein the adsorbent is a molecular sieve adsorbent, and the adsorbent adopts Ti-MOR molecular sieve; the remaining ammonia water after adsorption is sent to into the storage tank; part of the wastewater in the storage tank is reused as cooling water, and part of it is discharged.
[0043] The remaining ammonia water before treatment contains a tar concentration of 100 mg / L, a volatile ammonia content of 4 g / L, and a COD of 7000 mg / L. In the remaining ammonia water after treatment, the tar content is 1 mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen content is 50 mg / L. The COD content is 1000 mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com