Method for remediating polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composite contaminated soil by utilizing sulfate radical free radical advanced oxidation technology
A technology for polluted soil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, applied in the field of soil remediation, can solve the problems of low removal efficiency of PAHs, increase the difficulty of soil remediation, affect removal efficiency, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] The removal rate of sodium persulfate and ferrous ion to PAHs in polluted soil of embodiment 1
[0030] The soil of a PAHs-contaminated site was selected for advanced oxidation remediation of sulfate radicals, and the ratios of different ferrous ions and sodium persulfate were adjusted in order to obtain optimized degradation efficiency. The characteristics of PAHs pollution in the soil of the site are shown in Table 1.
[0031] Table 1 Contents of 16 PAHs in polluted soil
[0032]
[0033] Impurities in the PAH-contaminated soil were removed and the soil was air-dried, and the air-dried soil was crushed and passed through a 20-mesh sieve. The test soil that takes 5g polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution is placed in the 30ml brown glass bottle, sodium persulfate and ferrous ion of different concentrations are set, 1) sodium persulfate 0mmol / g, ferrous ion 0mmol / g (FOS0). 2) Sodium persulfate 0mmol / g, ferrous ion 0.5mmol / g (F0.5S0). 3) Sodium persulfate 1mmol / ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Adding chelating agent to remove PAHs in polluted soil under the optimum concentration of sodium persulfate and ferrous ion
[0037] On the basis of the sodium persulfate of 5mmol / g and the ferrous sulfate of 0.5mmol / g in Example 1, different types of chelating agents are added, 1) oxalic acid, 2) sodium oxalate, 3) citric acid, 4) Sodium citrate, 5) EDTA, 6) potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 7) sodium pyrophosphate. Set the same concentration as 0.5mmol / g and the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1.
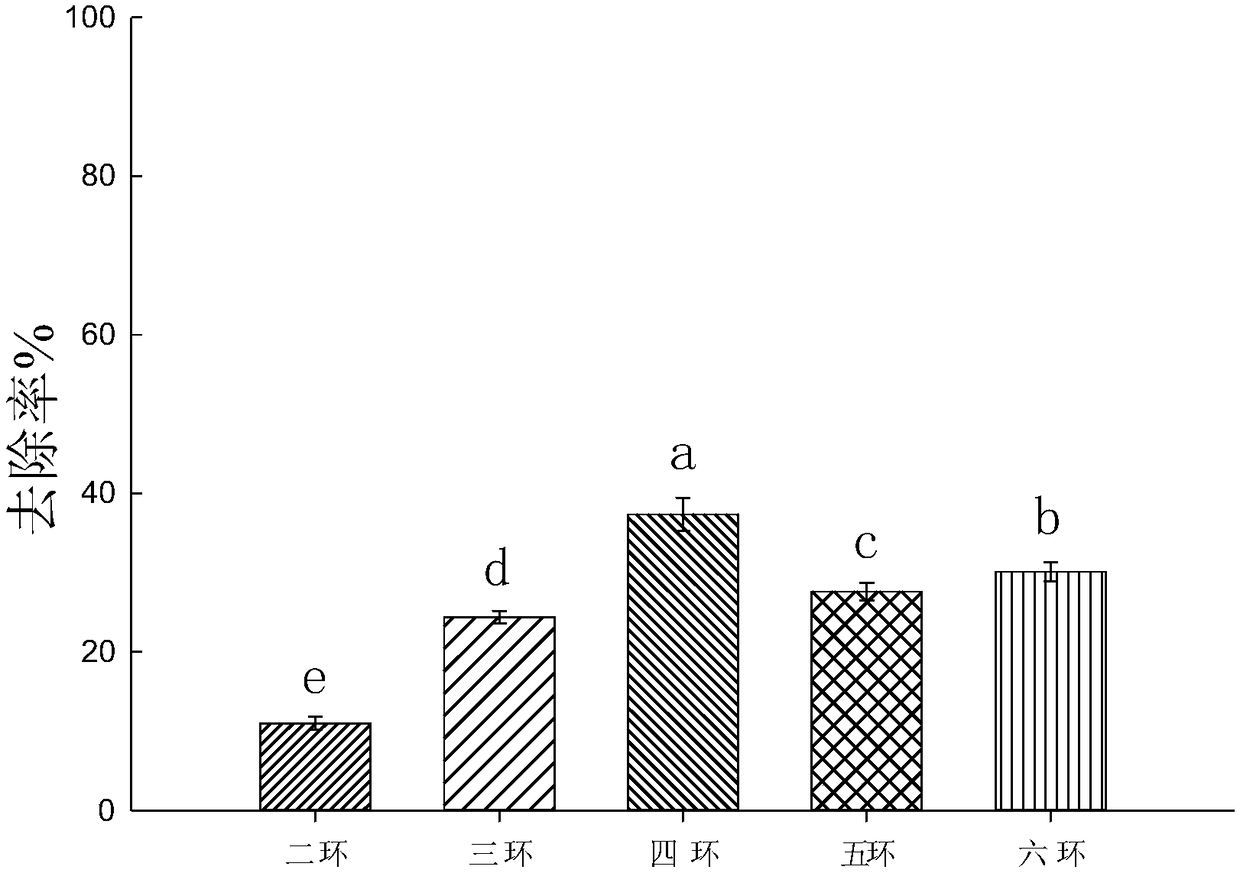
[0038] Such as image 3 As shown, the results showed that the addition of citric acid to different chelating agents had the highest improvement in the removal efficiency of PAHs in contaminated soil, reaching 49.9%, and the lowest was sodium oxalate at 35.0%.
[0039] Compare the removal efficiency of PAHs with different ring numbers, such as Figure 4 As shown, the removal rate of tetracyclic PAHs in polluted soil was further optimized by adding citri...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3 adds surfactant on the basis of optimal chelating agent to remove PAHs in polluted soil
[0041] On the basis of adding 0.5mmol / g of citric acid as a chelating agent in Example 2, it is set to add different types of surfactants: 1) Brij-35 (polyoxyethylene lauryl ether), 2) HPCD (hydroxypropyl-β -cyclodextrin), 3) APG (AlkylPolyglycoside, alkyl glycoside), 4) CA-720, each surfactant has 4 different concentrations, which are 500mg / l, 1000mg / l, 1500mg / l, 2000mg / l respectively, and the amount added is 900μL of surfactant solution for each treatment (that is, every 5 grams soil plus 900 μL surfactant solution). All the other steps are the same as in Example 2.
[0042] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the results show that in different surfactants CA-720 has the highest improvement in the degradation efficiency of PAHs in contaminated soil, with a removal rate of 80.8%, and Brij-35 is the lowest, with a removal rate of 69.7%.
[0043] Compare the removal effi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com