Knockout vector, targeting vector, in-vitro knockout method of PPARG gene in liver cell, and knockout liver cell
A technology for knocking out vectors and liver cells, which is applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of low knockout efficiency and cumbersome knockout process, and achieve the effects of high knockout efficiency, less off-target, and convenient construction and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
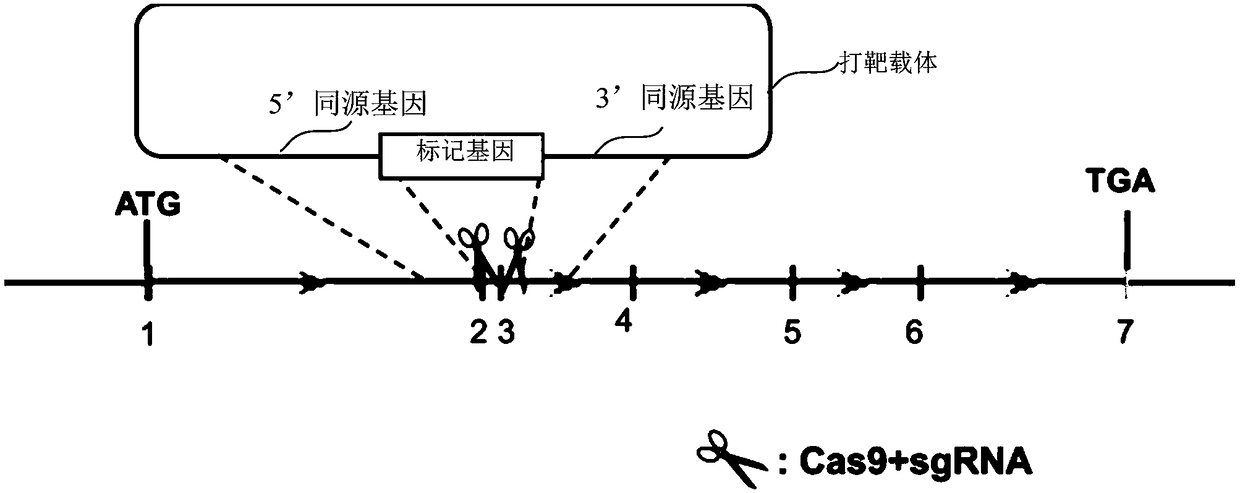
[0047] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a preparation method of the knockout vector, comprising the following steps:
[0048] S11, annealing the complementary DNA sequence to form a double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment;
[0049] S12, providing the CRISPR / Cas9 carrier backbone, the sequence of the cohesive end of the CRISPR / Cas9 carrier backbone can be complementary to the sequence of the cohesive end of the double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment; and
[0050] S13, connecting the CRISPR / Cas9 vector backbone and the double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment to form a closed circular plasmid.
[0051] In step S11, the double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment can be formed by annealing two single strands of the complementary DNA sequence. The annealing condition may be that the mixed aqueous solution of two single chains is placed in a water bath at a temperature of 95° C. to 100° C. for 3 minutes to 6 minutes, and then naturally cooled to room temperatu...
Embodiment
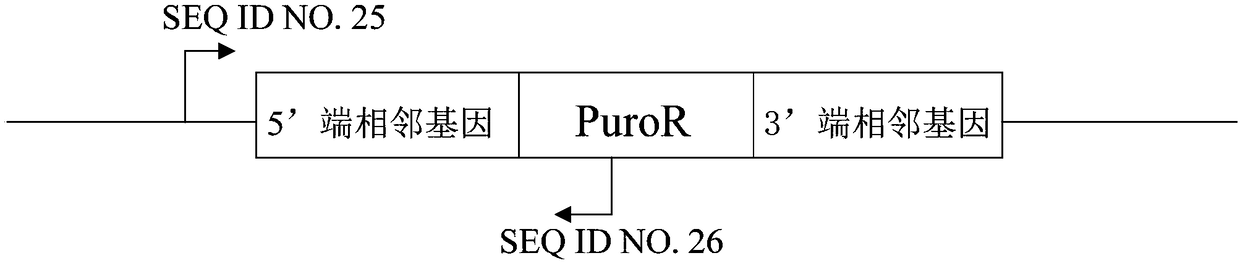
[0096] Preparation of knockout vectors:
[0097] Select SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6 of the PPARG gene in HL-7702 cells (human liver normal cells) These 6 specific sequences were used as the target sequences for knockout.
[0098] Provide such as SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8, SEQ ID NO.9 and SEQ ID NO.10, SEQ ID NO.11 and SEQ ID NO.12, SEQ ID NO.13 and SEQ ID NO.14, Single-stranded DNA sequences of SEQ ID NO.15 and SEQ ID NO.16 and SEQ ID NO.17 and SEQ ID NO.18.
[0099] The 12 single-stranded DNA sequences were respectively dissolved in pure water to adjust the final concentration to 100 μM.
[0100] Annealing: SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8, SEQ ID NO.9 and SEQ ID NO.10, SEQ ID NO.11 and SEQ ID NO.12, SEQ ID NO.13 and SEQ ID NO.14, 15 μL of each of SEQ ID NO.15 and SEQ ID NO.16, and SEQ ID NO.17 and SEQ ID NO.18 were mixed, put into a boiling water bath for 5 minutes, and then cooled to room temperature naturally to form 6 co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com