Feed ingredients comprising lysed microbial cells
A microbial cell and feed technology, applied in the field of feed ingredients containing lysed microbial cells, can solve the problem of increased availability of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, and achieve the effect of reducing transportation and storage costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0090] Example 1. Food Composition
[0091] DHA-enriched Schizochytrium cells (biomass) prepared by standard heterotrophic fermentation were dried and loaded using a standard impeller type mixer at loading levels of 10%, 20% and 30% by weight biomass with low Erucic acid canola oil blend. The biomass in the oil blend is then processed through a high pressure homogenizer or bead mill to produce a dispersion of lysed algal cells in the oil. For lysis in a high pressure homogenizer, a pressure of 200 bar to 1200 bar is used and is sufficient to lyse the cells.
example 2
[0092] Example 2. Analysis of mixtures and dispersions prepared from mixtures
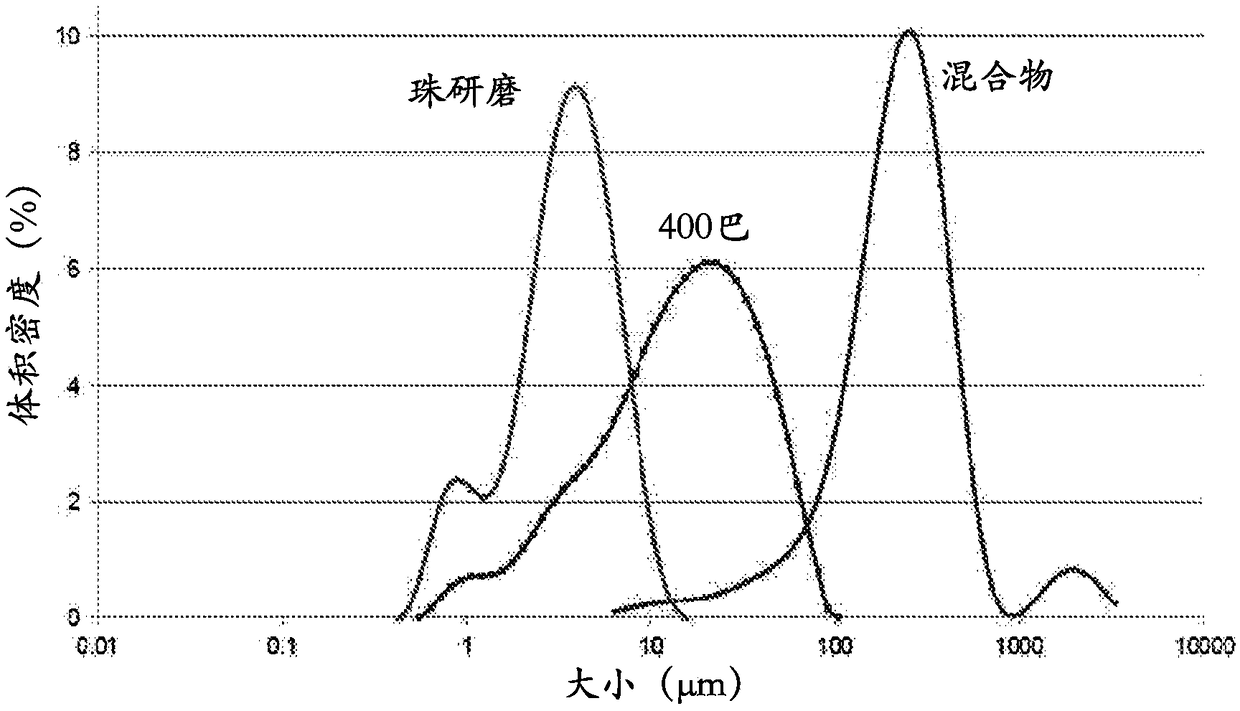
[0093] A 20% by weight biomass blend blended with the canola oil of Example 1 was prepared and analyzed by laser diffraction particle size analysis on a Malvern Mastersizer 3000. The mixture was also homogenized and bead milled at 400 bar, and the resulting dispersion was also analyzed. figure 1 It is shown that the bead milled dispersion has a lower average particle size than the homogenized dispersion, and both have a lower average particle size than the masterbatch.
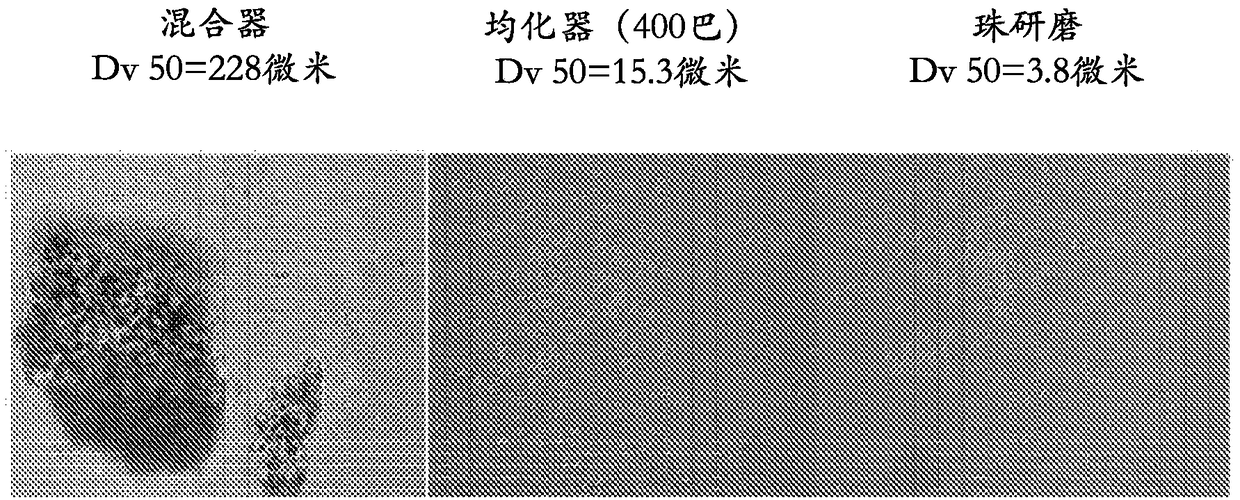
[0094] exist figure 2 The smaller size can also be seen in the photomicrograph of (400x magnification). The Dv50 value of the mixture (distribution value of 50% or less) was 228 μm, while the homogenized dispersion had a Dv50 of 15.3 μm, and the bead-milled dispersion had a Dv50 of 3.8 μm, indicating that the dispersion has a better on the characteristics of the sprayer.
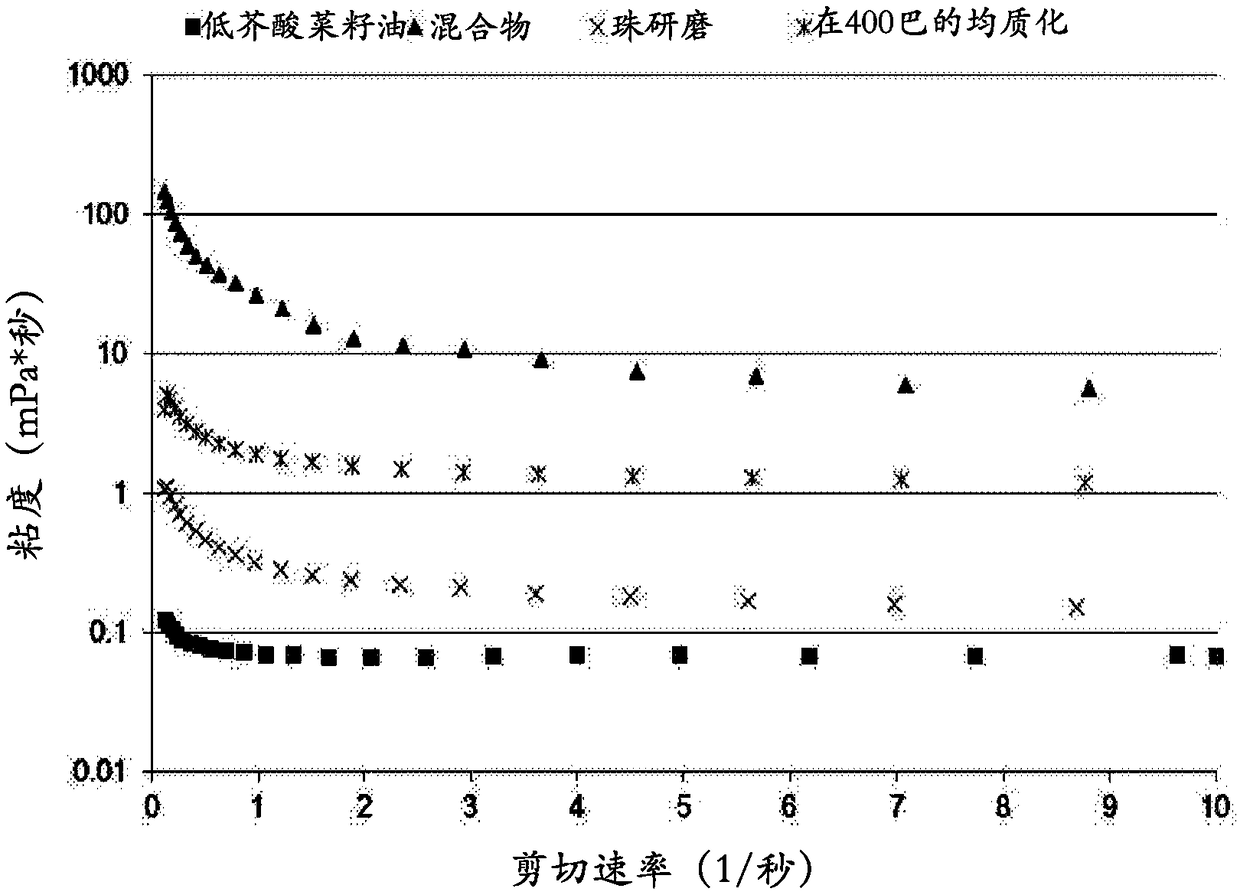
[0095] Measured with a Malvern Kinexus professional rh...
example 3
[0097] Example 3. Oxidation Stability Analysis
[0098] The dry biomass of Example 1 was combined with various antioxidants using a hand blender. Dried biomass with or without antioxidants was analyzed using Oxipress at about 80°C. Natural and synthetic antioxidants were used and included L-alpha-lecithin (soybean, Calbiochem #429415), starch (corn, Argo), ascorbic acid (Spectrum Chemical Co. )), ParadigmOx White Liquid (PWL-Gallate, Comming Health), RPT40 (Rosemary, Tocopherol, Ascorbyl Palmitate, Comming Health), NaturFortLGR105 (Green Tea and Rosemary Extract, Comming Health Bright Health), Rendox CQ (TBHQ, Comming Health), RendoxEQ (ethoxyquin, Comming Health), BHT (crystalline in ethanol, Comming Health), and Covi-ox T-30P ( mixed tocopherols). Figure 5 The surprising and unexpected oxidative stability of certain biomass-containing lecithins is shown.
[0099] The oxidative stability of the biomass was about 22 hours at 80°C when prepared with the antioxidant RPT40 (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Median particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com