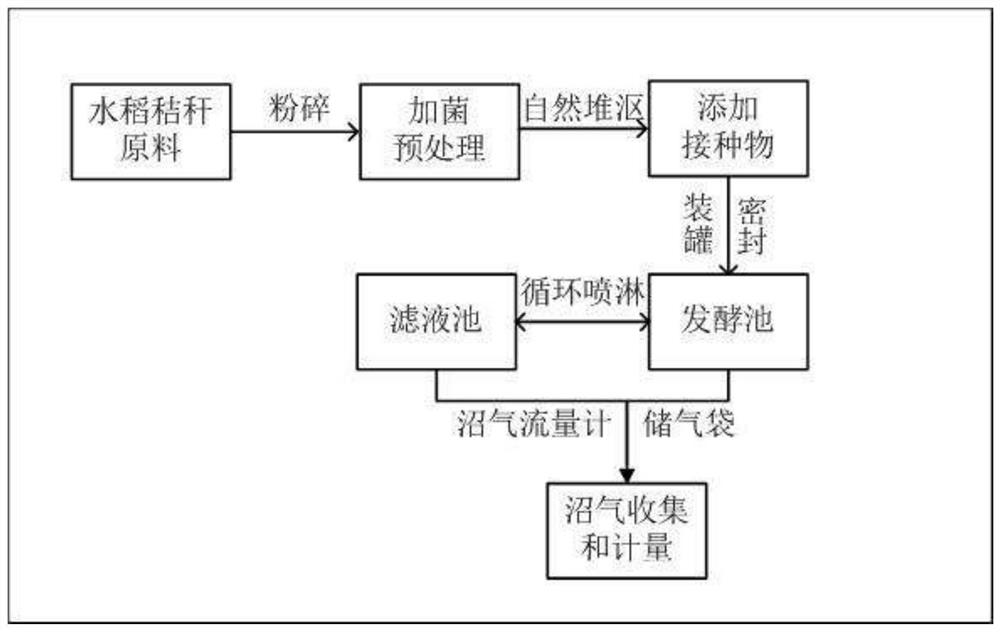
A kind of rice straw fermentation treatment process
A technology of rice straw and processing technology, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, waste fuel, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption for stirring, easy acid poisoning, and difficulty in feeding and discharging materials, and achieves efficient reuse of green environmental protection resources, stable methane concentration, The effect of small investment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Example 1: Effect of Fermentation Pretreatment on Rice Straw Gas Production
[0059] 1. Fermentation pretreatment of Absidia umbilicali: prepare the inoculant of Absidum umbilicali according to the above-mentioned method. The rice straw is pulverized by a pulverizer, and the particle size is 1-2 cm. Take 2kg of straw, take bacterium agent with a mass of 1% of the dry weight of rice straw and urea with a weight of 0.5% of the dry weight of rice straw, adjust the moisture content of the straw to 65%, cover it with film, and pretreat it for 3 days at a constant temperature of 35°C, as the experimental group . The rest of the conditions are the same, and the same mass of high-temperature sterilized bacteria agent is added as a blank group.
[0060] 2. Mix the pretreated rice straw fermentation products of the experimental group and the blank group with the domesticated inoculum. The mass of the domesticated inoculum is 30% to 50% of the total mass, and adjust the water co...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2: Effect of fermentation method on rice straw gas production
[0067] 1. Use the method of the experimental group in the first embodiment to carry out the same pretreatment on the experimental group and the blank group in the second embodiment.
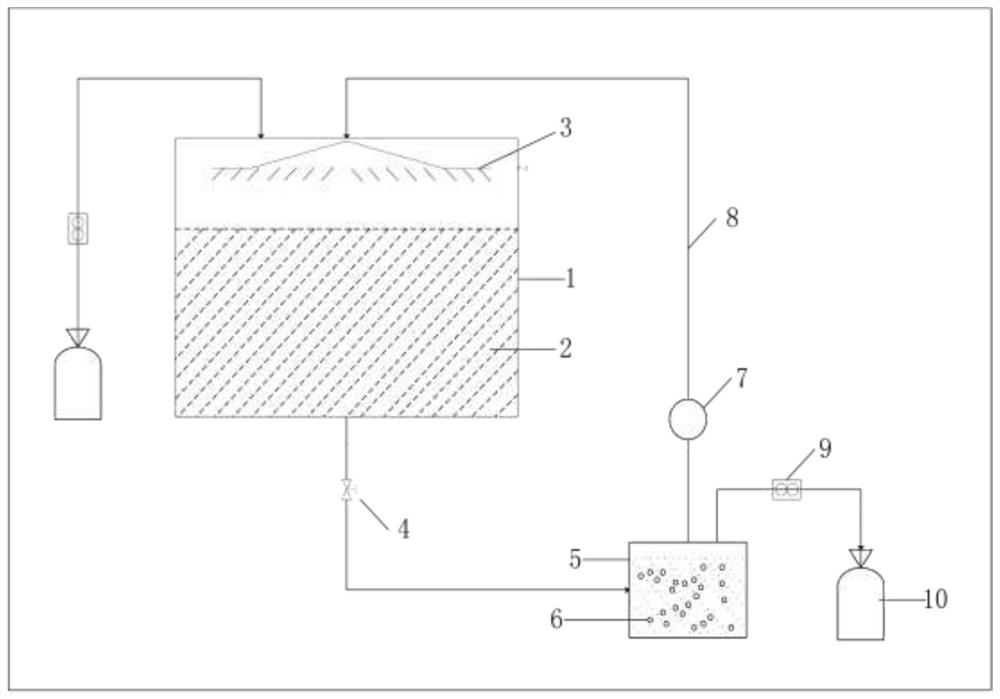
[0068] 2. Put the pretreated experimental group into the two-phase fermentation reactor, and put the blank group into the dry fermentation reactor. The blank group runs for 55 days, and the experimental group runs for 45 days.
[0069] The two-phase reactor of the experimental group included a filtrate spraying device. After loading the fermentation substrate into the reactor, add deionized water whose volume is 1 / 3 of the solvent volume of the reactor. The deionized water infiltrates all the fermentation substrate under the action of gravity, and then leaches out to form the water extract of the fermentation substrate to form a filtrate. The filtrate enters the filtrate spraying device, and sprays the fermentatio...
Embodiment 3
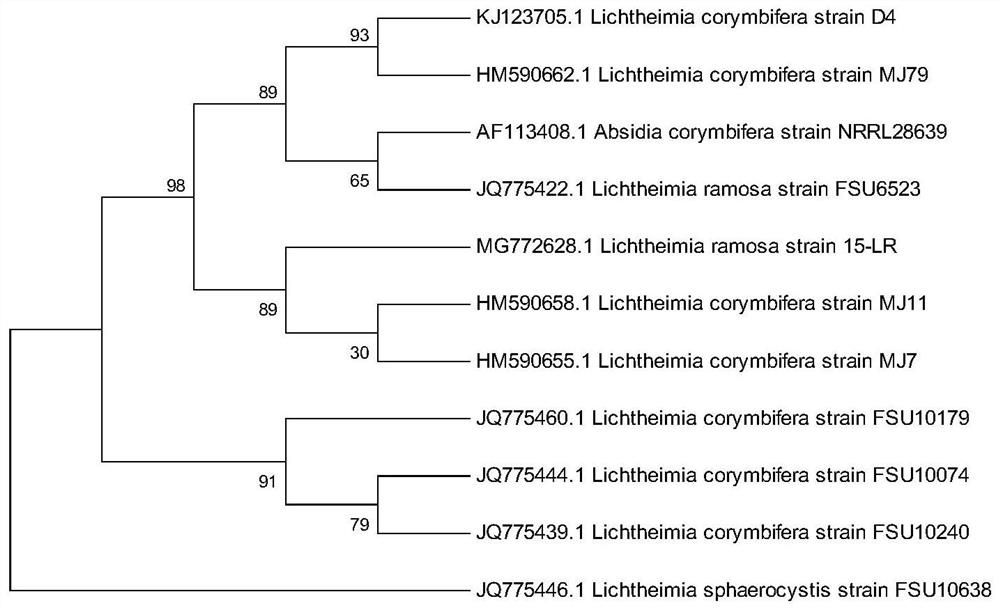
[0075] Example 3: Effects of Different Strains on Gas Production of Rice Straw
[0076] 1. Use the method of the experimental group in Example 2 to conduct experiments on the gas production effects of different strains of rice straw. The experimental treatment methods are exactly the same, only the strains used are different. Among them, the same amount of bacteria agent sterilized by high temperature was added as the blank group. The specific treatment of each group is shown in Table 5.
[0077] Table 5 Specific treatment table for each group
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] 2. Put each group after pretreatment into a two-phase fermentation reactor, spray the same amount of filtrate (3 times / day) to each group regularly every day, and take samples regularly to measure gas production and methane gas concentration. The specific results are shown in Table 6. The gas production rate in the table refers to the volume of biogas produced per kilogram of volatile solid matter.
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com